The QCC Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Quality Control Charts
Related Articles: The QCC Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Quality Control Charts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The QCC Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Quality Control Charts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The QCC Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Quality Control Charts
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The QCC Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Quality Control Charts
- 3.1 Understanding the Principles of QCC Maps
- 3.2 Types of QCC Maps
- 3.3 Applications of QCC Maps
- 3.4 Benefits of Implementing QCC Maps
- 3.5 FAQs about QCC Maps
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The QCC Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Quality Control Charts
Quality control charts, commonly known as QCC maps, are powerful visual tools used in quality management to monitor processes and identify potential issues. These charts provide a graphical representation of data collected over time, allowing for the detection of trends, patterns, and deviations from expected behavior. By understanding the underlying principles and applications of QCC maps, organizations can effectively implement robust quality control strategies, leading to enhanced product quality, reduced defects, and improved customer satisfaction.
Understanding the Principles of QCC Maps
QCC maps are based on statistical process control (SPC), a methodology for monitoring and controlling processes to ensure consistent output. The core principle behind SPC is the understanding that all processes exhibit natural variation. This variation is inherent in any process, regardless of how carefully it is controlled. QCC maps help differentiate between natural variation and assignable variation, which is caused by specific factors like equipment malfunction, operator error, or changes in raw materials.
The fundamental elements of a QCC map include:
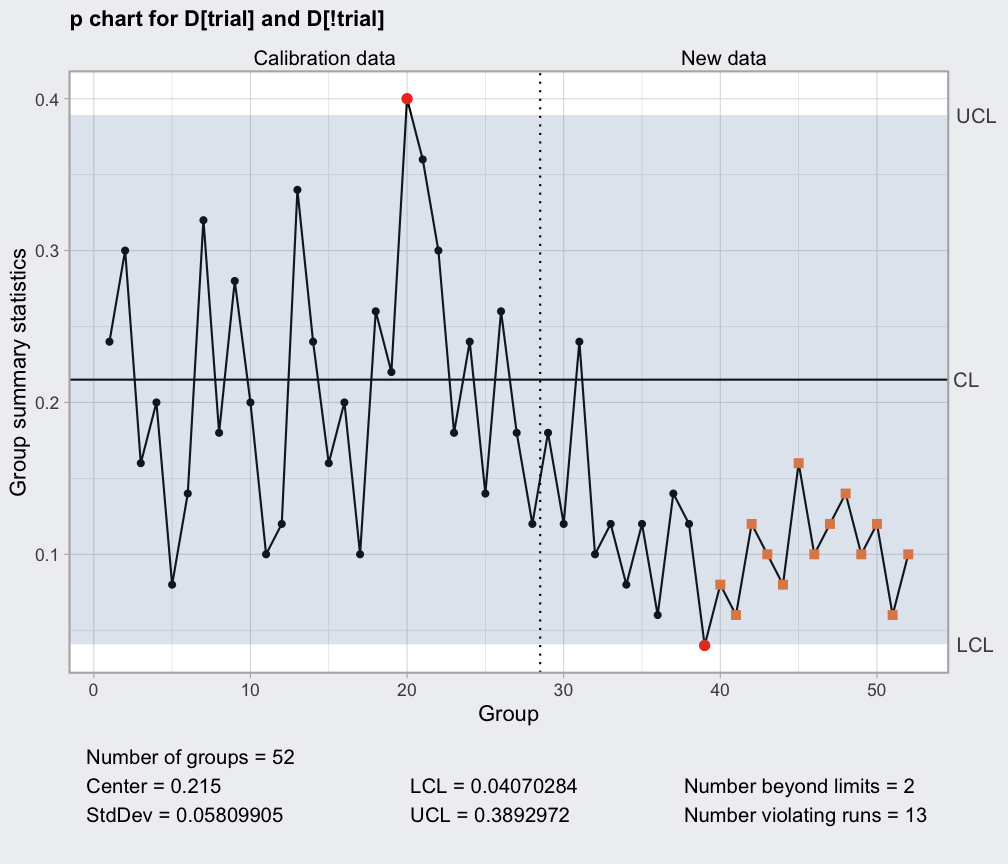
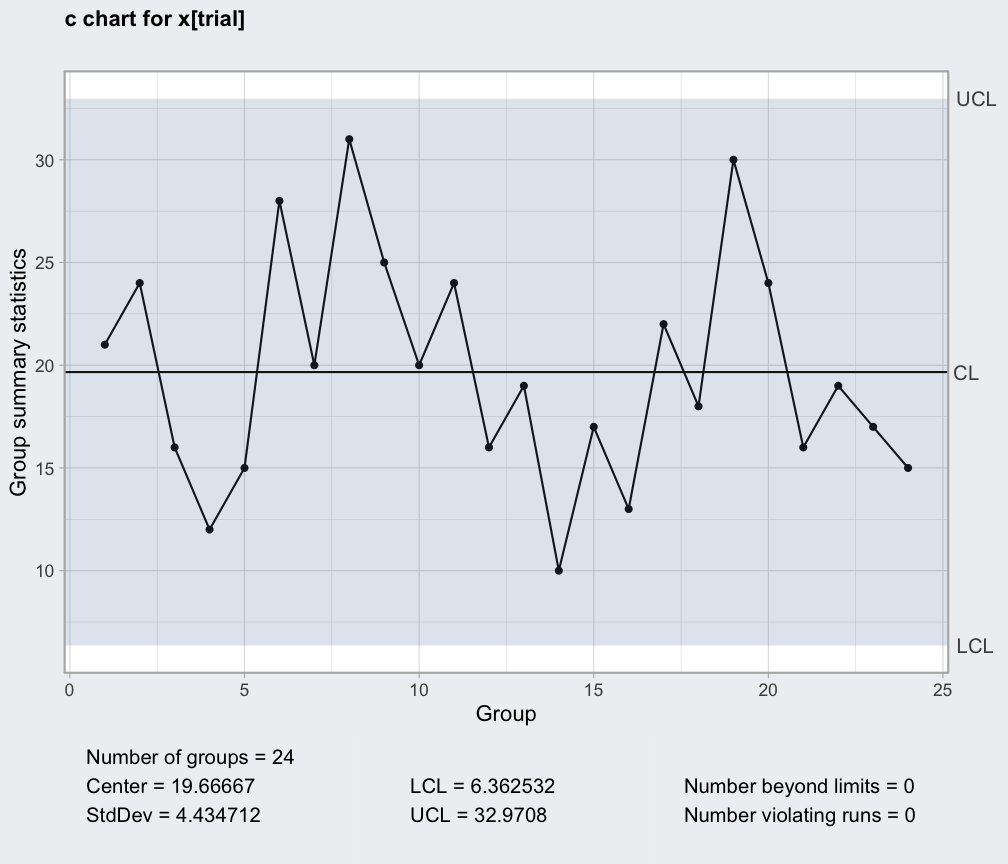
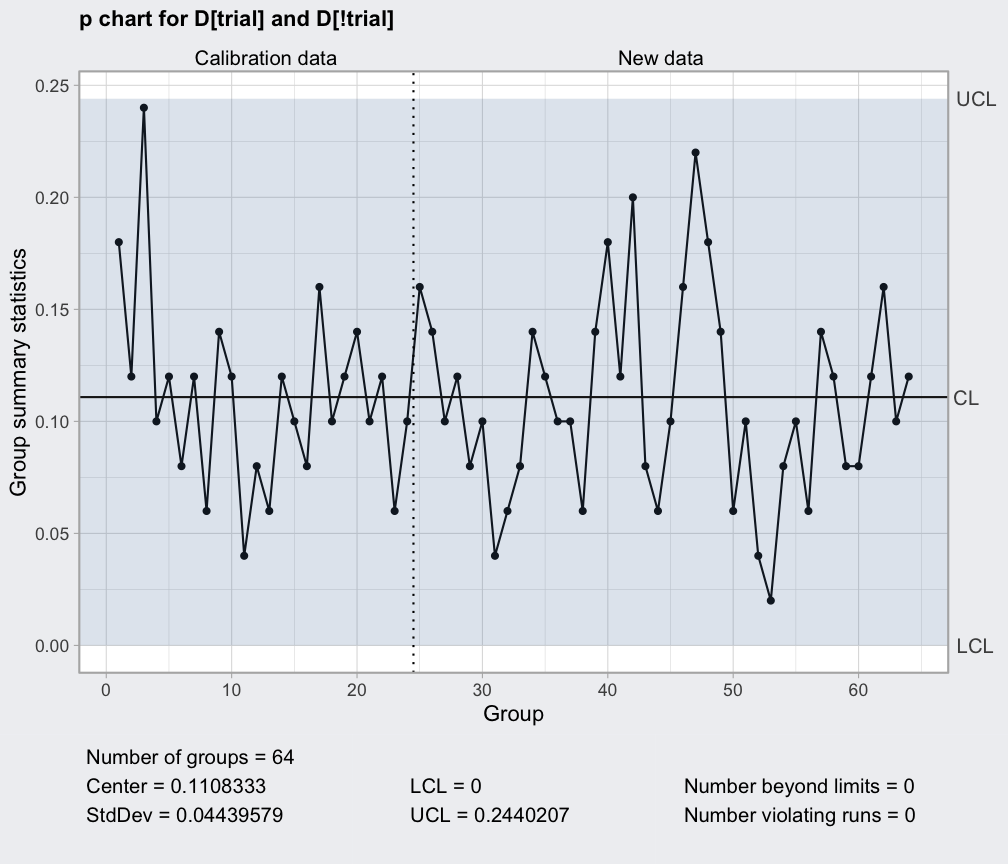
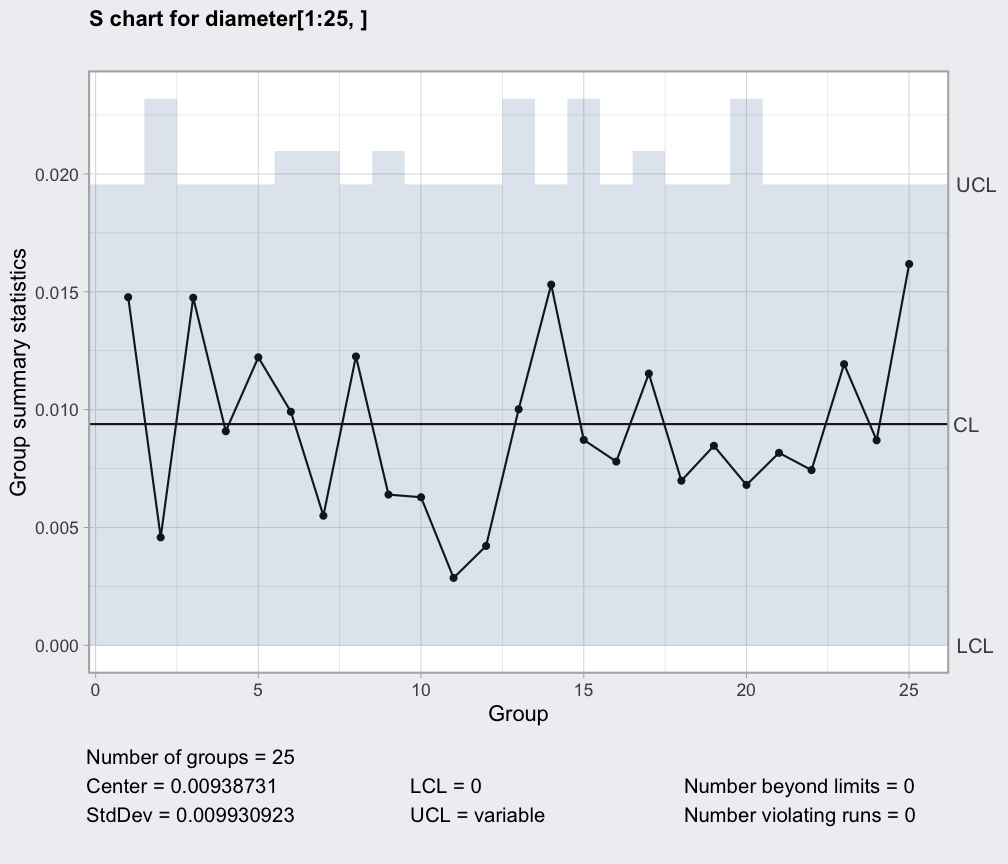
- Control Limits: These are statistical boundaries established around the expected process average. Data points falling within the control limits indicate that the process is operating within its normal range.
- Central Line: Represents the average value of the process data.
- Data Points: Individual observations plotted on the chart, reflecting the measured characteristic of the process over time.
- Time Axis: Represents the chronological order of data points, enabling the analysis of trends and patterns.
Types of QCC Maps
QCC maps are available in various forms, each designed to analyze different types of data and address specific quality control objectives. The most common types include:
- X-bar and R Chart: Used for monitoring the average (X-bar) and range (R) of a process. This chart is suitable for continuous data, such as measurements of length, weight, or temperature.
- p Chart: Used for monitoring the proportion of defective items in a sample. This chart is ideal for analyzing data with binary outcomes, such as pass/fail or good/bad.
- c Chart: Used for monitoring the number of defects per unit. This chart is useful for analyzing data where the number of defects is a primary concern.
