Unveiling the Jewel of Southeast Asia: Borneo’s Geographic Significance
Related Articles: Unveiling the Jewel of Southeast Asia: Borneo’s Geographic Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Jewel of Southeast Asia: Borneo’s Geographic Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Jewel of Southeast Asia: Borneo’s Geographic Significance
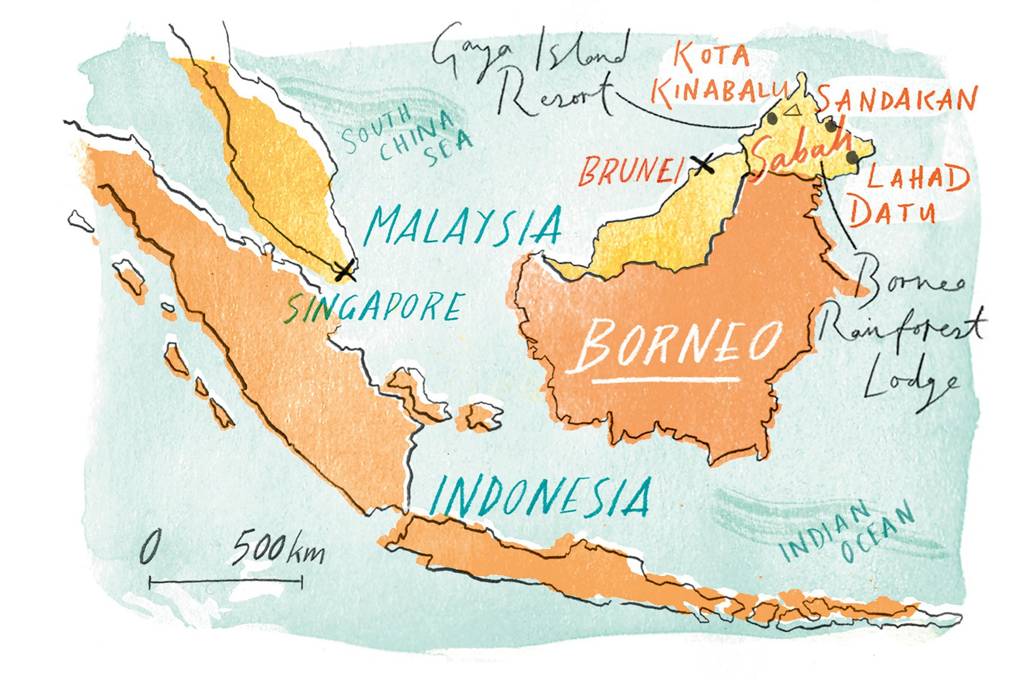
Borneo, the third-largest island in the world, is a captivating landmass teeming with biodiversity and rich cultural heritage. Located strategically in Southeast Asia, Borneo’s geographic location has shaped its unique identity and contributed to its immense ecological and cultural significance.
