Unveiling the Power of Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing and Optimizing Workflows
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing and Optimizing Workflows
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing and Optimizing Workflows. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing and Optimizing Workflows
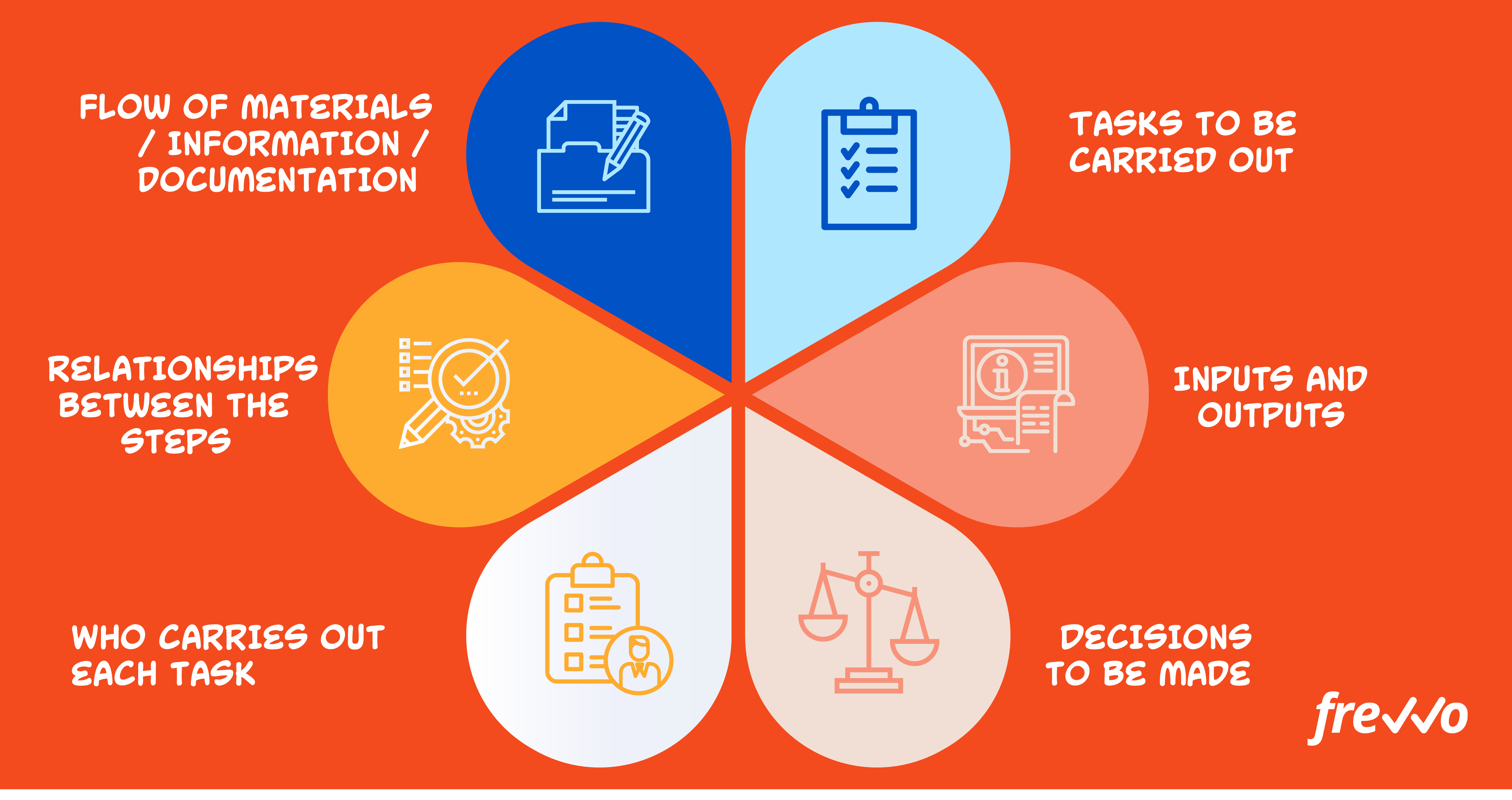
In the contemporary business landscape, where efficiency and clarity are paramount, process mapping emerges as a potent tool for streamlining operations and driving organizational success. Process mapping, also known as process flowcharting, involves the visual representation of a sequence of events or tasks, offering a comprehensive understanding of how work flows through an organization. This graphical depiction facilitates identification of bottlenecks, redundancies, and areas for improvement, ultimately enabling businesses to optimize their processes and achieve desired outcomes.
