Navigating the Fiery Landscape: Understanding Maps of Erupting Volcanoes
Related Articles: Navigating the Fiery Landscape: Understanding Maps of Erupting Volcanoes
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Fiery Landscape: Understanding Maps of Erupting Volcanoes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Fiery Landscape: Understanding Maps of Erupting Volcanoes
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Fiery Landscape: Understanding Maps of Erupting Volcanoes
- 3.1 Mapping the Path of Fire: A Visual Guide to Volcanic Activity
- 3.2 Beyond the Basics: Exploring the Layers of Information
- 3.3 Navigating the Data: Understanding Map Components
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Maps of Erupting Volcanoes
- 3.5 Tips for Using Maps of Erupting Volcanoes
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Navigating the Fiery Landscape
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Fiery Landscape: Understanding Maps of Erupting Volcanoes
![]()
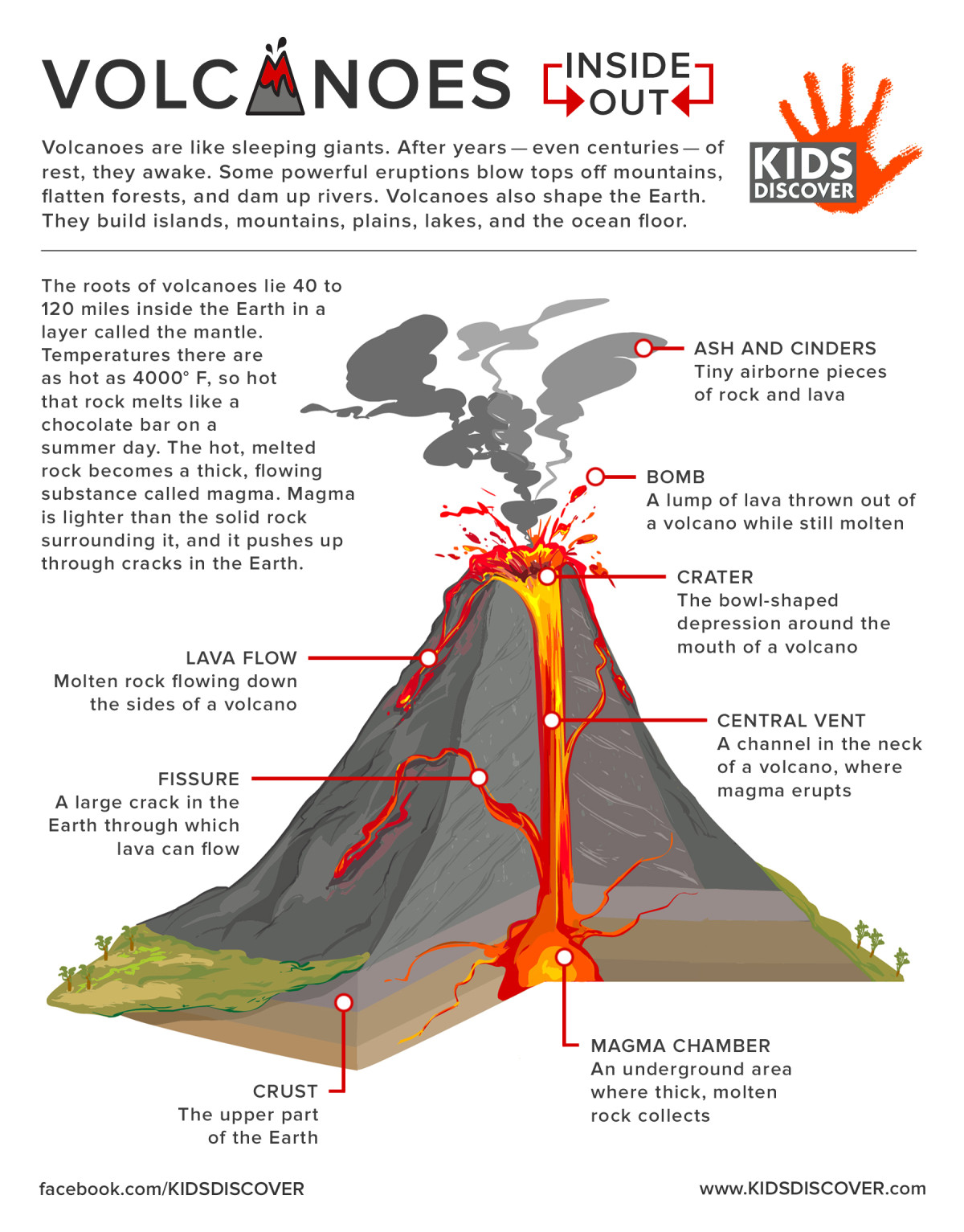
Volcanoes, with their awe-inspiring power and destructive potential, have captivated humanity for millennia. These geological marvels, often referred to as "fire mountains," are windows into the Earth’s dynamic interior, revealing the immense forces that shape our planet. While their beauty is undeniable, the threat of volcanic eruptions necessitates a deep understanding of these phenomena, and maps play a crucial role in this endeavor.
