Navigating the Flow of History: Exploring the Red River of the United States
Related Articles: Navigating the Flow of History: Exploring the Red River of the United States
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Flow of History: Exploring the Red River of the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Flow of History: Exploring the Red River of the United States
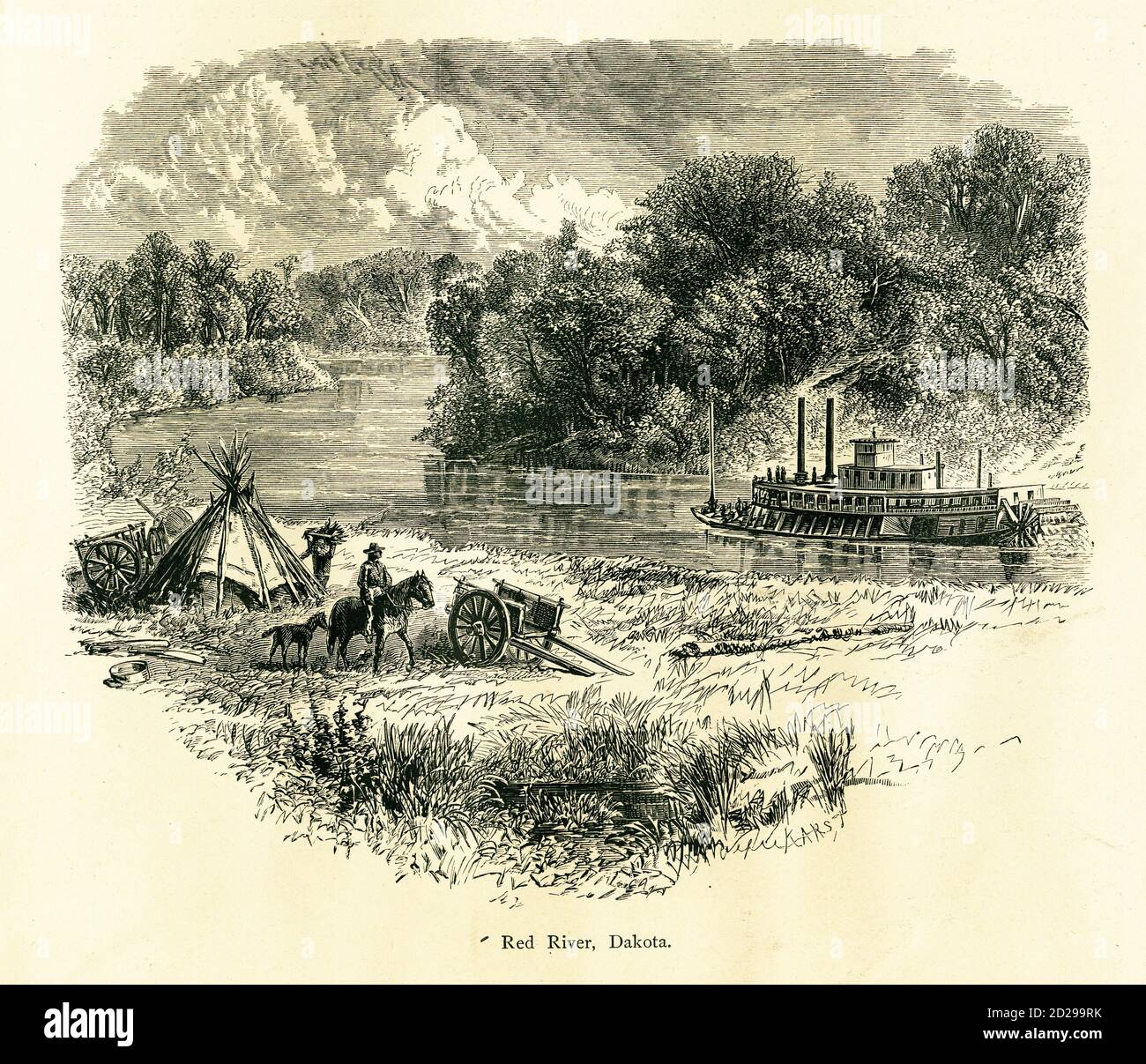

The Red River, a significant waterway traversing the heartland of the United States, holds a rich history and continues to play a vital role in the economic and cultural fabric of the region. Understanding its geographical significance, historical impact, and contemporary relevance requires a comprehensive exploration of the river’s course and its influence on the surrounding landscape.
