Unveiling the Decapolis: A Journey Through Ancient Cities
Related Articles: Unveiling the Decapolis: A Journey Through Ancient Cities
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Decapolis: A Journey Through Ancient Cities. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Decapolis: A Journey Through Ancient Cities
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Decapolis: A Journey Through Ancient Cities
- 3.1 A Geographic Tapestry: Mapping the Decapolis
- 3.2 Beyond Geography: The Decapolis’s Cultural and Political Significance
- 3.3 The Decapolis’s Legacy: A Lasting Impact on History
- 3.4 FAQs About the Decapolis:
- 3.5 Tips for Exploring the Decapolis:
- 3.6 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Decapolis: A Journey Through Ancient Cities
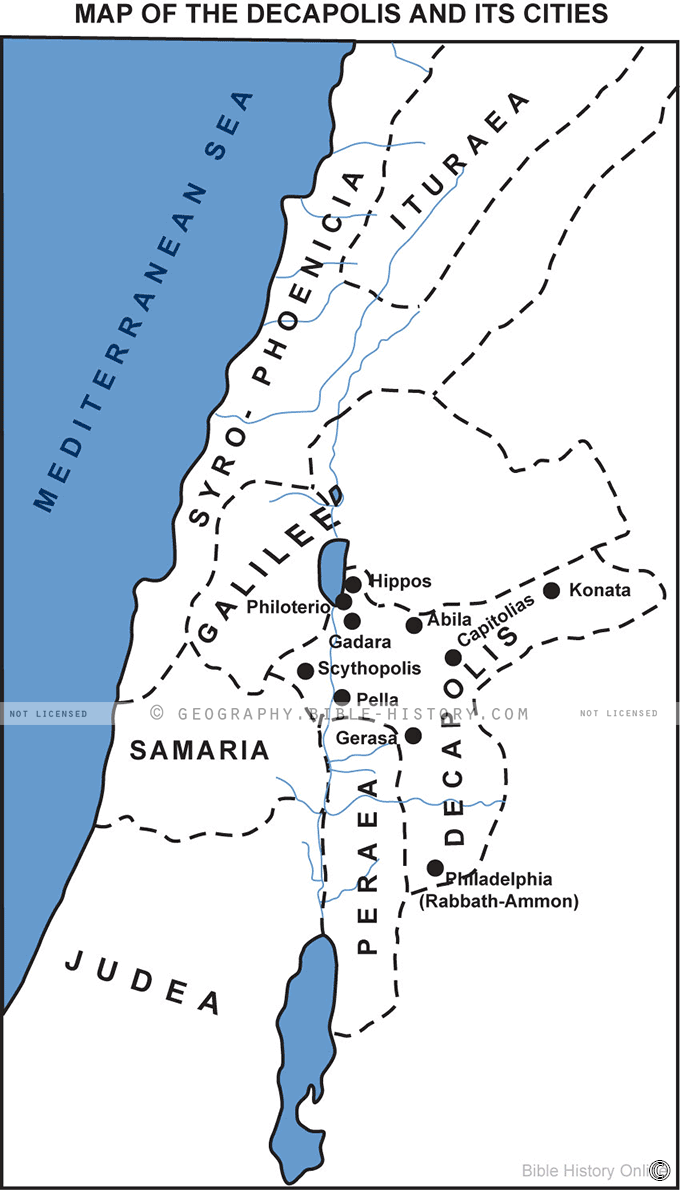
The Decapolis, meaning "Ten Cities" in Greek, was a league of ten Hellenistic cities located in the eastern part of the Roman province of Syria. This region, now encompassing parts of modern-day Jordan, Syria, and Israel, was a vibrant hub of culture, trade, and political influence during the Hellenistic and Roman periods. Understanding the Decapolis and its historical significance requires examining its geographical context, its political and social dynamics, and the legacy it left behind.
A Geographic Tapestry: Mapping the Decapolis
The Decapolis was not a contiguous territory but rather a collection of cities strategically positioned along important trade routes and natural resources. These cities were:
- Damascus (Syria): The largest and most important city in the Decapolis, Damascus was a major center of trade and commerce, strategically located on the Silk Road.
- Philadelphia (Amman, Jordan): Located in the Transjordan region, Philadelphia was a key administrative center and a vital link between the Decapolis and the Nabataean kingdom.
- Scythopolis (Beth She’an, Israel): Situated on the edge of the Jordan Valley, Scythopolis was a thriving agricultural center and a crossroads for trade routes.
- Gadara (Umm Qais, Jordan): Perched on a hill overlooking the Sea of Galilee, Gadara was known for its scenic beauty and its connection to the story of the Gadarene swine.
- Hippos (Sussita, Israel): A city with a prominent Hellenistic heritage, Hippos was located on a plateau overlooking the Sea of Galilee.
- Pella (Tabqat Fahl, Jordan): A city with a rich history dating back to the Bronze Age, Pella was known for its strategic location in the Jordan Valley.
