Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Germany: A Comprehensive Guide to the German Physical Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Germany: A Comprehensive Guide to the German Physical Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Germany: A Comprehensive Guide to the German Physical Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Germany: A Comprehensive Guide to the German Physical Map
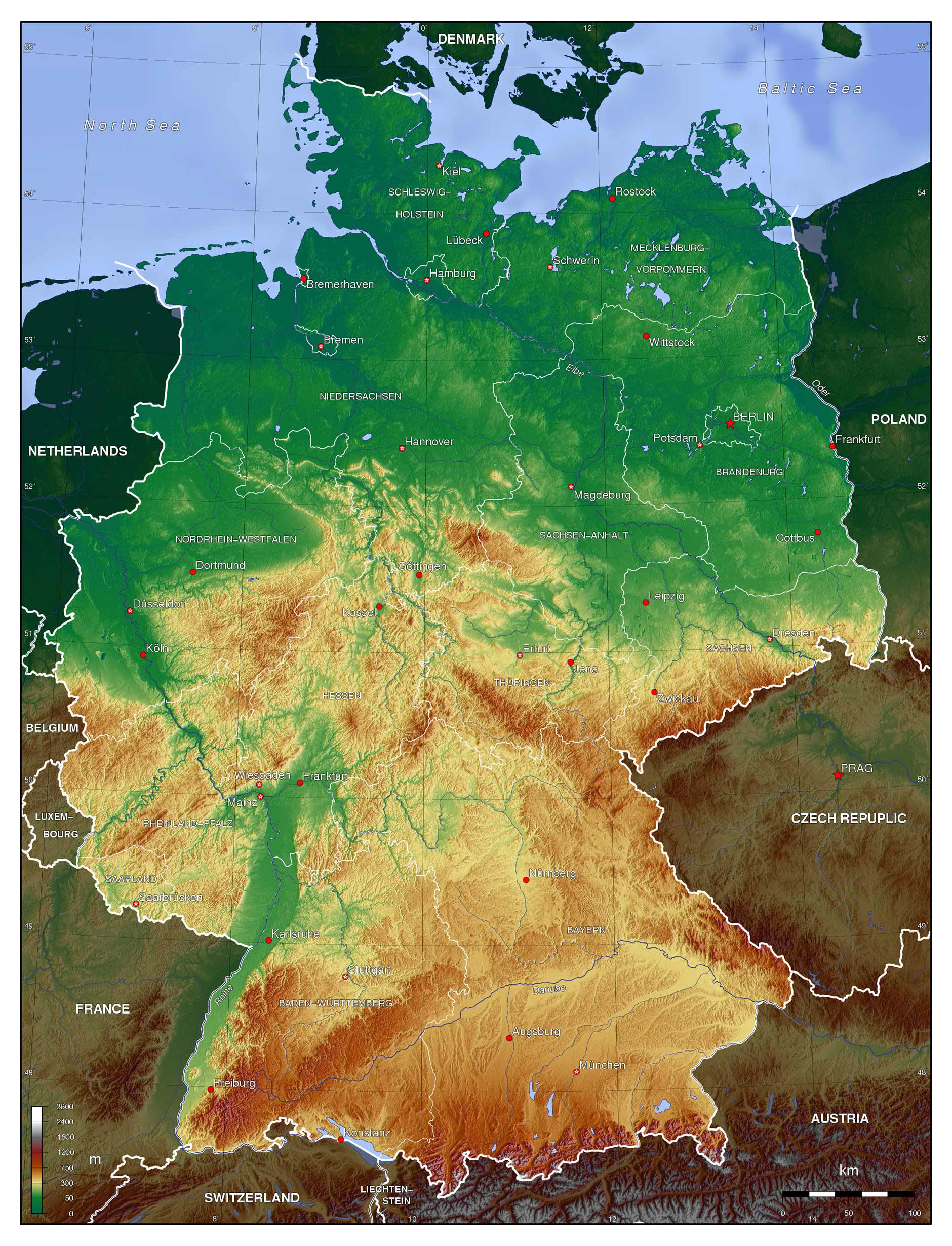
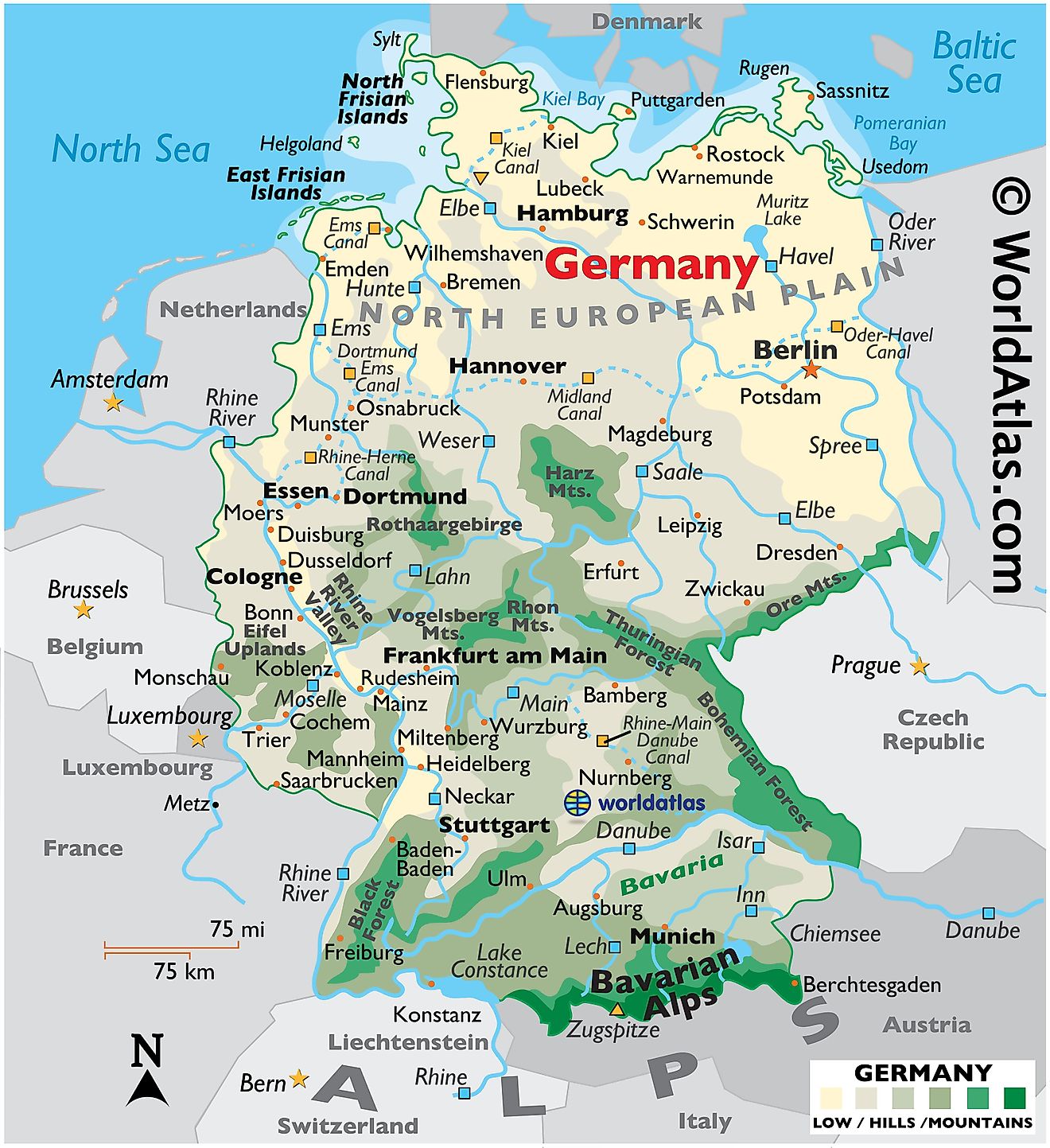