A River’s Journey: Tracing the Red River’s Path
The Red River originates in the Llano Estacado, a high plateau in western Texas, and meanders eastward for over 1,200 miles before emptying into the Mississippi River. Its journey encompasses portions of five states: Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Louisiana, and a small segment in New Mexico. This lengthy course traverses diverse landscapes, ranging from the arid plains of the Texas Panhandle to the fertile bottomlands of Louisiana.
A River of Significance: The Red River’s Historical Impact
The Red River has been a vital artery for human activity since prehistoric times. Indigenous peoples, including the Caddo, Wichita, and Comanche tribes, relied on the river for sustenance, trade, and transportation. European exploration and settlement further solidified the Red River’s importance. French explorers, seeking westward expansion, reached the river in the 17th century. In the 18th century, Spanish colonists established settlements along the river, and the region became a hub for trade and agriculture.
The Red River played a critical role in the westward expansion of the United States. The Louisiana Purchase in 1803 brought vast territories, including the Red River basin, under American control. The subsequent exploration and settlement of these lands, fueled by the promise of fertile farmland and economic opportunity, were significantly influenced by the river’s presence.
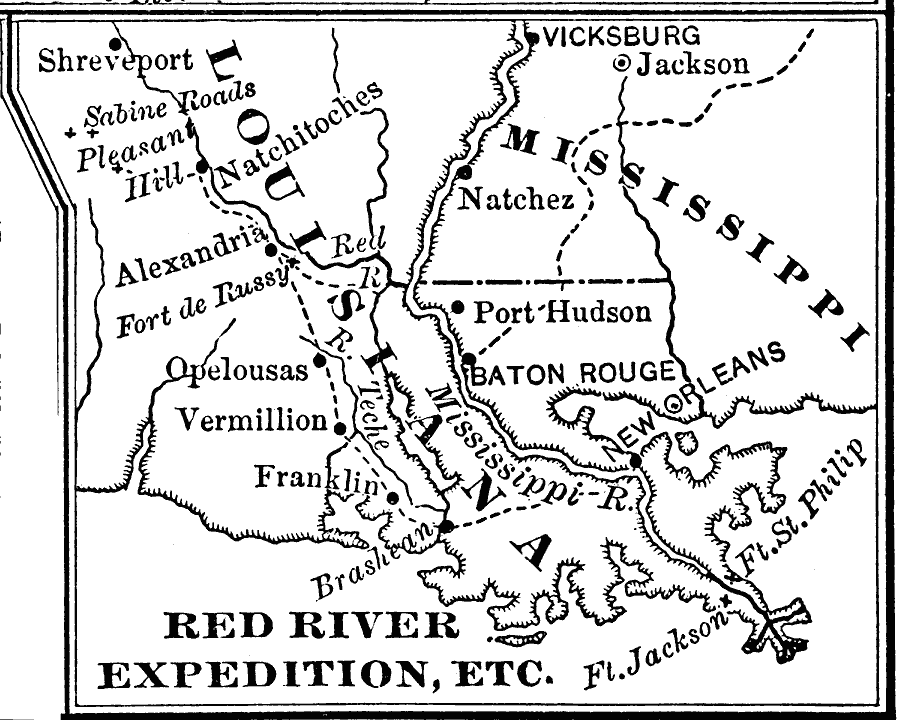
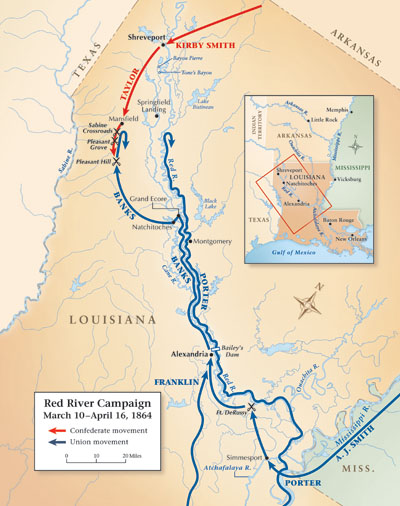
The Red River also witnessed the tumultuous events of the Civil War. Its banks served as battlegrounds, and the river itself became a strategic waterway for both the Union and Confederate armies. The Red River Campaign of 1864, a major military operation, saw fierce battles fought along the river’s course, leaving a lasting impact on the region’s history.