- Gerasa (Jerash, Jordan): Famous for its well-preserved Roman ruins, Gerasa was a prominent city in the Decapolis, known for its impressive architecture and urban planning.
- Dion (Dionysias, Jordan): Located near the Jordan River, Dion was a smaller city with a significant role in the Decapolis’ agricultural production.
- Canatha (Qanawat, Syria): A city known for its volcanic landscape and its role in the wine trade, Canatha was a significant player in the Decapolis economy.
- Raphana (unknown location): The exact location of Raphana remains a mystery, but scholars believe it was likely located in the Jordan Valley.
Mapping the Decapolis:
- Geographic Location: The Decapolis was strategically located in a region where the Mediterranean world met the eastern world, facilitating trade and cultural exchange.
- Trade Routes: The cities were connected by important trade routes, including the Silk Road, the King’s Highway, and the Via Maris, which facilitated the movement of goods and people.
- Natural Resources: The Decapolis was rich in natural resources, including fertile land for agriculture, access to water resources, and deposits of building materials.
Beyond Geography: The Decapolis’s Cultural and Political Significance
The Decapolis was more than just a collection of cities; it represented a unique cultural and political phenomenon in the ancient world.
Hellenistic Influence: The Decapolis cities were established during the Hellenistic period, following the conquests of Alexander the Great. They adopted Greek language, culture, and architectural styles, creating a distinct Hellenistic identity within the region.
Roman Integration: With the Roman conquest of the Levant, the Decapolis cities were integrated into the Roman Empire, becoming part of the province of Syria. This integration brought about a period of relative peace and prosperity, allowing the cities to flourish.
Local Autonomy: Despite their integration into the Roman Empire, the Decapolis cities retained a degree of local autonomy, allowing them to govern themselves and maintain their unique identities. This autonomy fostered a sense of civic pride and local identity.
Cultural Exchange: The Decapolis cities were centers of cultural exchange, where Greek, Roman, and local Eastern cultures interacted and blended. This cultural fusion resulted in a unique and vibrant artistic, religious, and social landscape.
Religious Diversity: The Decapolis cities were home to a diverse range of religious communities, including Jews, Christians, and pagans. This religious diversity contributed to the region’s cultural dynamism and fostered religious tolerance.
Political Significance: The Decapolis played a significant role in the political landscape of the Roman East. The cities were strategically located on the borders of Roman territories and were often involved in regional conflicts and alliances.
The Decapolis’s Legacy: A Lasting Impact on History
The Decapolis’s influence extended beyond its immediate geographical boundaries, leaving a lasting impact on the region’s history and culture.
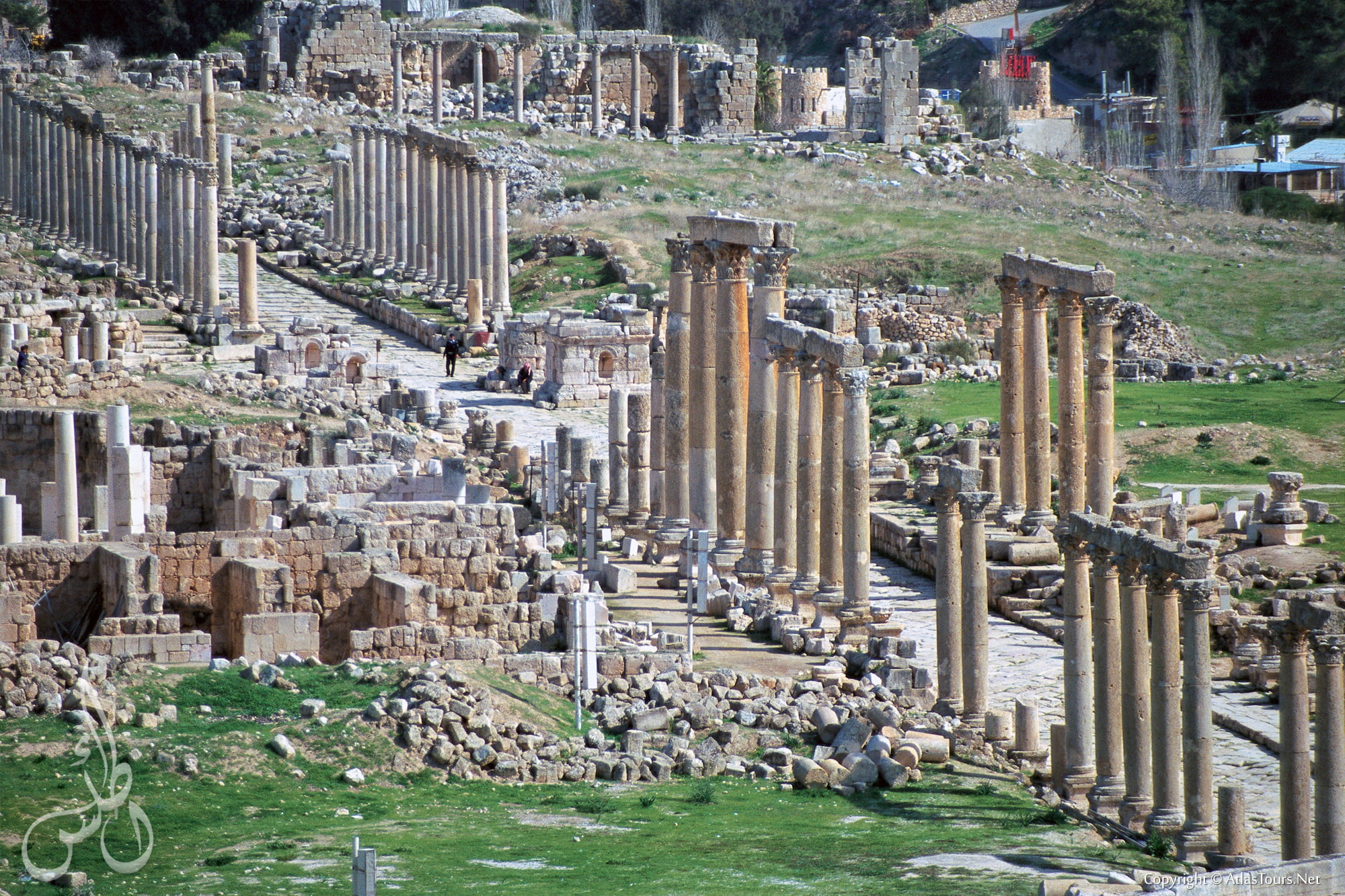
Architectural Heritage: The Decapolis cities are renowned for their impressive architectural heritage, with well-preserved Roman ruins, including temples, theaters, baths, and city walls. These ruins provide valuable insights into the urban planning, architecture, and lifestyle of the ancient world.
Religious Significance: The Decapolis was closely associated with the early history of Christianity, with several cities mentioned in the Bible. These cities played a significant role in the spread of Christianity throughout the Roman Empire.