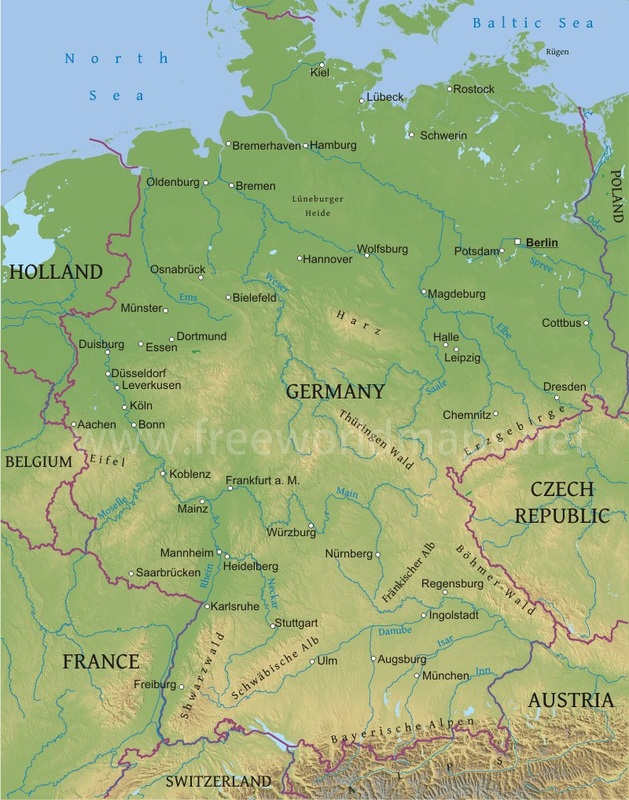
Germany, a nation nestled in the heart of Europe, boasts a captivating tapestry of landscapes, from the rugged peaks of the Alps to the serene shores of the Baltic Sea. Understanding the physical geography of Germany is crucial for appreciating its history, culture, and economic development. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the German physical map, exploring its diverse features and their impact on the nation’s identity.
