Navigating the Skagit River: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geography and Significance
Related Articles: Navigating the Skagit River: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geography and Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Skagit River: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geography and Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Skagit River: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geography and Significance

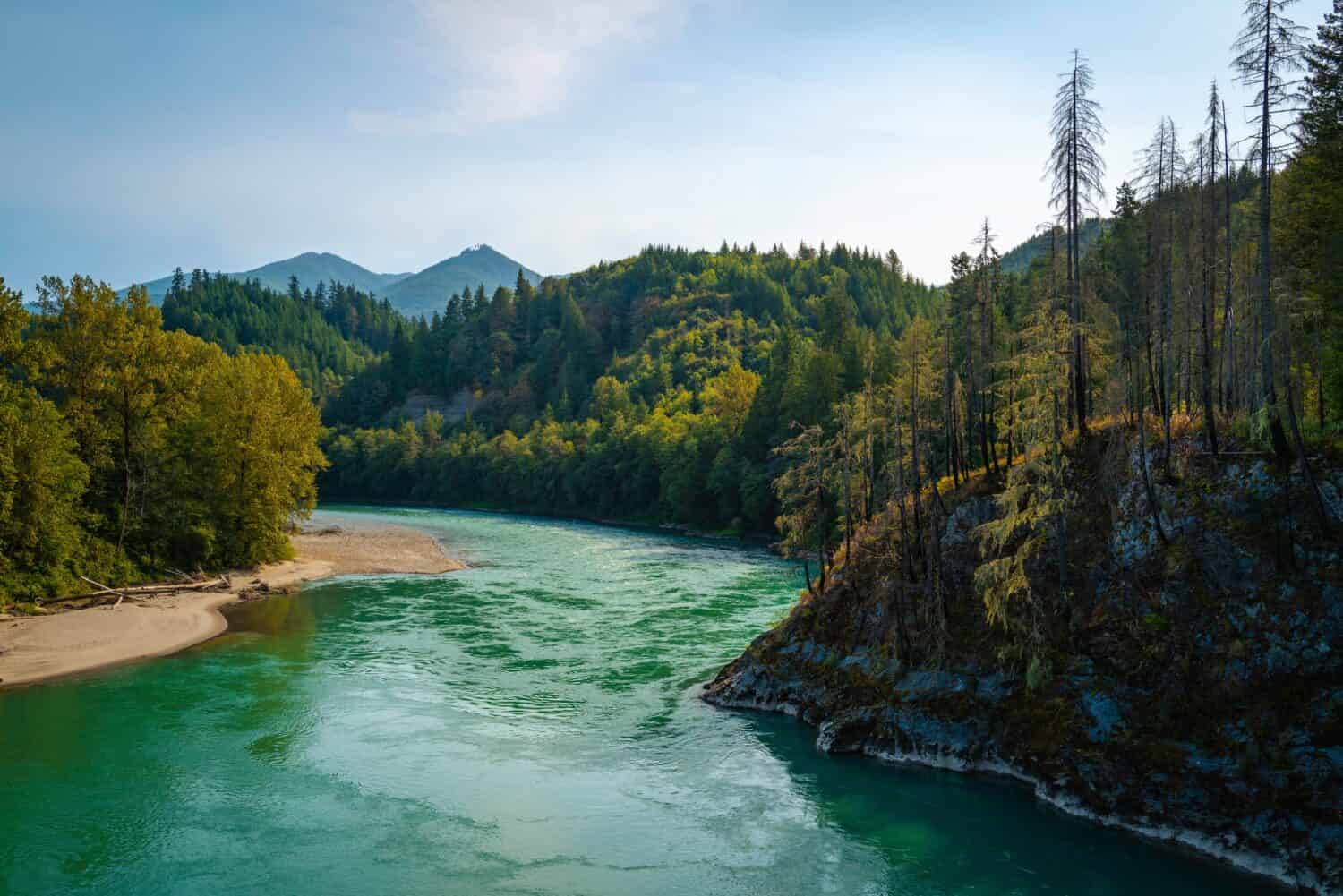
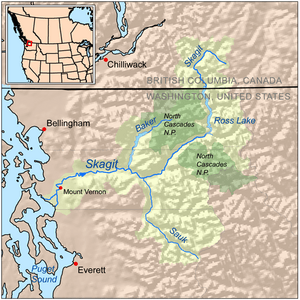
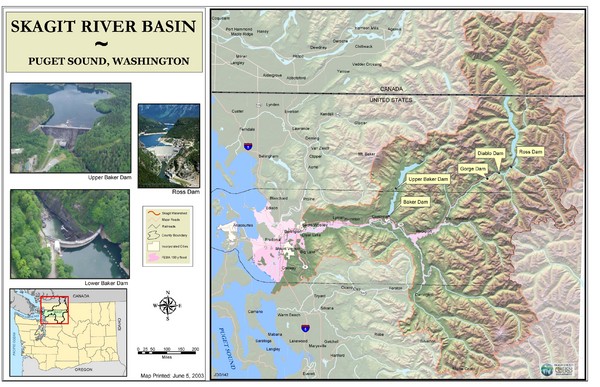
The Skagit River, a vibrant waterway traversing the heart of Washington state, is a captivating blend of natural beauty, cultural heritage, and ecological importance. Understanding its geography through a map is essential for appreciating the river’s multifaceted role in the region’s history, environment, and economy.