The Essence of Process Mapping: A Visual Journey Through Workflows
Process maps serve as visual blueprints, providing a clear and concise representation of a specific process. They utilize symbols and connecting lines to illustrate the flow of activities, decisions, and outputs, offering a comprehensive overview of how work is executed. This graphical depiction fosters a deeper understanding of the process, enabling stakeholders to identify key elements, potential challenges, and opportunities for enhancement.
Benefits of Embracing Process Mapping: A Catalyst for Organizational Transformation
The adoption of process mapping brings forth a myriad of benefits, empowering organizations to elevate their operational efficiency and achieve strategic objectives. These advantages include:
1. Enhanced Understanding and Communication: Process maps provide a common language for all stakeholders involved in a particular process, fostering clear communication and ensuring everyone is on the same page. This visual representation simplifies complex processes, making them readily accessible and understandable, even for those unfamiliar with the intricacies of the workflow.
2. Identification of Bottlenecks and Inefficiencies: By visually dissecting the flow of work, process maps reveal hidden inefficiencies and bottlenecks that may otherwise go unnoticed. This enables organizations to pinpoint areas where processes are unnecessarily complex, time-consuming, or prone to errors, paving the way for targeted improvements.
3. Streamlined Workflows and Reduced Costs: Through the identification and elimination of redundancies and bottlenecks, process mapping facilitates the streamlining of workflows. This optimization leads to reduced costs, improved productivity, and faster turnaround times, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
4. Improved Quality and Consistency: Process maps promote consistency by establishing standardized procedures and workflows. This standardization ensures that tasks are performed consistently, reducing the risk of errors and enhancing the quality of outputs.
5. Facilitating Innovation and Process Improvement: Process mapping acts as a catalyst for continuous improvement by providing a framework for identifying opportunities for innovation and process optimization. By visualizing the workflow, organizations can explore alternative approaches, streamline steps, and implement new technologies to enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
6. Enhanced Training and Onboarding: Process maps serve as valuable training tools, providing a clear and concise guide for new employees and those unfamiliar with specific processes. They simplify the onboarding process, enabling employees to quickly grasp the intricacies of their roles and responsibilities within the workflow.
7. Increased Accountability and Ownership: By clearly defining roles and responsibilities within a process, process maps foster accountability and ownership among team members. This shared understanding encourages collaboration and a sense of responsibility for the successful execution of the workflow.
Types of Process Maps: Tailoring the Visual Representation to Specific Needs
Different types of process maps cater to specific needs and objectives, offering tailored visual representations of workflows. The most common types include:
1. Swimlane Process Maps: These maps utilize horizontal lanes to depict the roles and responsibilities of different departments or individuals involved in a process. This visual representation clearly outlines the flow of work between different entities, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of the workflow.
2. Cross-Functional Process Maps: When multiple departments or teams collaborate on a process, cross-functional process maps provide a clear overview of the entire workflow. These maps highlight the interactions and dependencies between different teams, ensuring a seamless and efficient flow of work.