A Land of Contrasts: Geographical Features of Germany
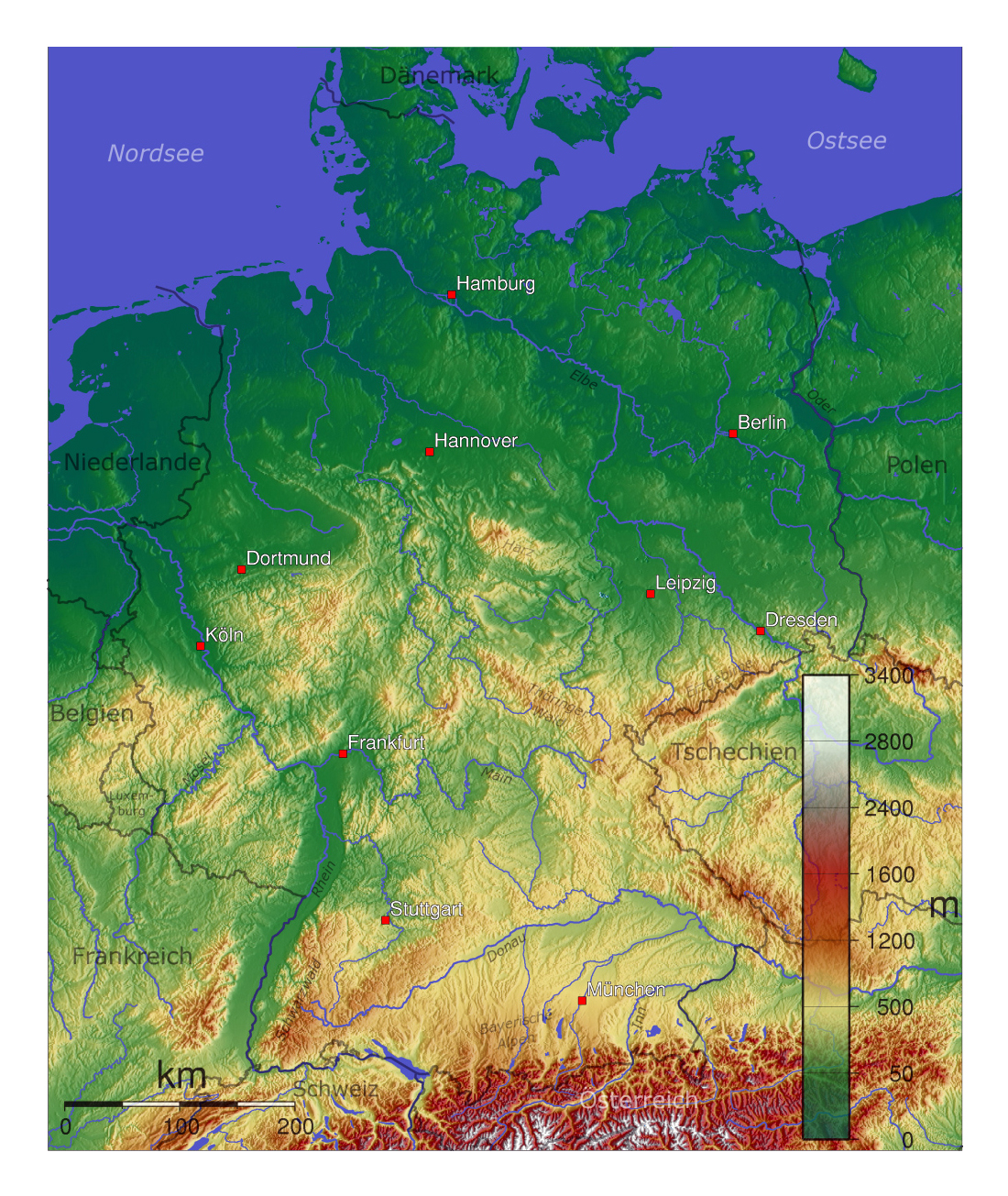
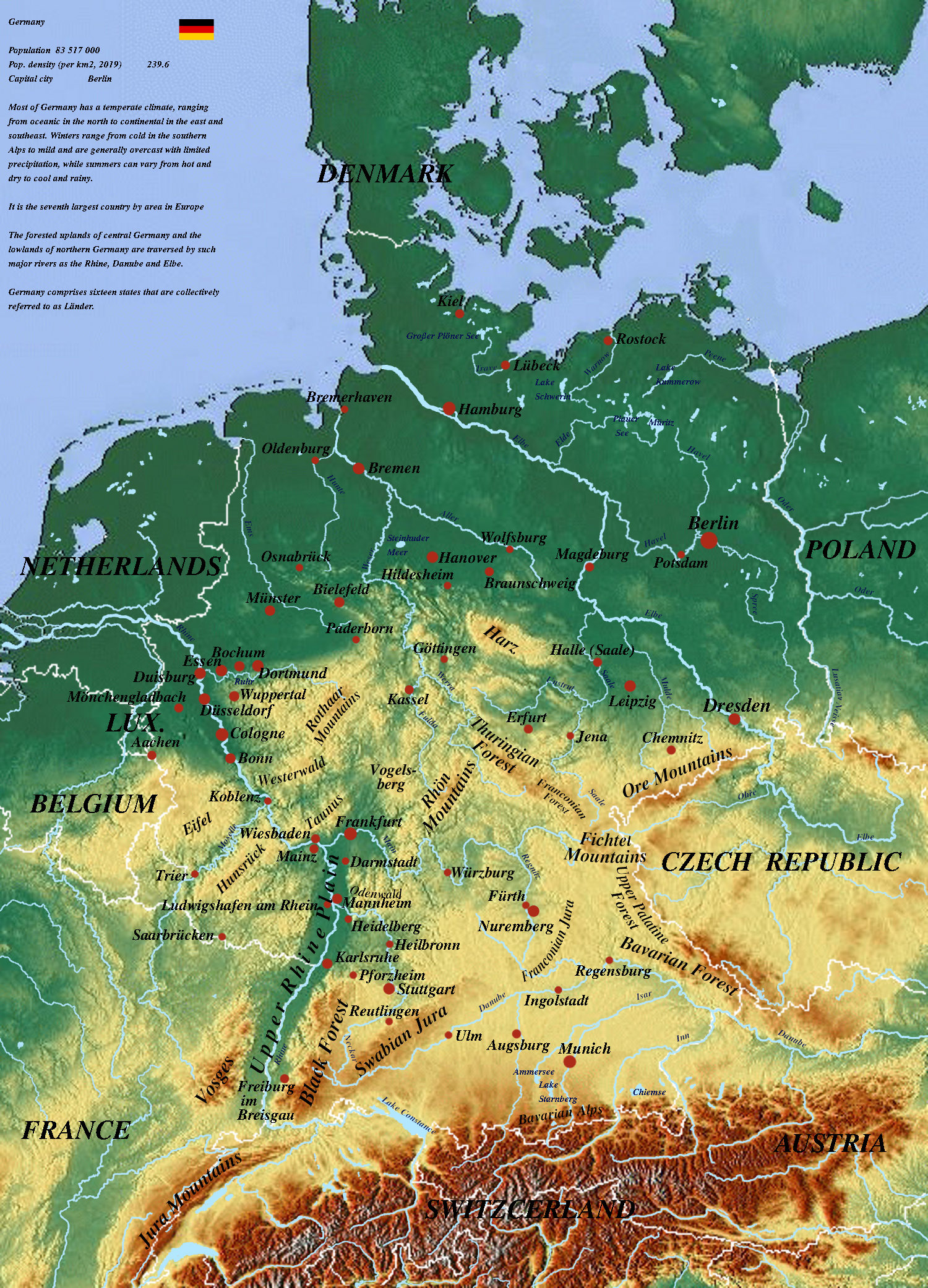
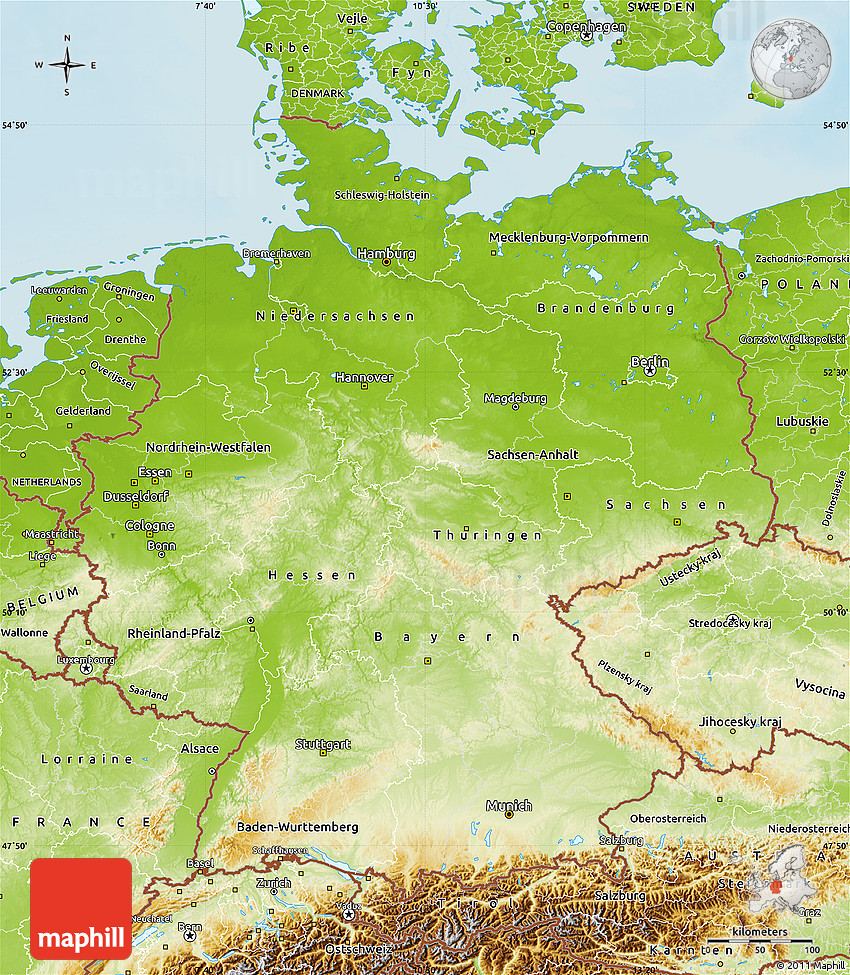
The German physical map reveals a country characterized by significant geographical diversity. Its landscape is sculpted by a unique interplay of mountain ranges, plains, rivers, and coastal areas, creating a mosaic of distinct regions with their own unique characteristics.
1. The Northern Lowlands:
- North German Plain: This vast, fertile plain stretches across northern Germany, encompassing the states of Schleswig-Holstein, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, and parts of Lower Saxony. The North German Plain is characterized by its flat topography, rich soils, and a network of rivers, making it a prime agricultural region.
- Coastal Areas: The North Sea and Baltic Sea coastlines offer a stark contrast to the interior. The North Sea coast is known for its windswept beaches, while the Baltic Sea coast features sandy beaches and sheltered inlets. These coastal regions are popular tourist destinations and support significant fishing industries.
2. The Central Uplands:
- Central German Uplands: This region, encompassing the states of Saxony, Thuringia, and parts of Hesse and Lower Saxony, features rolling hills, forested areas, and numerous valleys. The Central German Uplands are known for their rich history, cultural heritage, and diverse natural beauty.
- Harz Mountains: The Harz Mountains, located in the center of Germany, represent a prominent feature of the Central German Uplands. These mountains, with their rugged peaks and dense forests, offer opportunities for hiking, skiing, and outdoor recreation.
