Unraveling the Geography of North Carolina: A Detailed Exploration
Related Articles: Unraveling the Geography of North Carolina: A Detailed Exploration
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Geography of North Carolina: A Detailed Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Geography of North Carolina: A Detailed Exploration

North Carolina, a state nestled in the southeastern region of the United States, boasts a diverse landscape that reflects its rich history and dynamic environment. Understanding the geographic features of this state is crucial for comprehending its economic development, cultural identity, and ecological significance. This comprehensive analysis delves into the intricate geography of North Carolina, examining its topography, climate, natural resources, and human impact, providing a detailed overview for researchers, students, and anyone interested in exploring the state’s unique characteristics.
1. Topography: A Tapestry of Diverse Landscapes
North Carolina’s topography is a fascinating mosaic of rolling hills, mountain ranges, coastal plains, and diverse waterways. The state’s landscape can be broadly divided into three distinct physiographic regions:
a. Coastal Plain: This low-lying region stretches from the Atlantic Ocean westward, covering approximately 40% of the state’s land area. Characterized by its flat terrain and sandy soils, the Coastal Plain is home to expansive forests, agricultural lands, and numerous rivers and estuaries. The region’s fertile soil supports a thriving agricultural industry, with crops like tobacco, cotton, soybeans, and peanuts being major contributors to the state’s economy.
b. Piedmont: Located between the Coastal Plain and the Appalachian Mountains, the Piedmont region is a transition zone characterized by rolling hills and gently sloping terrain. Its fertile soil supports a wide range of agricultural activities, and the region is also home to several major cities, including Charlotte, Raleigh, and Greensboro. The Piedmont’s diverse landscape also attracts numerous outdoor enthusiasts, with opportunities for hiking, biking, and exploring the region’s rich history.
c. Appalachian Mountains: The majestic Appalachian Mountains, a prominent feature of North Carolina’s western landscape, are a testament to the state’s geological past. The Blue Ridge Mountains, a subrange of the Appalachians, dominate the western portion of the state, reaching elevations over 6,000 feet. This region is renowned for its breathtaking scenery, abundant forests, and numerous waterfalls. The mountains also play a vital role in the state’s economy, supporting industries like tourism, timber harvesting, and hydroelectric power generation.
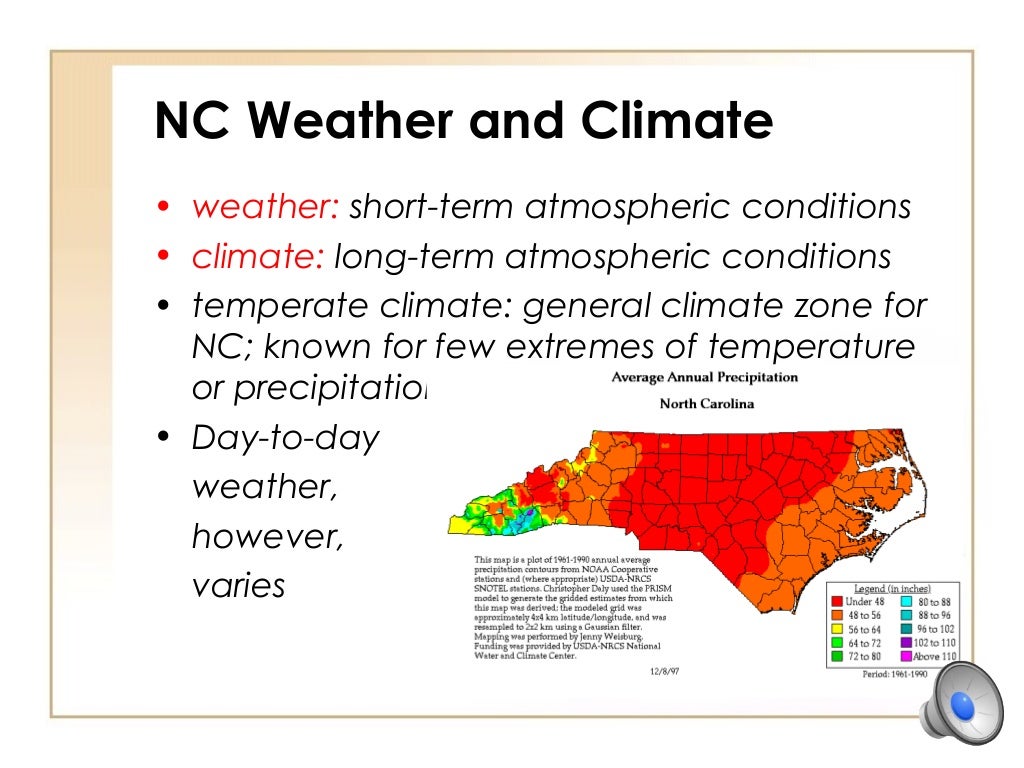
2. Climate: A Temperate Tapestry with Regional Variations
North Carolina’s climate is classified as humid subtropical, characterized by warm, humid summers and mild, cool winters. However, significant variations exist across the state, with the Coastal Plain experiencing milder temperatures and higher humidity compared to the mountainous regions.
a. Coastal Plain: The Coastal Plain enjoys a warm and humid climate, with average temperatures ranging from the mid-60s to the mid-80s Fahrenheit. The region is prone to hurricanes and other tropical storms, particularly during the summer months. The coastal areas also experience frequent fog and sea breezes.
b. Piedmont: The Piedmont region experiences a more moderate climate than the Coastal Plain, with cooler summers and slightly colder winters. The average temperature range is from the mid-50s to the low 80s Fahrenheit. The Piedmont is also less susceptible to hurricanes than the Coastal Plain, but it can experience occasional tornadoes and severe thunderstorms.
c. Appalachian Mountains: The mountainous regions of North Carolina experience a wide range of temperatures, with higher elevations experiencing colder winters and shorter growing seasons. Average temperatures range from the mid-40s to the mid-70s Fahrenheit. The mountains are also prone to heavy snowfall, especially during the winter months.