- u Chart: Similar to the c chart, but it considers the number of defects per unit of measure, such as per 100 units or per 1000 units.
Applications of QCC Maps
QCC maps find widespread applications across various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and service sectors. Some key applications include:
- Process Monitoring and Control: QCC maps allow for continuous monitoring of processes, enabling early detection of deviations from desired performance levels. This proactive approach facilitates timely intervention and corrective actions, preventing potential quality issues from escalating.
- Trend Analysis: By plotting data points over time, QCC maps reveal trends and patterns in process performance. This information helps identify potential areas for improvement, optimize process parameters, and implement preventive measures.
- Process Capability Assessment: QCC maps can assess the capability of a process to consistently meet specified quality requirements. By analyzing the distribution of data points, organizations can determine whether the process is capable of producing products within acceptable tolerances.
- Root Cause Analysis: When deviations from expected performance are identified, QCC maps provide valuable insights into the underlying causes. By investigating data points that fall outside the control limits, organizations can pinpoint the root causes of quality problems and implement effective corrective actions.
- Process Improvement: QCC maps are integral to process improvement initiatives. By identifying areas of variability and potential for improvement, QCC maps guide organizations in implementing changes that enhance process efficiency, reduce waste, and minimize defects.
Benefits of Implementing QCC Maps
The implementation of QCC maps offers numerous benefits for organizations striving for continuous quality improvement:
- Improved Product Quality: By monitoring and controlling processes, QCC maps help ensure consistent product quality, reducing the occurrence of defects and customer dissatisfaction.
- Reduced Costs: Early detection and correction of quality issues minimize rework, scrap, and warranty claims, leading to significant cost savings.
- Increased Efficiency: QCC maps identify process bottlenecks and areas for optimization, leading to improved efficiency and productivity.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Consistent product quality and timely resolution of issues enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: QCC maps provide objective data for decision-making, enabling organizations to make informed choices regarding process improvement initiatives.
FAQs about QCC Maps
1. What are the common challenges faced when implementing QCC maps?
- Resistance to Change: Implementing QCC maps often requires a shift in organizational culture and mindset. Overcoming resistance to change and fostering a culture of continuous improvement is crucial for successful implementation.
- Lack of Training and Expertise: Implementing QCC maps effectively requires a basic understanding of statistical concepts and data analysis. Providing adequate training and support to staff is essential.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Accurate and timely data collection is critical for effective QCC map implementation. Establishing robust data collection systems and ensuring data integrity are vital.
- Time and Resource Constraints: Implementing and maintaining QCC maps can require significant time and resources. Prioritizing projects, optimizing processes, and utilizing available resources effectively are crucial.
2. How can organizations ensure the effective implementation of QCC maps?
- Define Clear Objectives: Establish specific and measurable goals for QCC map implementation, aligning with overall quality improvement objectives.
- Select Appropriate Charts: Choose the most suitable QCC map type based on the nature of the data and the specific quality control objective.
- Establish Control Limits: Determine appropriate control limits based on historical data or industry standards, ensuring they accurately reflect the expected process performance.
- Train Staff: Provide comprehensive training to staff involved in data collection, chart analysis, and interpretation.
- Monitor and Review: Regularly monitor QCC maps, analyze data, and identify trends and patterns. Conduct periodic reviews to assess the effectiveness of implemented measures and make necessary adjustments.
3. What are some tips for using QCC maps effectively?
- Keep it Simple: QCC maps should be easy to understand and interpret, avoiding complex statistical jargon or unnecessary detail.
- Focus on Key Variables: Identify and monitor the most critical variables that significantly impact product quality.
- Use Real-Time Data: Utilize real-time data to ensure timely detection of deviations and enable rapid response.
- Involve Stakeholders: Engage stakeholders, including operators, engineers, and management, in the implementation and interpretation of QCC maps.
- Continuously Improve: QCC maps are not static tools. Regularly review and refine them based on new data, feedback, and evolving quality objectives.
Conclusion
QCC maps are indispensable tools for organizations seeking to achieve and maintain high levels of quality. By providing a visual representation of process data and enabling the identification of trends, patterns, and deviations, QCC maps empower organizations to proactively monitor, control, and improve their processes. Implementing QCC maps effectively requires a commitment to continuous improvement, a focus on data-driven decision-making, and a collaborative approach involving all stakeholders. By embracing the principles and applications of QCC maps, organizations can unlock a world of benefits, including enhanced product quality, reduced costs, increased efficiency, and improved customer satisfaction.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The QCC Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Quality Control Charts. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!