Understanding Taiwan’s Geographic Position: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: Understanding Taiwan’s Geographic Position: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Taiwan’s Geographic Position: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Taiwan’s Geographic Position: A Comprehensive Exploration

Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), occupies a strategically significant location in East Asia. Situated off the southeastern coast of mainland China, the island nation is separated by the Taiwan Strait, a body of water that plays a crucial role in regional dynamics. Understanding Taiwan’s geographic position is essential for appreciating its historical, political, and economic context.
Taiwan’s Location: A Crossroads of East Asia
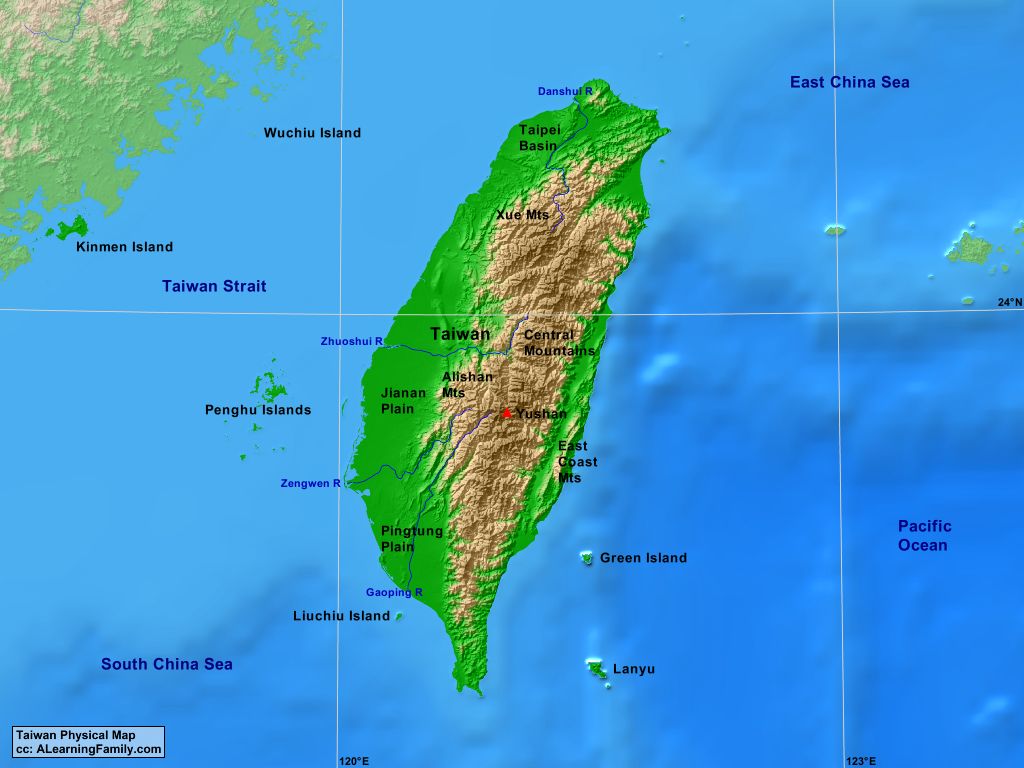
Taiwan’s geographical coordinates are approximately 23.5° N latitude and 121° E longitude. The island itself is roughly 36,193 square kilometers (13,974 square miles) in size, making it slightly larger than the Netherlands. Taiwan’s location, nestled between mainland China and the Pacific Ocean, has shaped its history and influenced its present-day significance.
Key Geographic Features
- Taiwan Strait: This 180-kilometer (112-mile) wide strait separates Taiwan from mainland China. It serves as a vital waterway for trade and transportation, but it also carries a heavy historical and political weight.
- Taiwan Island: The main island, often referred to as Formosa in historical texts, is characterized by its mountainous terrain. The Central Mountain Range runs down the island’s spine, with the highest peak, Yushan (Jade Mountain), reaching over 3,952 meters (12,966 feet).
- Adjacent Islands: Taiwan’s territory also includes several smaller islands, such as Penghu (Pescadores), Kinmen (Quemoy), and Matsu. These islands are strategically important for Taiwan’s defense and maritime claims.
- Pacific Ocean: Taiwan’s eastern coastline faces the vast Pacific Ocean, exposing it to the influences of typhoons and providing access to important shipping routes.
Historical Significance
Taiwan’s geographic position has played a crucial role in its history. The island has been a crossroads for various cultures and empires, from the Dutch and Spanish colonial periods to the Japanese occupation. Its strategic location made it a target for both conquest and trade.
Political Context
Taiwan’s location has also been a source of political tension. The island’s status is a complex and controversial issue, with the People’s Republic of China (PRC) claiming sovereignty over Taiwan. This ongoing dispute has led to a delicate geopolitical balance in the region.
Economic Importance
Taiwan’s location has facilitated its economic development. Its proximity to major Asian markets, including mainland China, Japan, and South Korea, has made it a key hub for manufacturing, trade, and investment. The island’s strategic location also allows it to leverage its maritime resources and develop its shipping industry.
Environmental Considerations
Taiwan’s location also presents environmental challenges. The island is susceptible to natural disasters like typhoons and earthquakes. Its proximity to mainland China also raises concerns about air pollution and environmental degradation.
Understanding the Importance of Taiwan’s Location
Taiwan’s location is not simply a geographical fact; it is a key element in understanding the island’s history, politics, economy, and environmental challenges. Its strategic position in East Asia makes it a vital player in regional affairs, and its future remains intertwined with the complexities of the Asia-Pacific region.
FAQs about Taiwan’s Location
1. What is the distance between Taiwan and mainland China?
The distance between Taiwan and mainland China varies depending on the specific points measured. The shortest distance across the Taiwan Strait is approximately 130 kilometers (81 miles).
2. Why is the Taiwan Strait important?
The Taiwan Strait is a vital waterway for trade and transportation between mainland China and Taiwan. It also holds significant strategic importance, as it serves as a buffer zone between the two sides and a potential flashpoint for conflict.
3. What are the main industries in Taiwan?
Taiwan’s economy is highly diversified, with key industries including electronics, semiconductors, information technology, textiles, and manufacturing.
4. Is Taiwan a country?
The political status of Taiwan is a complex and contentious issue. The People’s Republic of China claims sovereignty over Taiwan, while Taiwan maintains its own government and democratic system.
5. What are the main environmental challenges facing Taiwan?
Taiwan faces various environmental challenges, including typhoons, earthquakes, air pollution, and water resource management.
Tips for Understanding Taiwan’s Location
- Study a map: Familiarize yourself with Taiwan’s location on a map, noting its proximity to mainland China and the Pacific Ocean.
- Research historical events: Explore Taiwan’s historical interactions with other countries and empires, particularly its relationship with mainland China.
- Follow current events: Stay informed about the latest developments regarding Taiwan’s political status and its relationship with China.
- Learn about Taiwan’s culture and economy: Explore Taiwan’s unique cultural heritage and its economic contributions to the region.
- Consider the environmental challenges: Learn about the environmental threats facing Taiwan and the efforts being made to address them.
Conclusion
Taiwan’s geographic position is a defining factor in its history, politics, economy, and environmental challenges. Its strategic location at the crossroads of East Asia makes it a vital player in regional affairs, and its future remains intertwined with the complexities of the Asia-Pacific region. By understanding Taiwan’s location, we gain a deeper appreciation for the island’s significance and its role in the global landscape.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Taiwan’s Geographic Position: A Comprehensive Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!