A Journey Through the Skagit River’s Geography
The Skagit River originates in the Cascade Mountains, specifically at Ross Lake, a majestic reservoir created by the Ross Dam. The river’s journey begins at an elevation of approximately 1,600 feet, carving its path through rugged terrain and dense forests. As it descends, the river gathers tributaries, including the Suiattle River, the Sauk River, and the Baker River, further augmenting its volume and power.
A Detailed Look at the Skagit River’s Map
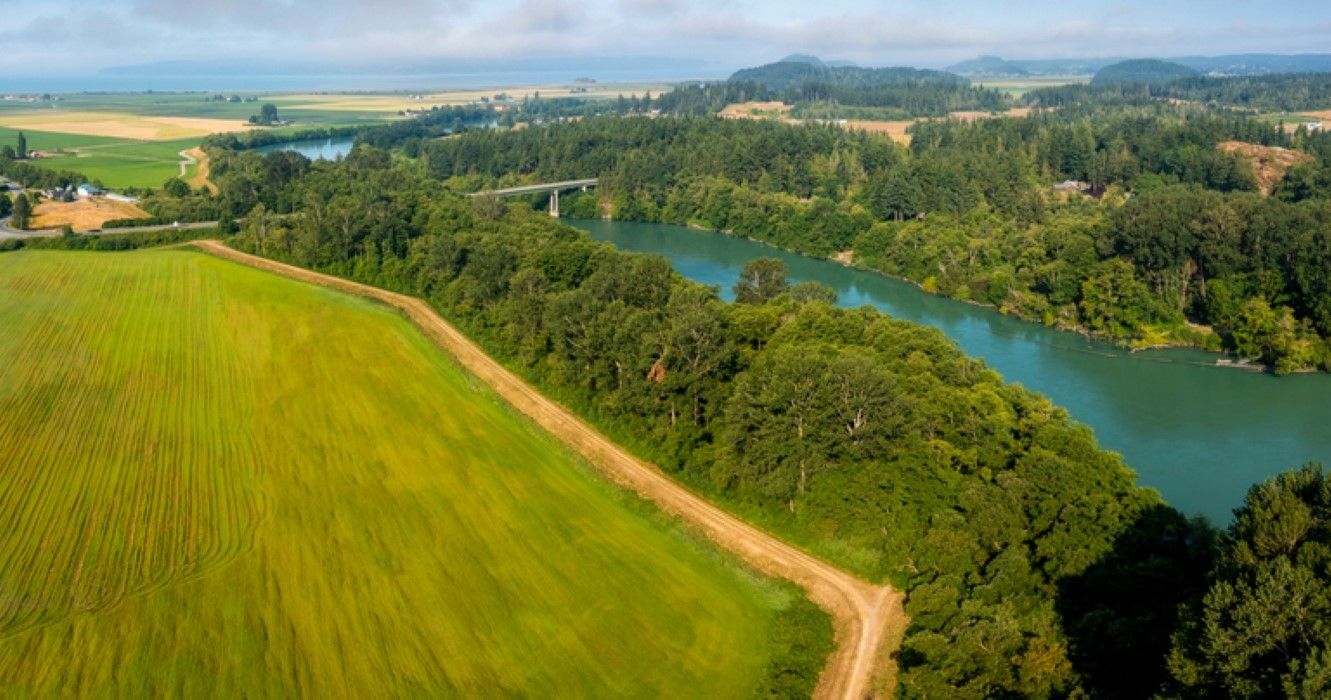
A map of the Skagit River reveals a fascinating tapestry of landscapes and human settlements. The river flows westward, winding its way through the Skagit Valley, a fertile agricultural region known for its bountiful crops and picturesque farms. The map showcases key landmarks, including the cities of Sedro-Woolley, Mount Vernon, and Burlington, each contributing to the river’s economic and cultural significance.