Mapping the Path of Fire: A Visual Guide to Volcanic Activity
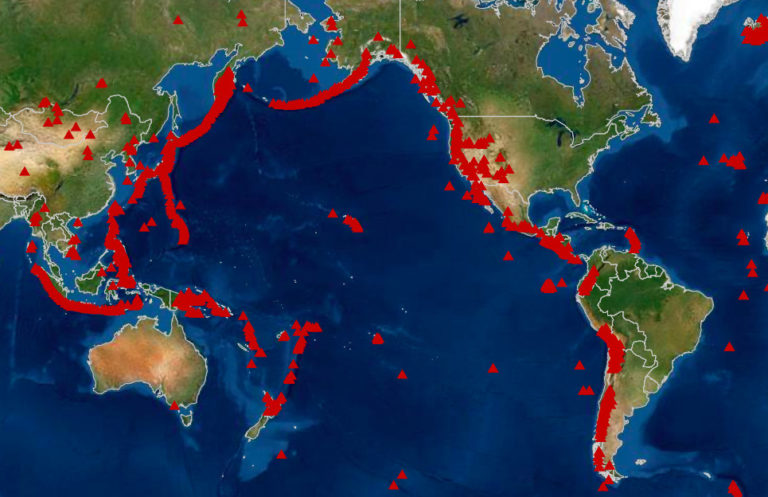
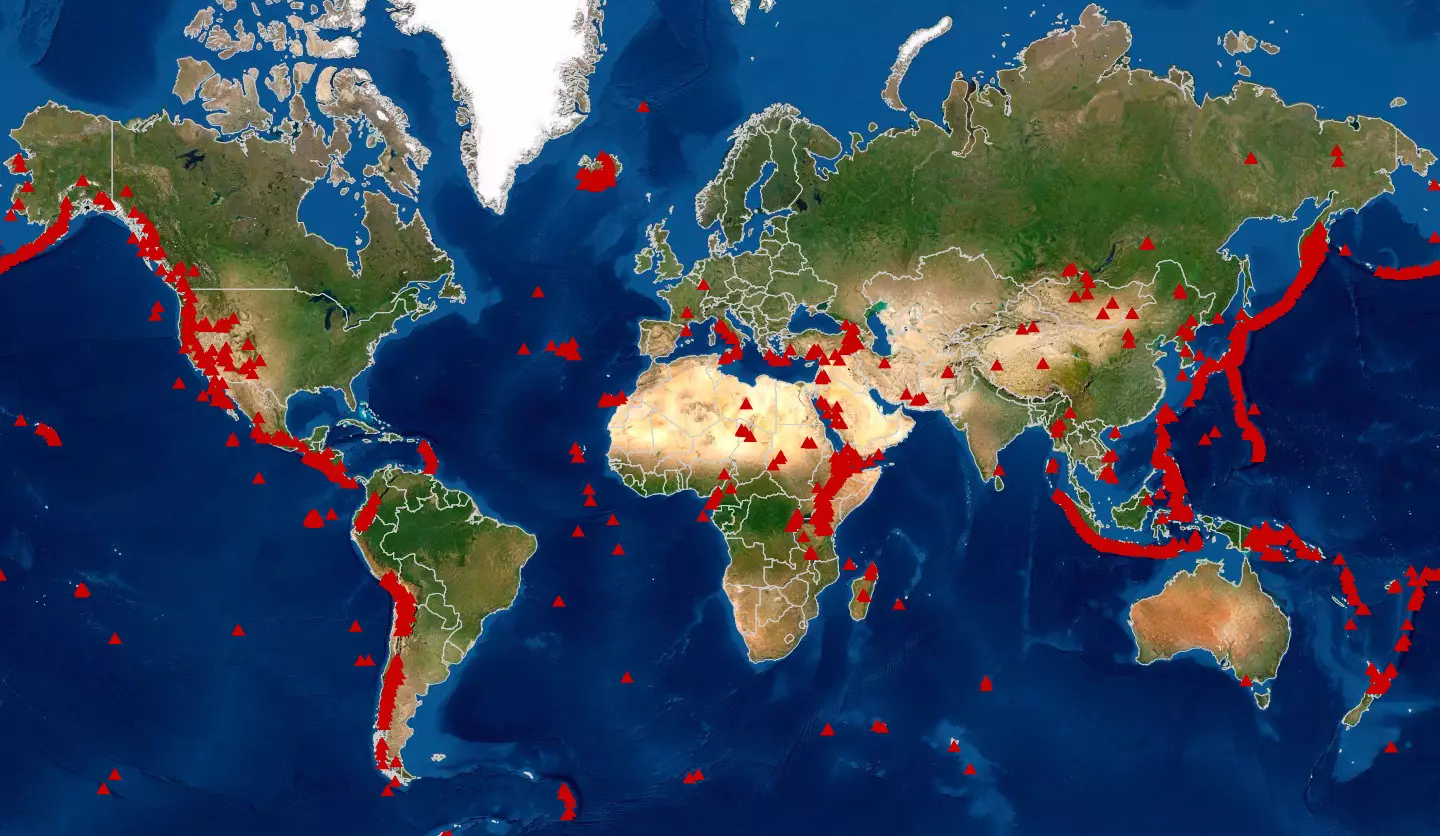
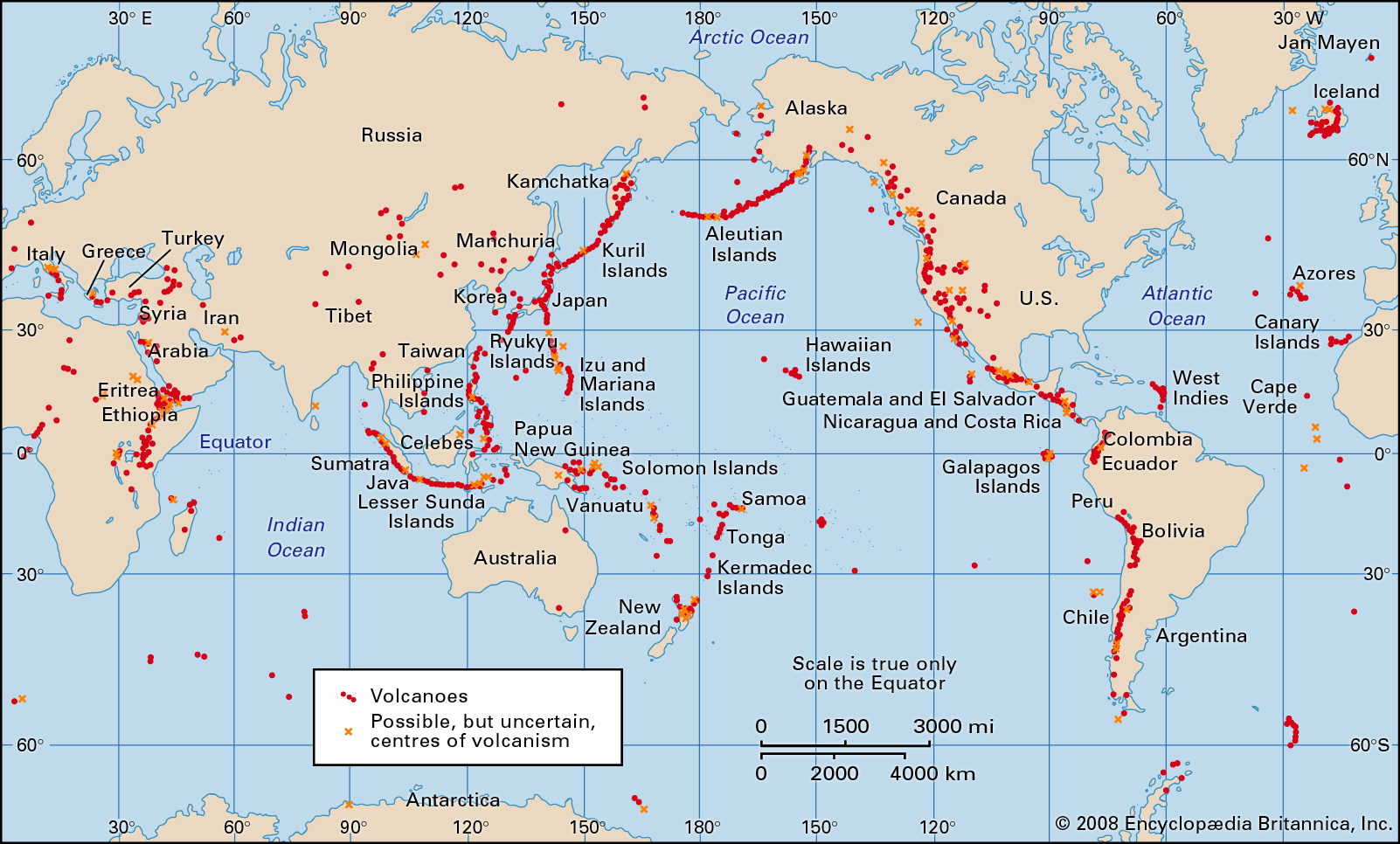
Maps of erupting volcanoes serve as vital tools for scientists, emergency responders, and the public alike. They provide a visual representation of active volcanic regions, allowing for the monitoring of eruptions, assessment of potential hazards, and effective planning for mitigation strategies.