Beyond History: The Red River’s Contemporary Importance
Today, the Red River continues to hold immense significance. It serves as a vital source of water for agriculture, industry, and municipal use. The river’s fertile bottomlands support a thriving agricultural industry, producing cotton, soybeans, and other crops. The Red River also provides opportunities for recreation, attracting anglers, boaters, and wildlife enthusiasts.
However, the Red River also faces environmental challenges. Pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, and urban development has impacted the river’s water quality. Additionally, the river’s flow is subject to fluctuations due to dam construction and drought. These challenges necessitate ongoing efforts to protect and restore the Red River’s ecological integrity.
A River of Diversity: Exploring the Red River’s Cultural Landscape
The Red River’s journey through diverse landscapes has fostered a rich cultural tapestry. The river’s banks are home to numerous historical sites, museums, and cultural centers that celebrate the region’s heritage. From the ancient mounds of the Caddo tribe to the historical forts of the Spanish colonial era, the Red River’s legacy is etched into the landscape.
The river’s cultural influence extends beyond its historical significance. The Red River is a source of inspiration for artists, musicians, and writers, who draw upon its beauty and history to create works that celebrate the region’s unique character. The Red River’s diverse cultural heritage is a testament to its enduring impact on the lives of those who live and work along its banks.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into the Red River’s Significance
1. What is the Red River’s average flow rate?
The Red River’s average flow rate varies significantly depending on the season and location. However, the river’s average discharge at the Red River Bridge near Shreveport, Louisiana, is approximately 10,000 cubic feet per second.
2. How many dams are located on the Red River?
The Red River has several dams, including the Denison Dam, the Lake Texoma Dam, and the Walter F. George Dam. These dams regulate the river’s flow for water management, power generation, and flood control.
3. What are the major tributaries of the Red River?
The Red River has numerous tributaries, including the Washita River, the Little River, and the Kiamichi River. These tributaries contribute significantly to the river’s overall flow and water quality.
4. What are the major cities located along the Red River?
Major cities located along the Red River include Shreveport, Louisiana; Texarkana, Texas/Arkansas; and Wichita Falls, Texas. These cities have grown and prospered due to the river’s economic and strategic importance.
5. What are the major environmental challenges facing the Red River?
The Red River faces several environmental challenges, including water pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, and urban development. Additionally, the river’s flow is subject to fluctuations due to dam construction and drought.
Tips: Engaging with the Red River’s Legacy
1. Visit historical sites and museums: Explore the region’s rich history by visiting historical sites, museums, and cultural centers located along the Red River.
2. Engage in recreational activities: Take advantage of the Red River’s recreational opportunities by fishing, boating, or hiking along its banks.
3. Support environmental conservation efforts: Contribute to the protection and restoration of the Red River by supporting organizations working to address water pollution and habitat degradation.
4. Explore the region’s cultural heritage: Immerse yourself in the Red River’s diverse cultural heritage by attending local festivals, concerts, and art exhibitions.
5. Learn about the region’s history: Read books, watch documentaries, and visit online resources to gain a deeper understanding of the Red River’s historical significance.
Conclusion: A River’s Enduring Influence
The Red River, with its winding course and rich history, serves as a vital artery for the American heartland. From its prehistoric origins to its contemporary importance, the river has witnessed and shaped the region’s development. Its cultural significance, economic value, and environmental challenges continue to inspire and challenge those who interact with this remarkable waterway. Understanding the Red River’s journey, its impact, and its ongoing significance is essential for appreciating the complex interplay of history, culture, and environment that defines the American landscape.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Flow of History: Exploring the Red River of the United States. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!