Navigating the Shifting Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Eastern Europe’s Geography and Identity
Related Articles: Navigating the Shifting Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Eastern Europe’s Geography and Identity
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Shifting Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Eastern Europe’s Geography and Identity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Shifting Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Eastern Europe’s Geography and Identity
Eastern Europe, a region often viewed as a bridge between the West and the East, has a rich history and a dynamic present. Understanding its geography and its people is crucial for grasping the complexities of the modern world. This article delves into the intricate tapestry of Eastern Europe, providing a comprehensive exploration of its landscape, cultural diversity, and evolving political dynamics.
Defining Eastern Europe: A Region of Diverse Identities
Defining the precise boundaries of Eastern Europe is a complex endeavor, often debated among scholars and geographers. While there is no universally accepted definition, the region is generally understood to encompass countries located east of Germany and north of the Balkans. This includes:
- Baltic States: Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania
- Eastern Slavic Countries: Belarus, Ukraine, Russia (though often considered part of both Eastern Europe and Northern Asia)
- Central European Countries with Eastern European Influences: Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, Moldova
This geographic delineation highlights the region’s unique position as a crossroads of cultures, languages, and historical experiences. Eastern Europe’s identity is shaped by its shared history under the Soviet Union, its ongoing transition towards democracy and market economies, and its diverse cultural heritage.
A Glimpse into the Diverse Landscape
Eastern Europe’s topography is as varied as its cultural tapestry. From the rolling plains of the Ukrainian Steppe to the majestic Carpathian Mountains, the region boasts a captivating array of natural landscapes.
- The Baltic Sea Region: The Baltic States, bordering the Baltic Sea, are characterized by their low-lying plains and abundant coastal areas. This region is known for its stunning beaches, lush forests, and numerous lakes.
- The Carpathian Mountains: Stretching across Slovakia, Ukraine, Romania, and Poland, the Carpathians offer breathtaking mountain scenery. The region is home to diverse flora and fauna, including the iconic brown bear and the elusive lynx.
- The Black Sea Coast: Countries like Bulgaria, Romania, and Ukraine boast picturesque Black Sea coastlines. This region is known for its sandy beaches, bustling resorts, and historic port cities.
- The Eastern European Plain: Spanning vast areas of Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus, this flat, fertile region is ideal for agriculture and is the heartland of Eastern Europe’s agricultural production.
Cultural Tapestry: A Mosaic of Traditions and Influences
Eastern Europe is a melting pot of cultures, each with its unique history, language, and traditions. The region’s cultural diversity is shaped by centuries of interactions with various empires, including the Byzantine Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Russian Empire.
- Slavic Heritage: The majority of Eastern European countries are home to Slavic populations, with distinct languages and cultural traditions. Eastern Slavic cultures, exemplified by Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus, have strong ties to Orthodox Christianity and a rich literary heritage.
- Baltic Influence: The Baltic States, with their unique history and cultural identity, have been influenced by Scandinavian and Germanic cultures. Their languages belong to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family.
- Central European Connections: Countries like Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, and Hungary share cultural and historical connections with Central Europe. Their traditions are influenced by Roman Catholicism and have been shaped by the Habsburg Empire.
- Byzantine Legacy: The influence of the Byzantine Empire is evident in the Orthodox Christian traditions of countries like Bulgaria, Romania, and Serbia. The region boasts stunning Byzantine architecture, such as the Hagia Sophia in Istanbul.
Political Landscape: A Complex and Evolving Reality
Eastern Europe’s political landscape has undergone significant transformations since the fall of the Soviet Union. The region is now characterized by a diverse range of political systems, from democracies to authoritarian regimes.
- Transition to Democracy: Many Eastern European countries have successfully transitioned to democracy after the collapse of the Soviet Union. These countries have embraced free and fair elections, independent judiciaries, and respect for human rights.
- Economic Integration: The region has actively sought economic integration with the European Union. Many countries have joined the EU, enjoying its benefits of free trade and access to the single market.
- Challenges and Tensions: Despite progress, Eastern Europe faces numerous challenges, including economic inequality, corruption, and political instability. The region is also subject to geopolitical tensions, particularly with Russia, which continues to exert influence in its neighboring states.
Navigating the Future: Opportunities and Challenges
Eastern Europe stands at a crossroads, facing both opportunities and challenges in the 21st century. The region is poised to benefit from its strategic location, its growing economies, and its diverse cultural heritage. However, it also faces significant obstacles, including economic disparities, political instability, and the lingering effects of the Soviet past.
- Economic Growth and Innovation: Eastern European countries are attracting foreign investment and experiencing rapid economic growth. The region is home to a skilled workforce and is increasingly becoming a hub for technology and innovation.
- Cultural Diplomacy and Tourism: Eastern Europe’s rich cultural heritage is a significant asset. The region is attracting increasing numbers of tourists, eager to explore its historic cities, stunning landscapes, and unique cultural traditions.
