Understanding Syria’s Position in the Middle East: A Geographical Analysis
Related Articles: Understanding Syria’s Position in the Middle East: A Geographical Analysis
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Syria’s Position in the Middle East: A Geographical Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding Syria’s Position in the Middle East: A Geographical Analysis
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Syria’s Position in the Middle East: A Geographical Analysis
- 3.1 A Crossroads of Cultures and Civilizations
- 3.2 Geopolitical Significance: A Vital Strategic Location
- 3.3 The Impact of Geography on Syria’s Present and Future
- 3.4 FAQs: Understanding Syria’s Geographic Context
- 3.5 Tips: Navigating Syria’s Complex Geography
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Land of Complexity and Potential
- 4 Closure
Understanding Syria’s Position in the Middle East: A Geographical Analysis

Syria, a nation steeped in history and cultural significance, occupies a strategically vital location in the Middle East. Its geographical position has shaped its political landscape, economic potential, and cultural interactions throughout history. This article delves into the intricacies of Syria’s geographical context, exploring its physical characteristics, geopolitical significance, and the impact of its location on its present and future.
A Crossroads of Cultures and Civilizations
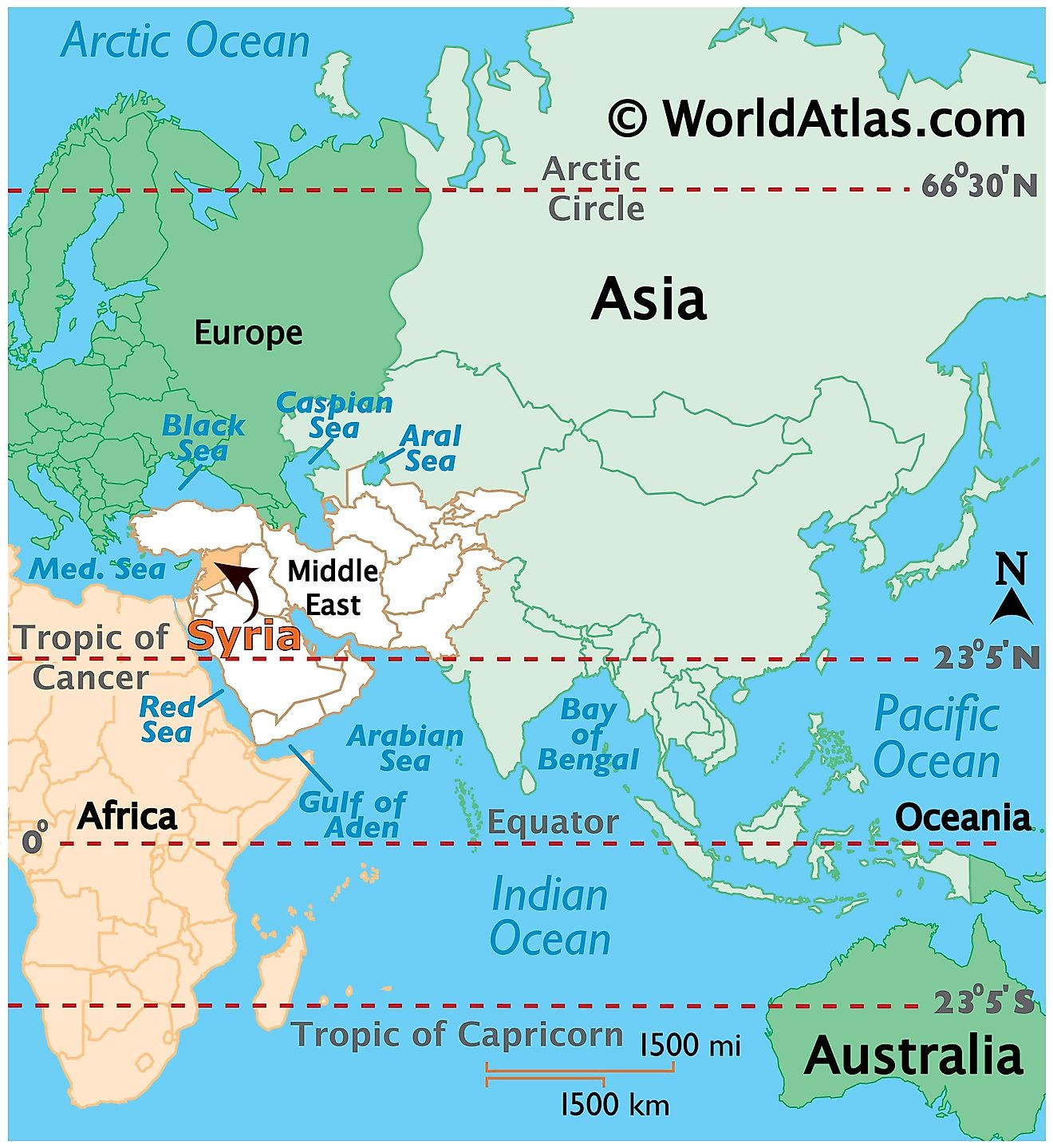
Syria’s geographic location at the heart of the Middle East makes it a crossroads of cultures and civilizations. Situated between the Mediterranean Sea to the west and the Arabian Desert to the east, it acts as a bridge between Europe, Asia, and Africa. This unique position has fostered diverse cultural influences, leaving an indelible mark on the nation’s history, architecture, and traditions.