3. Natural Resources: A Wealth of Assets
North Carolina is endowed with a rich array of natural resources, playing a significant role in the state’s economy and supporting diverse industries.
a. Forests: Forests cover approximately 53% of North Carolina’s land area, making it one of the most forested states in the United States. These forests are a valuable source of timber, pulpwood, and other wood products, supporting a thriving forest products industry. They also provide vital ecosystem services, including carbon sequestration, water filtration, and wildlife habitat.
b. Minerals: North Carolina is home to a variety of mineral resources, including granite, limestone, sand, gravel, and clay. These minerals are used in construction, manufacturing, and other industries. The state also has significant deposits of phosphate rock, a crucial component of fertilizer.
c. Water Resources: North Carolina is blessed with abundant water resources, including rivers, lakes, and groundwater. The state’s rivers are vital for transportation, hydropower generation, and recreation. The numerous lakes provide opportunities for fishing, boating, and other water-based activities. Groundwater is a significant source of drinking water for many communities across the state.
4. Human Impact: Shaping the Landscape
Human activities have significantly shaped the geography of North Carolina, leaving both positive and negative impacts on the state’s natural environment.
a. Agriculture: Agriculture has been a cornerstone of North Carolina’s economy for centuries, shaping the state’s landscape and contributing to its cultural identity. However, agricultural practices, including deforestation, soil erosion, and pesticide use, have had significant environmental consequences.
b. Urbanization: The rapid growth of cities and towns in North Carolina has led to increased land conversion, habitat fragmentation, and air and water pollution. While urbanization has brought economic benefits, it has also placed significant pressure on the state’s natural resources.
c. Industrial Development: North Carolina has a long history of industrial development, with manufacturing, textiles, and energy production playing major roles in the state’s economy. Industrial activities have contributed to air and water pollution, and the disposal of industrial waste has posed environmental challenges.
d. Climate Change: The impacts of climate change are already being felt in North Carolina, with rising sea levels threatening coastal communities, more frequent and intense storms increasing the risk of flooding, and changes in precipitation patterns impacting agriculture and water resources.
5. Geographic Significance: A Crossroads of Culture and Commerce
North Carolina’s unique geography has played a pivotal role in shaping the state’s history, culture, and economy. The state’s location on the Atlantic coast has made it a hub of trade and commerce, while its diverse landscape has attracted settlers, artists, and entrepreneurs. The state’s geographic features have also influenced its cultural identity, with traditions rooted in its agricultural heritage, coastal lifestyle, and Appalachian heritage.
6. The Importance of Understanding North Carolina’s Geography
A comprehensive understanding of North Carolina’s geography is essential for addressing a wide range of challenges and opportunities facing the state. From managing natural resources and mitigating the impacts of climate change to promoting economic development and preserving cultural heritage, knowledge of the state’s geographic features is crucial for informed decision-making.
7. FAQs
Q: What are the major mountain ranges in North Carolina?
A: The major mountain ranges in North Carolina are the Blue Ridge Mountains, the Great Smoky Mountains, and the Unaka Mountains, all part of the larger Appalachian Mountain system.
Q: What is the highest point in North Carolina?
A: The highest point in North Carolina is Mount Mitchell, located in the Black Mountains, with an elevation of 6,684 feet.
Q: What are the major rivers in North Carolina?
A: Some of the major rivers in North Carolina include the Cape Fear River, the Neuse River, the Roanoke River, the Yadkin River, and the Catawba River.
Q: What are the major cities in North Carolina?
A: Some of the major cities in North Carolina include Charlotte, Raleigh, Greensboro, Durham, Winston-Salem, Fayetteville, and Asheville.
Q: What are the major industries in North Carolina?
A: North Carolina’s major industries include manufacturing, agriculture, tourism, finance, healthcare, and technology.
8. Tips
- Explore the state’s parks and natural areas: North Carolina is home to a vast network of state parks, national forests, and other protected areas, offering opportunities to experience the state’s diverse landscapes firsthand.
- Visit historical sites and museums: The state’s rich history is reflected in its numerous historical sites and museums, providing insights into the state’s past and cultural heritage.
- Learn about the state’s agricultural heritage: North Carolina has a long and rich agricultural history, with farms and farmers’ markets offering opportunities to learn about the state’s food production and culinary traditions.
- Support local businesses and organizations: By supporting local businesses and organizations, you can contribute to the state’s economic vitality and community development.
9. Conclusion
North Carolina’s geography is a testament to the state’s dynamic and diverse landscape, reflecting its rich history, cultural identity, and economic development. From its coastal plains to its mountain ranges, the state’s topography, climate, natural resources, and human impact have shaped its unique characteristics. By understanding the complexities of North Carolina’s geography, we can better appreciate its beauty, address its challenges, and harness its potential for a sustainable and prosperous future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Geography of North Carolina: A Detailed Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!