- Geopolitical Challenges: The region’s geopolitical landscape remains complex. The ongoing conflict in Ukraine and the tensions with Russia pose significant challenges to stability and security.
FAQs
1. What are the major languages spoken in Eastern Europe?
Eastern Europe is home to a variety of languages, including Slavic languages (Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian, Polish, Czech, Slovak), Baltic languages (Lithuanian, Latvian, Estonian), and Hungarian.
2. What are the main religions practiced in Eastern Europe?
The dominant religions in Eastern Europe are Eastern Orthodox Christianity, Roman Catholicism, and Islam. There are also significant minorities of other religions, including Judaism and Protestantism.
3. What are the main economic sectors in Eastern Europe?
Eastern European economies are diverse, with significant contributions from agriculture, manufacturing, tourism, and technology.
4. What are some of the major challenges facing Eastern Europe?
Eastern Europe faces challenges such as economic inequality, corruption, political instability, and geopolitical tensions.
5. What are some of the opportunities for Eastern Europe in the future?
Eastern Europe has opportunities for economic growth, cultural diplomacy, and regional cooperation.
Tips for Understanding Eastern Europe
- Engage with local cultures: Immerse yourself in Eastern European culture by visiting museums, attending festivals, and interacting with local people.
- Learn about the region’s history: Understanding Eastern Europe’s complex history is crucial for grasping its present and future.
- Stay informed about current events: Keep up-to-date on political and economic developments in the region through reliable news sources.
- Be open to new perspectives: Challenge your preconceived notions and be open to learning about different cultures and viewpoints.
Conclusion
Eastern Europe is a region of immense complexity and dynamism. Its geographical diversity, rich cultural heritage, and evolving political landscape make it a fascinating subject of study. By understanding its history, geography, and current challenges, we can gain a deeper appreciation for this vital region and its role in shaping the modern world. As Eastern Europe continues to navigate its unique path, it remains a region of immense potential and captivating complexity.
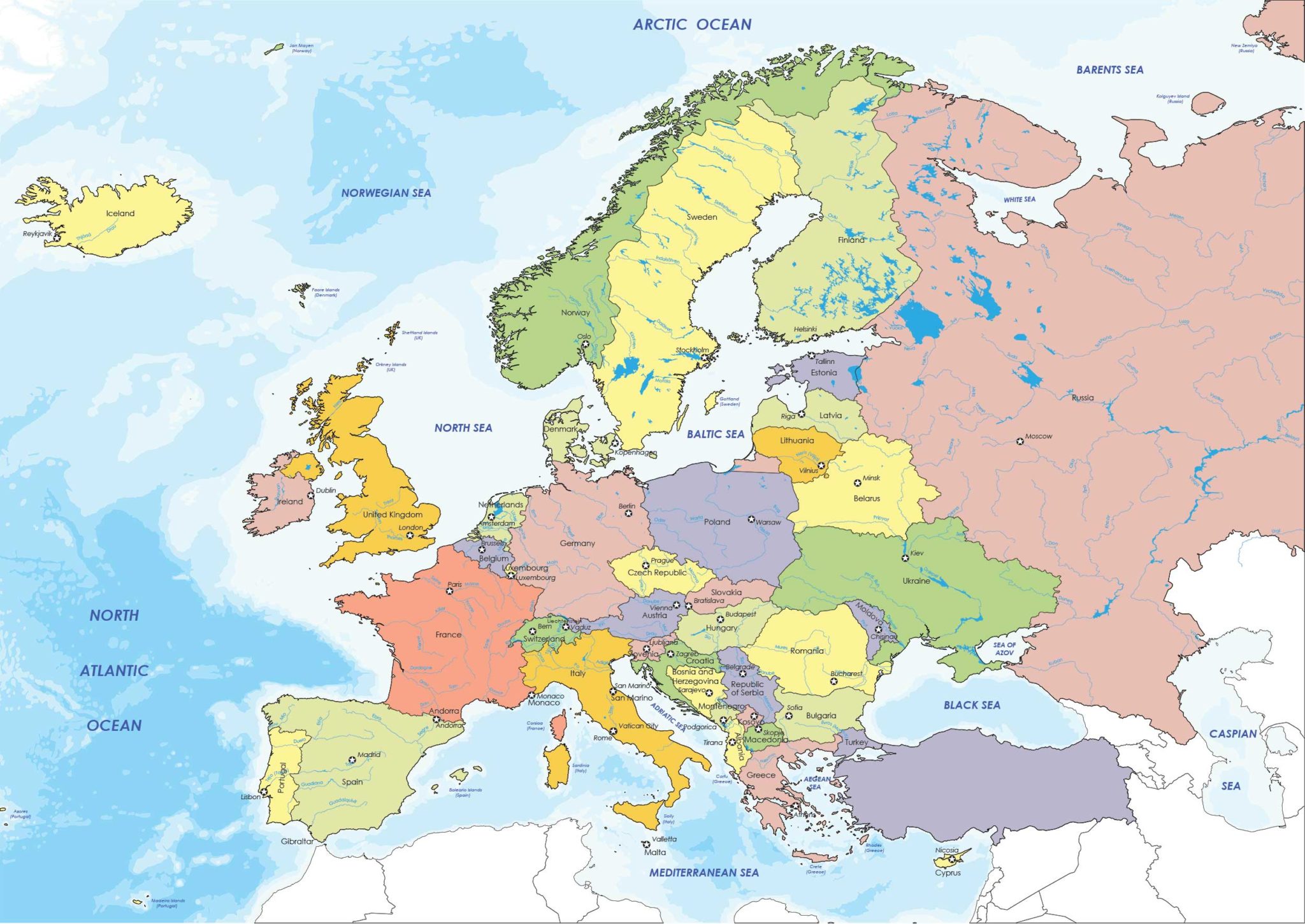

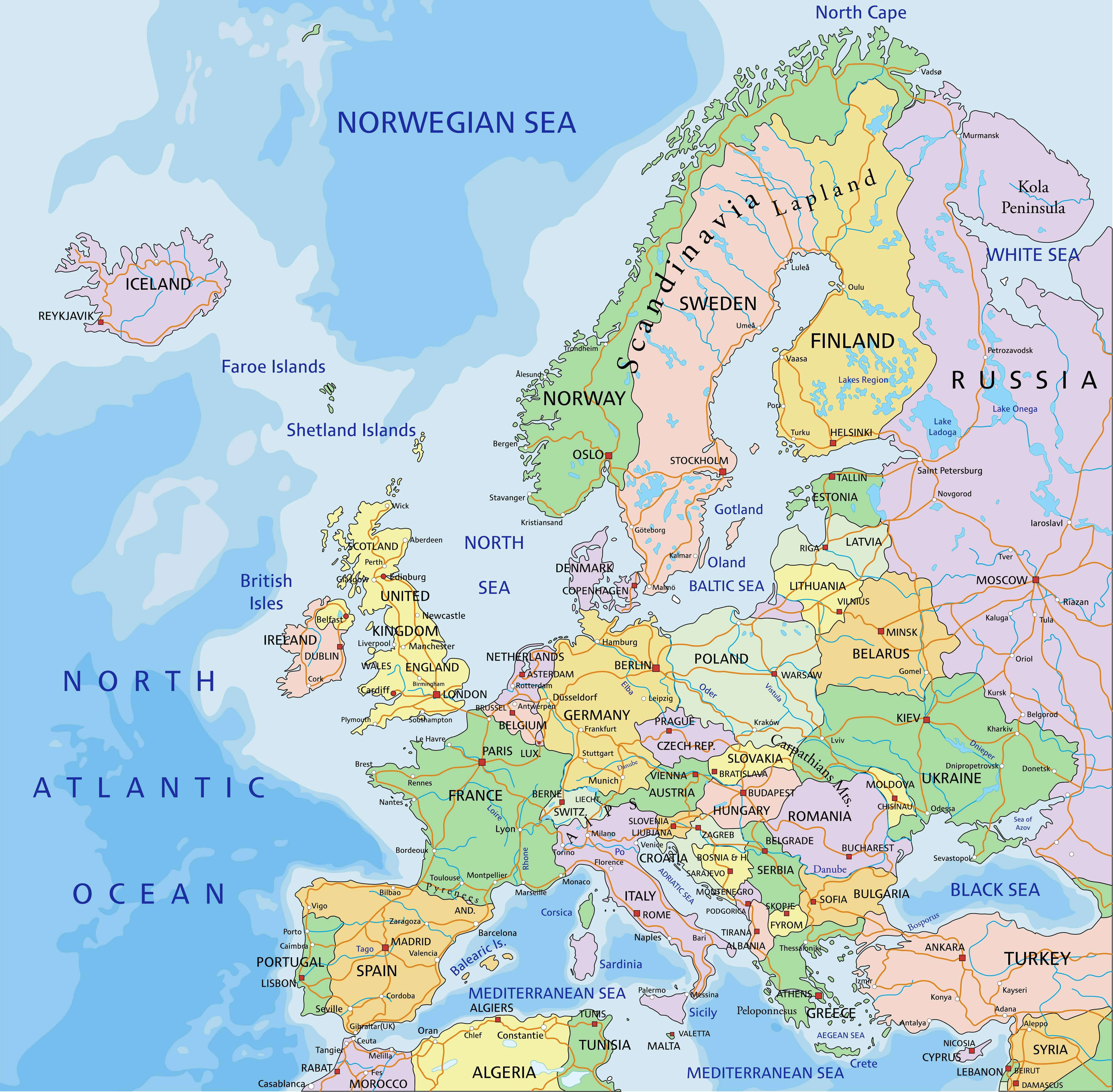




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Shifting Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of Eastern Europe’s Geography and Identity. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