A Tapestry of Nations: The Geopolitical Landscape of Borneo
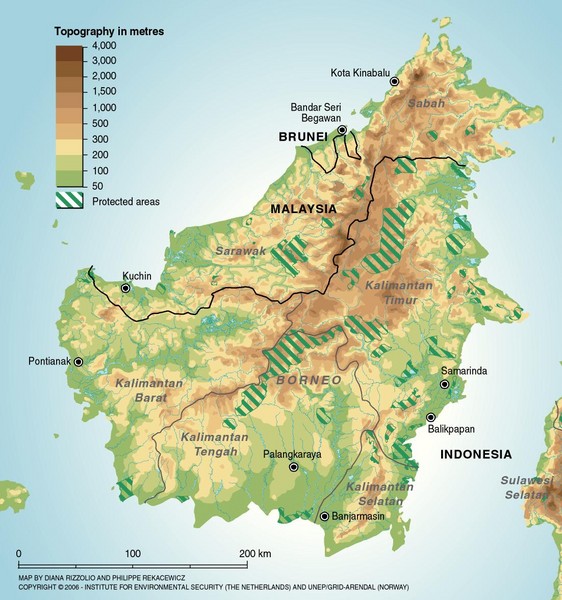
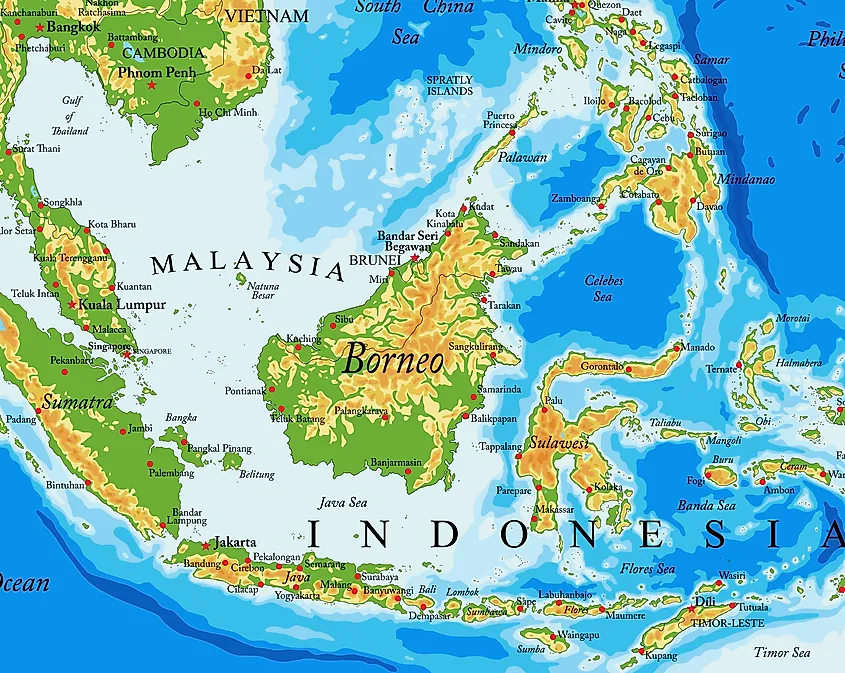
Borneo is divided among three nations: Malaysia, Indonesia, and Brunei Darussalam.
- Malaysian Borneo, also known as East Malaysia, comprises the states of Sabah and Sarawak, situated on the northern and northwestern parts of the island.
- Indonesian Borneo, or Kalimantan, encompasses the largest portion of the island, stretching across the central, southern, and eastern regions.
- Brunei Darussalam, a small sultanate, occupies a sliver of land on the northern coast, nestled between Sabah and Sarawak.
A Maritime Crossroads: Borneo’s Strategic Location
Borneo’s location at the heart of Southeast Asia makes it a vital maritime crossroads. The island sits at the confluence of the South China Sea, the Celebes Sea, and the Java Sea, connecting major shipping routes and facilitating trade between Southeast Asian nations and beyond. This strategic position has played a pivotal role in Borneo’s history, fostering cultural exchanges and economic development.
A Land of Natural Wonders: Borneo’s Diverse Ecosystems
Borneo’s diverse ecosystems are a testament to its geographic location. The island boasts a remarkable array of habitats, ranging from lush rainforests and towering mountains to vast peat swamps and pristine coral reefs. This geographic diversity has created a haven for an extraordinary array of flora and fauna, making Borneo a global biodiversity hotspot.
- Rainforests: Borneo’s rainforests, some of the oldest and most extensive in the world, are home to an estimated 15,000 plant species, including rare orchids and carnivorous pitcher plants.
- Mountains: The island’s mountainous regions, including Mount Kinabalu in Sabah, provide a cool haven for unique flora and fauna adapted to high altitudes.
- Peat Swamps: Borneo’s peat swamps are vital carbon sinks, playing a crucial role in regulating the global climate. They are also home to a diverse range of wildlife, including the endangered proboscis monkey.
- Coral Reefs: Borneo’s coastal waters are adorned with vibrant coral reefs, teeming with marine life, including colorful fish, sea turtles, and sharks.
