Understanding the Significance of the Equator: A Comprehensive Guide to its Representation on Maps
Related Articles: Understanding the Significance of the Equator: A Comprehensive Guide to its Representation on Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Significance of the Equator: A Comprehensive Guide to its Representation on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Significance of the Equator: A Comprehensive Guide to its Representation on Maps
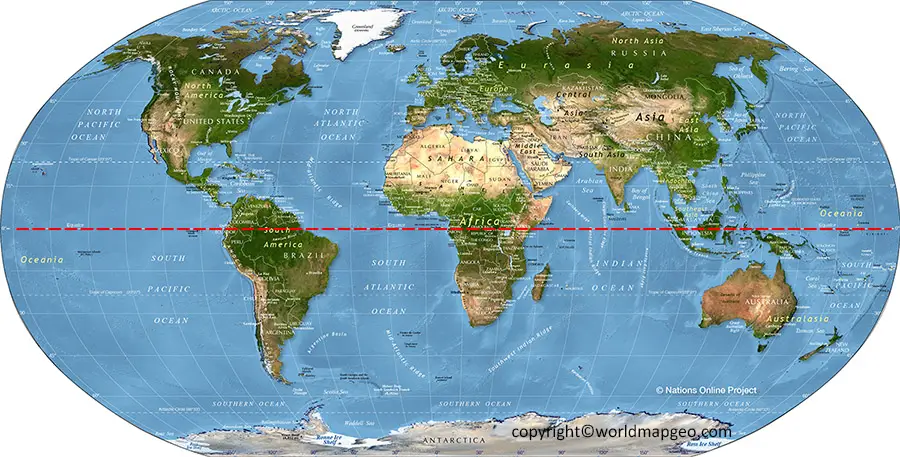
The Earth’s equator, an imaginary line circling the globe at zero degrees latitude, holds immense geographical and scientific significance. It serves as a crucial reference point for understanding the Earth’s shape, climate, and global positioning systems. This article delves into the importance of visualizing the equator on maps, exploring its role in various applications and highlighting its contribution to our comprehension of the planet.
The Equator: A Defining Line
The equator is not merely a line on a map; it represents a fundamental division of the Earth. It divides the planet into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, with every point on the equator equidistant from both poles. This unique characteristic leads to several important implications:
- Climate Patterns: The equator experiences the most direct sunlight throughout the year, leading to consistently high temperatures and tropical climates. The areas north and south of the equator experience a greater variation in temperature due to the changing angle of sunlight.
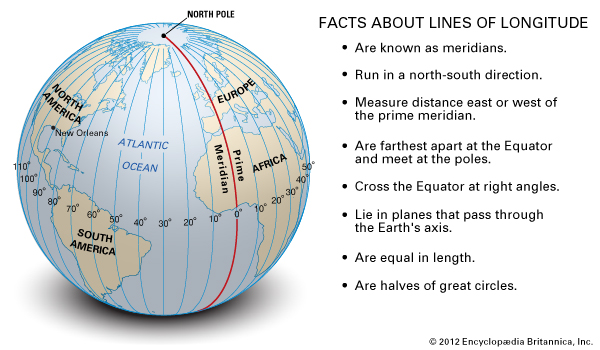
- Time Zones: The equator plays a vital role in establishing time zones. As the Earth rotates, different longitudes experience sunrise and sunset at different times. The International Date Line, which roughly follows the 180th meridian, is positioned to ensure consistency in timekeeping across the globe.
- Navigation: The equator serves as a reference point for navigation, particularly in maritime and aerial transportation. Navigational systems utilize latitude and longitude coordinates, with the equator forming the base for latitude measurements.
Visualizing the Equator on Maps: Importance and Applications
Representing the equator on maps is crucial for various reasons:
- Geographical Orientation: Maps with a clearly marked equator provide a visual representation of the Earth’s division into hemispheres, aiding in understanding the relative positions of countries, continents, and other geographical features.
- Climate Analysis: The equator’s position on maps allows for a visual understanding of climate zones and patterns. This is especially useful for studying the distribution of biomes, rainfall patterns, and the impact of climate change.
- Global Positioning Systems (GPS): GPS systems rely on latitude and longitude coordinates, with the equator serving as the reference point for latitude measurements. Visualizing the equator on maps facilitates a clearer understanding of how GPS coordinates are determined and used.
- Scientific Research: Researchers across various disciplines, including geography, meteorology, and oceanography, utilize maps with the equator to analyze and interpret data related to the Earth’s surface, atmosphere, and oceans.
Types of Maps and Equator Representation
Different types of maps employ various methods to represent the equator:
- World Maps: World maps, depicting the entire globe, typically show the equator as a straight line running horizontally across the center. This representation, while simplified, provides a clear understanding of the equator’s position relative to other continents and oceans.
- Regional Maps: Maps focusing on specific regions, such as continents or countries, may also include the equator depending on the map’s purpose and scale. For instance, a map of Africa will likely show the equator to highlight its position relative to the continent’s diverse climate zones.