The Skagit River’s Tributaries: A Network of Life
The Skagit River’s network of tributaries adds complexity and richness to its ecosystem. The Suiattle River, with its pristine headwaters, provides a haven for native trout species. The Sauk River, known for its dramatic canyon, offers opportunities for whitewater rafting and kayaking. The Baker River, with its powerful flow, contributes significantly to the Skagit River’s volume and hydroelectric potential.
The Skagit Delta: Where River Meets Sea
The Skagit River’s journey culminates at the Skagit Delta, where the river meets the waters of Puget Sound. This unique area is a critical habitat for numerous bird species, including the endangered Puget Sound Bald Eagle. The delta’s rich sediment deposits support a vibrant ecosystem of shellfish and other marine life.
The Skagit River’s Significance: A Legacy of Nature and Culture
The Skagit River holds immense cultural and ecological significance. For centuries, the Skagit River has been a vital resource for the Skagit and Swinomish tribes, who have long relied on its bounty for sustenance and cultural practices. The river’s fertile banks have supported agriculture for generations, contributing to the region’s economic prosperity.
The Skagit River’s Role in Recreation and Tourism
The Skagit River is a popular destination for outdoor enthusiasts, offering a variety of recreational opportunities. From fishing and kayaking to hiking and camping, the river provides a gateway to the natural beauty of the region. The Skagit Valley Tulip Festival, a vibrant celebration of spring, draws visitors from around the world, highlighting the area’s agricultural heritage.
The Skagit River’s Challenges and Conservation Efforts
The Skagit River faces challenges, including habitat fragmentation, water quality degradation, and the impacts of climate change. Conservation efforts are underway to protect the river’s ecosystem and ensure its sustainability for future generations. These initiatives focus on restoring riparian habitats, improving water quality, and mitigating the effects of climate change.
FAQs about the Skagit River
Q: What is the length of the Skagit River?
A: The Skagit River is approximately 115 miles long.
Q: Where is the Skagit River located?
A: The Skagit River is located in northwestern Washington state, flowing from the Cascade Mountains to Puget Sound.
Q: What are the major cities located along the Skagit River?
A: The major cities located along the Skagit River include Sedro-Woolley, Mount Vernon, and Burlington.
Q: What are the primary tributaries of the Skagit River?
A: The primary tributaries of the Skagit River include the Suiattle River, the Sauk River, and the Baker River.
Q: What are some of the recreational activities available on the Skagit River?
A: Recreational activities on the Skagit River include fishing, kayaking, hiking, camping, and wildlife viewing.
Tips for Exploring the Skagit River
- Plan your trip: Research the various points of interest along the river and choose activities that align with your interests.
- Respect the environment: Pack out what you pack in, stay on designated trails, and avoid disturbing wildlife.
- Be aware of water conditions: Check water levels and flow rates before engaging in any water-based activities.
- Learn about the local history and culture: Visit museums and historical sites to gain a deeper understanding of the Skagit River’s significance.
Conclusion
The Skagit River, a vital waterway in Washington state, weaves a tapestry of natural beauty, cultural heritage, and ecological importance. Understanding its geography through a map allows us to appreciate the river’s multifaceted role in the region’s history, environment, and economy. As we navigate the river’s journey, we gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of nature and the importance of preserving this valuable resource for future generations.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Skagit River: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geography and Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!