A Tapestry of Cultures: Borneo’s Rich Heritage
Borneo’s geographic location has facilitated the convergence of diverse cultures, creating a vibrant tapestry of traditions, languages, and beliefs. The island’s indigenous peoples, with their unique customs and traditions, have long inhabited Borneo, shaping its cultural landscape.
- Indigenous Communities: Borneo is home to numerous indigenous communities, each with its own distinct language, customs, and beliefs. These communities have a deep connection to the land and its resources, preserving traditional knowledge and practices.
- Religious Diversity: Borneo’s cultural landscape is enriched by the presence of various religions, including Islam, Christianity, Buddhism, and traditional animistic beliefs. This religious diversity reflects the island’s historical interactions and cultural exchanges.
- Art and Crafts: Borneo’s indigenous communities are renowned for their intricate art and crafts, reflecting their deep connection to nature and their unique cultural identities. From traditional textiles to intricate wood carvings, these artistic expressions showcase the rich cultural heritage of Borneo.
Borneo’s Importance: A Global Treasure
Borneo’s strategic location, diverse ecosystems, and rich cultural heritage make it a global treasure. The island plays a crucial role in:
- Biodiversity Conservation: Borneo’s rainforests and other ecosystems serve as a vital refuge for endangered species, including orangutans, pygmy elephants, and clouded leopards.
- Climate Regulation: Borneo’s rainforests and peat swamps act as carbon sinks, playing a critical role in mitigating climate change.
- Economic Development: Borneo’s rich natural resources, including timber, oil, and gas, contribute significantly to the economies of the nations it encompasses.
- Cultural Preservation: Borneo’s indigenous communities and their cultural traditions are an invaluable asset to the world, preserving ancient knowledge and practices.
FAQs: Unveiling Borneo’s Geographic Mystery
Q: What is the capital of Borneo?
A: Borneo is not a single country but an island divided among three nations. Each nation has its own capital:
- Malaysia: Kuala Lumpur (capital of the country, not specifically Borneo)
- Indonesia: Jakarta (capital of the country, not specifically Borneo)
- Brunei Darussalam: Bandar Seri Begawan
Q: What is the largest city in Borneo?
A: The largest city in Borneo is Balikpapan, located in Indonesian Borneo.
Q: What is the main language spoken in Borneo?
A: There is no single main language spoken in Borneo, as the island is home to diverse indigenous communities, each with its own language. The official languages of the nations that share Borneo are:
- Malaysian Borneo: Malay (official), English
- Indonesian Borneo: Indonesian (official)
- Brunei Darussalam: Malay (official), English
Q: What are the main industries in Borneo?
A: Borneo’s economy is driven by:
- Natural resource extraction: Timber, oil, and gas are major industries.
- Agriculture: Palm oil, rubber, and cocoa are significant agricultural products.
- Tourism: Borneo’s natural beauty and cultural attractions draw visitors from around the world.
Tips: Exploring Borneo’s Geographic Wonders
- Research your destination: Borneo is a vast and diverse island, so research the specific region you plan to visit to understand its unique culture, attractions, and climate.
- Respect local customs: Be mindful of local customs and traditions, especially when visiting indigenous communities.
- Support sustainable tourism: Choose eco-friendly accommodations and tour operators that prioritize conservation and community development.
- Learn about Borneo’s biodiversity: Educate yourself about the island’s rich biodiversity and the threats it faces, such as deforestation and habitat loss.
Conclusion: Borneo’s Enduring Legacy
Borneo’s geographic location has shaped its unique identity, fostering a rich tapestry of cultures, ecosystems, and economic opportunities. The island’s strategic position at the heart of Southeast Asia has connected it to the world, making it a vital crossroads for trade, cultural exchange, and conservation efforts. As a global treasure, Borneo’s future depends on preserving its natural wonders and cultural heritage for generations to come.


/GettyImages-569909451-58f6525c5f9b581d59ea7b6e.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Jewel of Southeast Asia: Borneo’s Geographic Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!