3. The Southern Highlands:
- Bavarian Alps: The Bavarian Alps, located in the south of Germany, are the country’s highest mountain range. These majestic peaks, including the iconic Zugspitze, attract climbers, skiers, and nature enthusiasts from around the globe.
- Black Forest: The Black Forest, situated in southwestern Germany, is a vast and densely forested mountain range. This region is known for its picturesque villages, traditional crafts, and renowned cuckoo clocks.
4. Rivers and Waterways:
- The Rhine: The Rhine River, one of Europe’s most important waterways, flows through Germany from its source in the Swiss Alps to its mouth in the Netherlands. The Rhine is a vital transportation route, connecting major cities and industries across Germany.
- The Danube: The Danube River, the second-longest river in Europe, flows through Germany for a short distance before entering Austria. The Danube is a significant waterway for shipping and tourism, connecting Germany to other countries in Central and Eastern Europe.
- Other Rivers: Germany is home to numerous other rivers, including the Elbe, Weser, and Oder. These rivers have played a vital role in shaping the country’s history, culture, and economy.
The Impact of Geography on Germany’s Development:
The diverse geography of Germany has profoundly influenced its history, culture, and economic development. The fertile plains of the north have supported agriculture and provided a base for population growth. The mountainous regions have offered natural resources and opportunities for tourism and recreation. The rivers have served as vital transportation routes, facilitating trade and communication.
1. Agriculture:
- The fertile plains of northern Germany have long been a center for agriculture, producing a wide range of crops, including wheat, barley, potatoes, and sugar beets.
- The mountainous regions, while less suitable for large-scale agriculture, support livestock farming and forestry.
2. Industry:
- The abundance of coal and iron ore in the Ruhr Valley, located in the western part of Germany, fueled the country’s industrial revolution in the 19th century.
- The rivers, especially the Rhine, have facilitated the transportation of goods and raw materials, contributing to Germany’s industrial growth.
3. Tourism:
- Germany’s diverse landscapes, from the towering Alps to the scenic Black Forest, attract millions of tourists annually.
- The country’s rich cultural heritage, including its historic cities and castles, further enhances its appeal to tourists.
4. Environmental Challenges:
- Germany’s diverse geography also presents environmental challenges, such as air pollution in urban areas, water pollution from industrial activities, and deforestation.
- The country has implemented numerous environmental policies to address these challenges and promote sustainable development.
FAQs: Exploring the German Physical Map in Depth
1. What are the highest mountains in Germany?
The highest mountain in Germany is the Zugspitze, located in the Bavarian Alps, with an elevation of 2,962 meters (9,718 feet).
2. What are the largest rivers in Germany?
The largest rivers in Germany are the Rhine, Danube, Elbe, Weser, and Oder.
3. What are the main climate zones in Germany?
Germany experiences a temperate climate with four distinct seasons. The northern lowlands have a more maritime climate, while the southern highlands have a more continental climate.
4. What are the most important agricultural regions in Germany?
The most important agricultural regions in Germany are the North German Plain, the Lower Rhine Valley, and the Bavarian Plateau.
5. What are the main industrial regions in Germany?
The main industrial regions in Germany are the Ruhr Valley, the Rhine-Main region, and the Stuttgart region.
6. What are the most popular tourist destinations in Germany?
The most popular tourist destinations in Germany include Berlin, Munich, Cologne, Hamburg, and the Black Forest.
7. What are the major environmental challenges facing Germany?
The major environmental challenges facing Germany include air pollution, water pollution, deforestation, and climate change.
Tips for Navigating the German Physical Map:
- Use a detailed physical map of Germany: A physical map provides a visual representation of the country’s terrain, elevation, and major geographical features.
- Explore online resources: Numerous websites and online maps offer detailed information about Germany’s geography.
- Visit Germany: Experiencing the diverse landscapes of Germany firsthand is the best way to understand its physical map.
Conclusion: Appreciating the Beauty and Significance of the German Physical Map
The German physical map is a testament to the country’s diverse and captivating landscape. Its mountains, plains, rivers, and coastal areas have shaped its history, culture, and economy, creating a unique and fascinating nation. By understanding the physical geography of Germany, we gain a deeper appreciation for its rich history, vibrant culture, and enduring spirit.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Germany: A Comprehensive Guide to the German Physical Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!