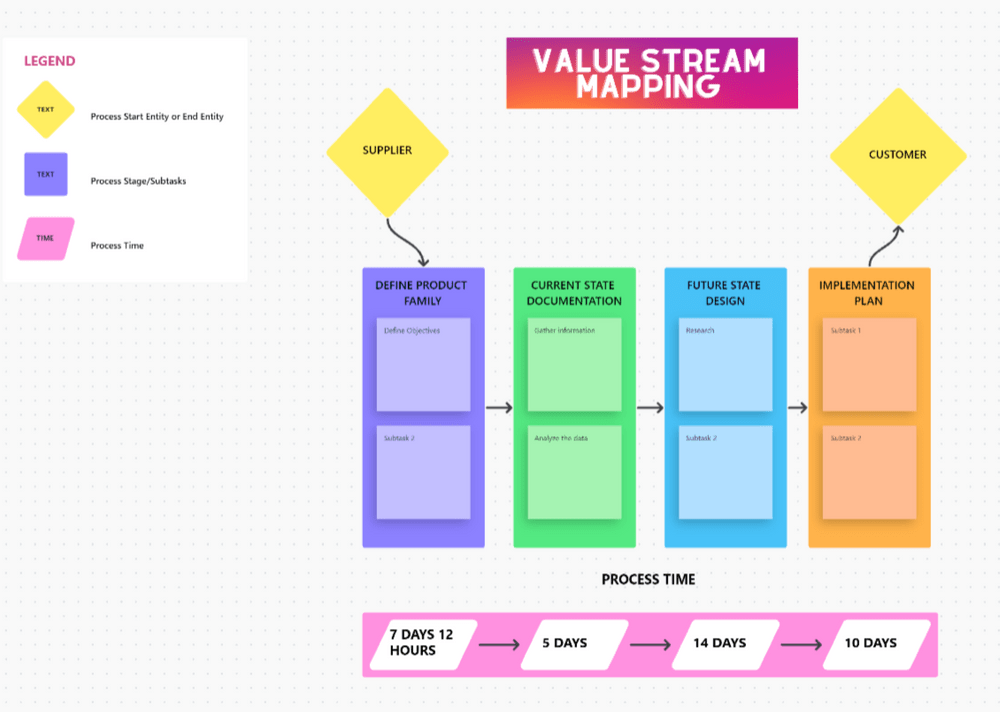
3. Value Stream Maps: Value stream maps focus on the entire value chain, from the initial customer request to the final delivery of the product or service. These maps highlight the activities that add value to the customer and identify non-value-adding activities that can be eliminated or optimized.
4. SIPOC Maps: SIPOC maps are used to define the scope of a process, focusing on the key elements of Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, and Customers. This type of map provides a high-level overview of the process, outlining the key stakeholders and their roles in the workflow.
5. Workflow Diagrams: Workflow diagrams depict the sequence of steps involved in a process, using symbols to represent tasks, decisions, and outputs. These diagrams offer a simplified representation of the workflow, focusing on the flow of information and the progression of activities.
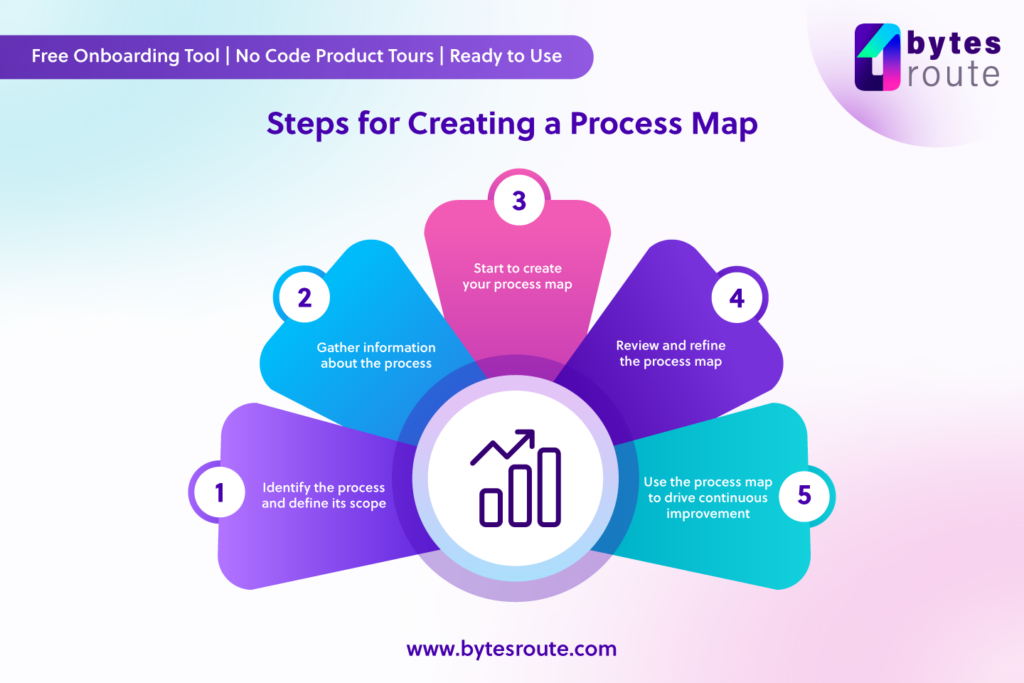
Creating a Process Map: A Step-by-Step Guide to Visualizing Workflows
Creating a process map involves a systematic approach, ensuring that the visual representation accurately reflects the workflow and provides valuable insights. The following steps serve as a comprehensive guide:
1. Define the Scope of the Process: Clearly define the boundaries of the process being mapped, identifying the starting point and the desired end outcome. This step ensures that the map focuses on the specific workflow and avoids unnecessary complexities.