- Thematic Maps: Thematic maps, designed to illustrate specific data or concepts, may emphasize the equator’s role in defining climate zones, time zones, or other geographical features.
FAQs about the Equator on Maps
Q1: Why is the equator important for understanding time zones?
A: The Earth’s rotation and the equator’s position at zero degrees latitude are crucial for establishing time zones. As the Earth rotates, different longitudes experience sunrise and sunset at different times. The equator serves as a reference point for dividing the globe into 24 time zones, each representing a one-hour difference.
Q2: How does the equator influence climate patterns?
A: The equator receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year, leading to consistently high temperatures and tropical climates. The areas north and south of the equator experience a greater variation in temperature due to the changing angle of sunlight.
Q3: What are some examples of how the equator is used in navigation?
A: The equator serves as a reference point for latitude measurements, which are essential for navigation. GPS systems, maritime charts, and aerial navigation systems all rely on latitude and longitude coordinates, with the equator forming the base for latitude measurements.
Q4: How is the equator represented on different types of maps?
A: World maps typically depict the equator as a straight line running horizontally across the center. Regional maps may also include the equator depending on the map’s purpose and scale. Thematic maps, designed to illustrate specific data or concepts, may emphasize the equator’s role in defining climate zones, time zones, or other geographical features.
Tips for Understanding the Equator on Maps
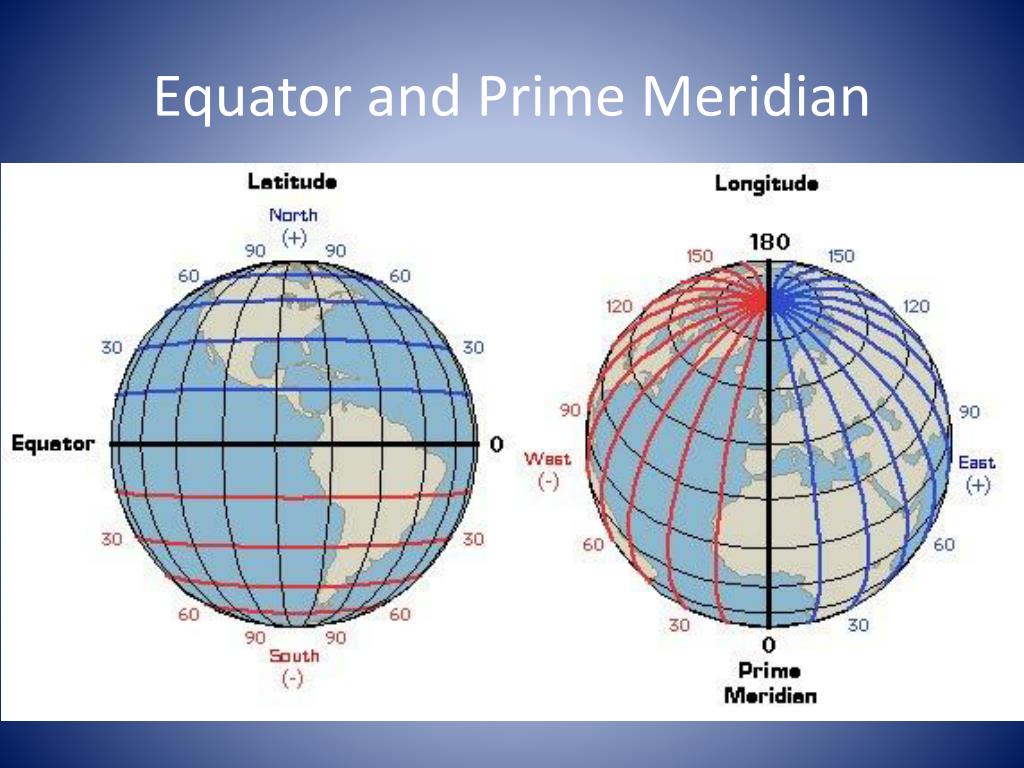
- Focus on the Latitude: The equator represents zero degrees latitude, with all points on the equator having the same latitude. This is crucial for understanding the Earth’s shape and the relationship between latitude and longitude.
- Consider the Scale: The equator’s representation on maps varies depending on the map’s scale. World maps will show the equator as a straight line, while regional maps may depict it as a curved line.
- Utilize Online Resources: Numerous online mapping tools and resources provide interactive maps with clearly marked equator lines, allowing for exploration and analysis.
- Relate the Equator to Other Features: Understanding the equator’s position relative to other geographical features, such as continents, oceans, and climate zones, enhances its significance and utility.
Conclusion
The equator, as represented on maps, is a crucial reference point for understanding the Earth’s shape, climate, and global positioning systems. Its presence on maps provides a visual representation of the Earth’s division into hemispheres, aids in understanding climate zones and patterns, and facilitates navigation. By understanding the equator’s significance and how it is depicted on maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for our planet’s complex geography and the systems that govern it.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Significance of the Equator: A Comprehensive Guide to its Representation on Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!