Cultural Legacy: The Decapolis cities contributed to the development of a unique cultural identity in the region, blending Hellenistic, Roman, and local Eastern influences. This cultural legacy is reflected in the region’s art, literature, and traditions.
Economic Importance: The Decapolis cities were important centers of trade and commerce, connecting the Mediterranean world with the East. Their economic activity contributed to the prosperity of the region and the Roman Empire.
Historical Studies: The Decapolis provides a valuable case study for understanding the complexities of Hellenistic and Roman societies, the dynamics of cultural exchange, and the impact of political and economic forces on urban development.
FAQs About the Decapolis:
1. What is the significance of the Decapolis?
The Decapolis was a significant league of Hellenistic cities in the Roman East, representing a unique blend of cultures and political structures. It played a key role in trade, cultural exchange, and the spread of Christianity.
2. Why were the Decapolis cities important?
The Decapolis cities were strategically located along trade routes, had access to natural resources, and enjoyed a degree of local autonomy, making them important centers of economic activity, cultural exchange, and political influence.
3. What is the Decapolis known for?
The Decapolis is known for its well-preserved Roman ruins, its diverse cultural heritage, its association with early Christianity, and its strategic location in the Roman East.
4. Where are the Decapolis cities located?
The Decapolis cities are located in modern-day Jordan, Syria, and Israel, with most cities situated in the Transjordan region.
5. What happened to the Decapolis?
The Decapolis cities declined with the decline of the Roman Empire and the rise of Islam in the region. However, their architectural and cultural legacy continues to be a significant part of the region’s history and identity.
Tips for Exploring the Decapolis:
- Plan your trip: Research the Decapolis cities and choose the ones that interest you the most. Consider the time you have available and the transportation options.
- Visit the archaeological sites: Explore the well-preserved Roman ruins in cities like Jerash, Amman, and Beth She’an.
- Learn about the history: Read about the history of the Decapolis cities and their role in the ancient world.
- Engage with the local culture: Interact with the local people and learn about their traditions and customs.
- Enjoy the natural beauty: Explore the scenic landscapes surrounding the Decapolis cities, including the Jordan Valley, the Sea of Galilee, and the Transjordan region.
Conclusion:
The Decapolis, a league of ten Hellenistic cities in the Roman East, stands as a testament to the dynamic interplay of cultures, trade, and political forces in the ancient world. Its cities, strategically positioned along trade routes and rich in natural resources, served as centers of economic activity, cultural exchange, and religious diversity. The Decapolis’s legacy, embodied in its architectural heritage, its association with early Christianity, and its contribution to the region’s cultural identity, continues to resonate in the modern world. Understanding the Decapolis allows us to gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of ancient societies and the lasting impact they have had on the world we live in today.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Decapolis: A Journey Through Ancient Cities. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!