2. Gather Information and Data: Collect relevant information and data about the process, including documentation, interviews with stakeholders, and observation of the workflow in action. This comprehensive data gathering enables a thorough understanding of the process and its intricacies.
3. Identify the Key Activities and Decisions: Analyze the collected data to identify the key activities and decisions involved in the process. This step involves breaking down the workflow into individual tasks and defining the decision points that influence the flow of work.
4. Determine the Sequence of Activities: Establish the sequence of activities and decisions within the process, outlining the logical flow of work from start to finish. This step ensures that the map accurately reflects the chronological order of tasks and decisions.
5. Choose the Appropriate Symbols and Notation: Select the appropriate symbols and notation for representing the various elements of the process, ensuring consistency and clarity in the visual representation. Common symbols include rectangles for activities, diamonds for decisions, and arrows for flow direction.
6. Create the Process Map: Using the chosen symbols and notation, construct the process map, visually representing the flow of activities, decisions, and outputs. This step involves connecting the symbols with arrows to illustrate the sequence of tasks and the flow of work.
7. Validate and Refine the Process Map: Once the map is created, review it with key stakeholders to ensure accuracy and completeness. This validation process involves seeking feedback, addressing any discrepancies, and refining the map to accurately reflect the workflow.
8. Implement and Monitor the Process Map: After finalizing the process map, integrate it into the organization’s workflow and monitor its impact. This step involves tracking key metrics, identifying areas for improvement, and continuously refining the process map to ensure its effectiveness.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions About Process Mapping
1. What are the different types of process mapping software available?
A plethora of process mapping software exists, each offering unique features and functionalities. Some popular options include Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, Draw.io, and Creately. These tools provide templates, symbols, and collaboration features, streamlining the process of creating and sharing process maps.
2. How can I effectively use process mapping to improve customer service?
Process mapping can be applied to enhance customer service by visualizing the customer journey and identifying areas for improvement. Mapping the entire customer interaction process, from initial contact to resolution, allows businesses to identify potential bottlenecks, streamline workflows, and improve customer satisfaction.
3. How can I involve stakeholders in the process mapping process?
Engaging stakeholders throughout the process mapping journey is crucial for ensuring buy-in and successful implementation. This can be achieved through workshops, interviews, and regular feedback sessions, allowing stakeholders to contribute their expertise and perspectives.
4. How can I measure the success of my process mapping efforts?
Measuring the success of process mapping requires identifying key metrics and tracking their progress over time. This may include metrics such as reduced cycle time, improved quality, increased productivity, and reduced costs.
Tips for Effective Process Mapping: Enhancing the Visual Representation
1. Keep it Simple and Clear: Avoid overwhelming the map with unnecessary details or complex jargon. Use clear language and simple symbols to ensure that the map is easily understandable by all stakeholders.
2. Focus on Value-Adding Activities: Highlight the activities that directly contribute to the desired outcome, minimizing the focus on non-value-adding tasks that can be eliminated or optimized.
3. Use Color and Visual Cues: Employ color and visual cues to differentiate between different elements of the process, enhancing clarity and readability. This can include using different colors for different departments or highlighting key decision points.
4. Promote Collaboration and Feedback: Encourage collaboration among stakeholders throughout the process mapping journey, seeking feedback and incorporating diverse perspectives to ensure a comprehensive and effective representation of the workflow.
Conclusion: Embracing Process Mapping for Enhanced Efficiency and Success
Process mapping stands as a powerful tool for organizations seeking to optimize their workflows, drive efficiency, and achieve strategic objectives. By visually representing processes, businesses gain a deeper understanding of their operations, identify areas for improvement, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. Embracing process mapping empowers organizations to streamline their workflows, enhance communication, and ultimately achieve greater success in today’s dynamic and competitive landscape.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing and Optimizing Workflows. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!