The Levant: A Region of Historical Significance
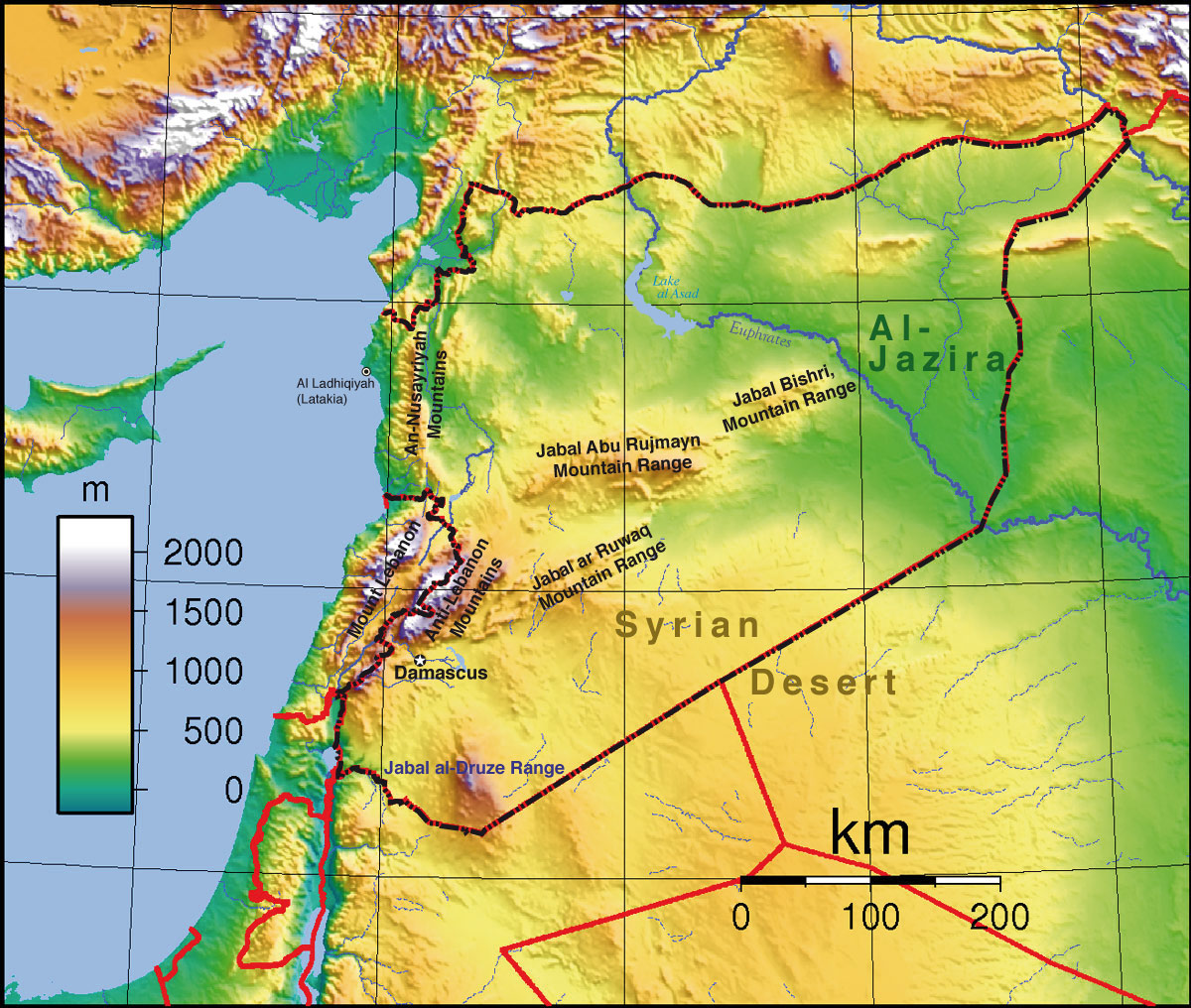
Syria is an integral part of the Levant, a historical region encompassing parts of modern-day Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, and Palestine. This area has witnessed the rise and fall of numerous empires, including the Phoenicians, Romans, Ottomans, and the British. Its strategic location has made it a coveted territory for centuries, resulting in a complex tapestry of cultures and civilizations.
Physical Features: A Diverse Landscape
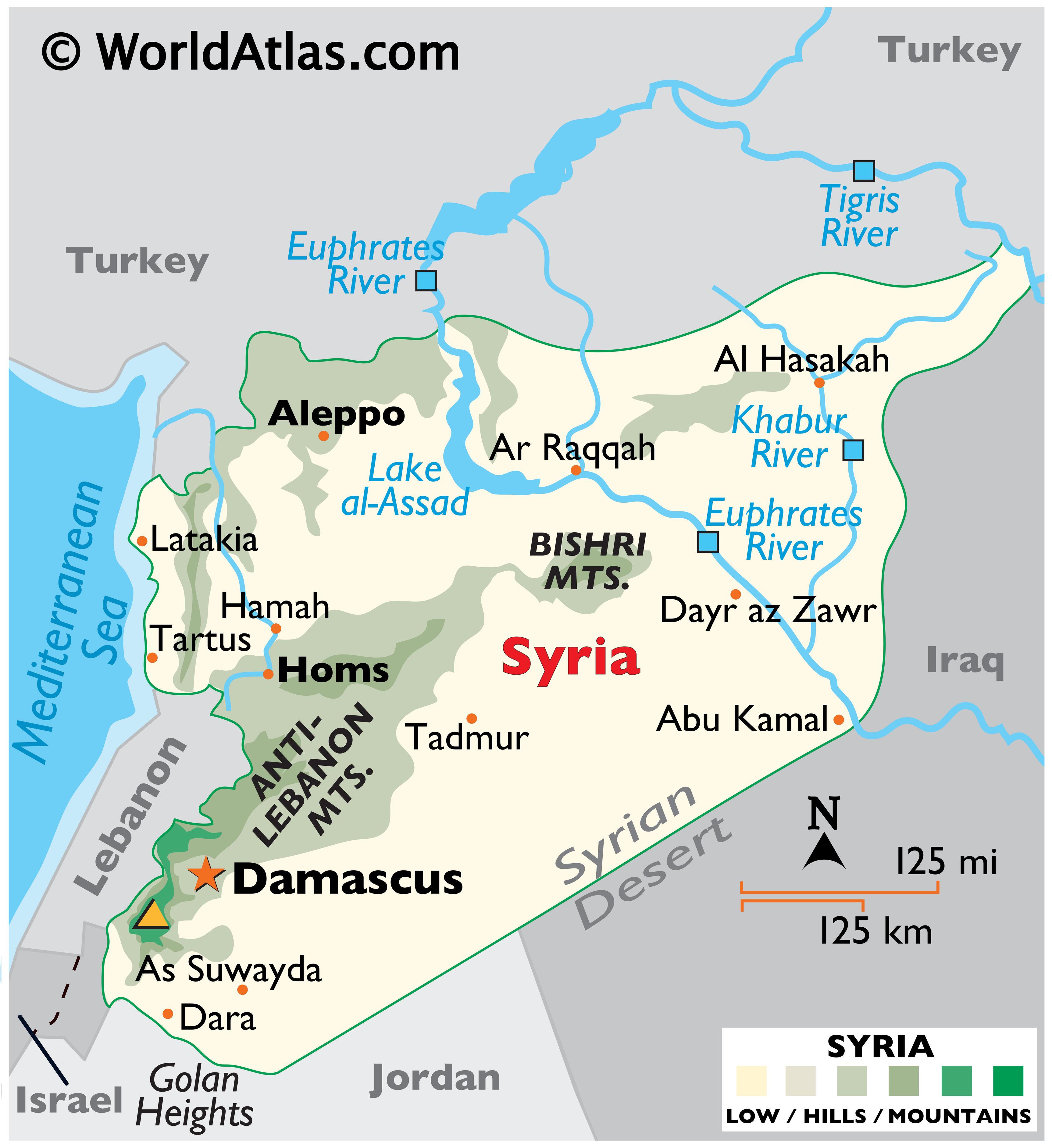
Syria’s landscape is as diverse as its history, encompassing a range of geographical features. The western coastal plain, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, offers fertile land for agriculture and boasts picturesque beaches. The mountainous region in the west, including the Anti-Lebanon and Jabal al-Druze ranges, provides natural barriers and harbors diverse ecosystems. The eastern region is dominated by the Syrian Desert, a vast expanse of arid land stretching towards the Arabian Peninsula.
Water Resources: A Precious Commodity
Water resources are crucial for Syria’s survival, given its semi-arid climate. The Euphrates River, flowing from Turkey through Syria and Iraq, is a vital source of water for irrigation and drinking. However, the availability of water is increasingly strained due to factors like climate change, population growth, and upstream dam construction.
Geopolitical Significance: A Vital Strategic Location
Syria’s strategic location has made it a pivotal player in regional politics for centuries. Its proximity to major powers like Turkey, Israel, and Iran, coupled with its access to key trade routes, has made it a target of both cooperation and conflict.
Bordering Nations: A Complex Web of Relationships
Syria shares borders with several countries, each presenting unique challenges and opportunities. Its border with Turkey has been a source of tension due to the ongoing Syrian civil war and the presence of Kurdish groups. Its border with Israel has been a major point of conflict, with a long history of wars and disputes. Its borders with Lebanon, Jordan, and Iraq are characterized by complex cultural and economic ties, often intertwined with political complexities.
Trade Routes: A Gateway to the Region
Syria’s location has made it a crucial link in international trade routes connecting Europe, Asia, and Africa. Historically, its ports, such as Latakia and Tartus, have served as important hubs for maritime trade. The country’s strategic position along the "Silk Road" has further enhanced its economic potential.
The Impact of Geography on Syria’s Present and Future
Syria’s geographical location has played a pivotal role in shaping its present and future. Its diverse landscape, strategic position, and historical significance have both facilitated and hindered its development.
Challenges and Opportunities: A Balancing Act
Syria’s geographical location presents both challenges and opportunities. Its proximity to conflict zones and the presence of complex geopolitical dynamics pose significant challenges to stability and development. However, its strategic location offers potential for economic growth, cultural exchange, and regional cooperation.
The Syrian Civil War: A Geopolitical Earthquake
The ongoing Syrian civil war, fueled by internal conflicts and external interventions, has had a devastating impact on the country’s social fabric, economy, and infrastructure. The conflict has further complicated Syria’s geopolitical landscape, raising concerns about regional stability and security.
Reconstruction and Development: A Long and Difficult Path
The path to reconstruction and development in Syria is long and arduous. The country faces immense challenges, including rebuilding infrastructure, restoring economic stability, and addressing the social and political consequences of the civil war. Its geographical location can play a vital role in attracting foreign investment and fostering regional cooperation, but overcoming the legacy of conflict will require sustained efforts and international support.
FAQs: Understanding Syria’s Geographic Context
Q1. What are the major geographical features of Syria?
A1. Syria’s landscape is diverse, encompassing a coastal plain, mountainous regions, and the vast Syrian Desert. The western coastal plain offers fertile land for agriculture, while the mountainous regions provide natural barriers and diverse ecosystems. The eastern region is dominated by the Syrian Desert, a vast expanse of arid land.
Q2. What is the geopolitical significance of Syria’s location?
A2. Syria’s strategic location at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa makes it a key player in regional politics. Its proximity to major powers, access to key trade routes, and diverse cultural influences have made it a target of both cooperation and conflict.
Q3. How has Syria’s geography impacted its history and culture?
A3. Syria’s location has made it a crossroads of civilizations, with diverse cultural influences shaping its history, architecture, and traditions. The Levant, encompassing parts of Syria, has witnessed the rise and fall of numerous empires, leaving an indelible mark on the region’s cultural landscape.
Q4. What are the major challenges facing Syria in terms of its geographical context?
A4. Syria faces challenges related to water scarcity, the ongoing civil war, and the complex geopolitical dynamics of the region. Its proximity to conflict zones and the presence of diverse ethnic and religious groups have exacerbated tensions and hindered stability.
Q5. What are the potential opportunities for Syria in terms of its geographical location?
A5. Syria’s strategic location offers potential for economic growth, cultural exchange, and regional cooperation. Its access to key trade routes and its diverse cultural heritage can attract foreign investment and foster regional integration.
Tips: Navigating Syria’s Complex Geography
Tip 1: Study maps and geographical features to gain a deeper understanding of Syria’s diverse landscape and its strategic location.
Tip 2: Research the historical significance of Syria’s location, exploring the rise and fall of empires and the cultural influences that have shaped the region.
Tip 3: Stay informed about the ongoing Syrian civil war and its impact on the country’s political landscape, economy, and social fabric.
Tip 4: Consider the challenges and opportunities presented by Syria’s geographical context, exploring the potential for economic development, cultural exchange, and regional cooperation.
Tip 5: Engage in thoughtful discussions about Syria’s future, considering the role of international cooperation, reconstruction efforts, and the need for sustainable development.
Conclusion: A Land of Complexity and Potential
Syria’s geographical location has shaped its history, culture, and present-day challenges. Its strategic position at the heart of the Middle East has made it a crossroads of civilizations, a target of geopolitical interests, and a land of both immense potential and complex challenges. Understanding Syria’s geographical context is crucial for comprehending its past, present, and future, fostering a nuanced perspective on its role in the region and the world. As Syria navigates the path to reconstruction and development, its geographical location will continue to play a vital role in shaping its destiny.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Syria’s Position in the Middle East: A Geographical Analysis. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!