These maps are not static representations; they are constantly evolving, reflecting the dynamic nature of volcanic activity. They incorporate data from various sources, including:
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites equipped with advanced sensors monitor volcanic activity, capturing images of ash plumes, lava flows, and thermal anomalies. These images provide a broad overview of the eruption’s scale and progression.
- Ground-Based Monitoring: Networks of seismometers, tiltmeters, and gas sensors deployed around volcanoes provide real-time data on seismic activity, ground deformation, and gas emissions. These data points are crucial for predicting the likelihood and intensity of an eruption.
- Historical Records: Historical accounts of past eruptions, including eyewitness reports and geological evidence, provide valuable context for understanding the behavior of a specific volcano.
The Importance of Visual Representation:
Maps offer a clear and intuitive way to understand complex information. They visually depict:
- Location: The precise location of active volcanoes, enabling scientists and authorities to prioritize areas for monitoring and intervention.
- Type of Eruption: The type of eruption, be it effusive (slow-moving lava flows) or explosive (violent ash plumes and pyroclastic flows), dictates the nature of the threat and the necessary response.
- Threat Zones: Maps delineate areas at risk from various volcanic hazards, such as lava flows, ashfall, and pyroclastic flows. This information guides evacuation plans and emergency response efforts.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring the Layers of Information
Modern maps of erupting volcanoes transcend simple location markers. They incorporate multiple layers of data, providing a comprehensive picture of the eruption’s dynamics:
- Real-Time Data: Maps often integrate live data feeds from monitoring stations, allowing users to track the evolution of the eruption in real-time.
- Hazard Zones: Different hazard zones are color-coded to represent the severity of the threat, enabling users to quickly grasp the potential impact of the eruption.
- Historical Data: Historical eruption records are overlaid on the map, providing context for the current eruption and informing predictions of future activity.
- Population Density: Maps can incorporate population density data, highlighting areas with high concentrations of people at risk from volcanic hazards.
The Benefits of Multi-layered Maps:
By integrating various data sources, these maps provide a powerful tool for:
- Risk Assessment: By analyzing the location, type of eruption, and potential hazards, scientists can assess the risks posed by a volcanic eruption to surrounding communities.
- Emergency Response Planning: Maps help emergency responders prioritize evacuation routes, allocate resources, and coordinate rescue efforts.
- Public Awareness: Publicly accessible maps provide valuable information to residents living near active volcanoes, enabling them to prepare for potential eruptions and stay informed about evolving situations.
Navigating the Data: Understanding Map Components
To effectively interpret maps of erupting volcanoes, it is essential to understand the key components:
- Legend: The legend explains the symbols, colors, and abbreviations used on the map, providing a key to understanding the data presented.
- Scale: The scale indicates the relationship between the map’s dimensions and the actual distance on the ground. This allows users to accurately estimate distances and assess the extent of potential hazards.
- North Arrow: The north arrow indicates the direction of north, ensuring proper orientation and understanding of the map’s layout.
- Data Sources: The map should clearly indicate the sources of data used, allowing users to assess the reliability and accuracy of the information presented.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Maps of Erupting Volcanoes
1. How often are maps of erupting volcanoes updated?
Maps are updated frequently, often in real-time, based on data from monitoring stations and satellite imagery. The frequency of updates depends on the intensity of the eruption and the availability of data.
2. What types of information are typically included on maps of erupting volcanoes?
Maps typically include information on the location of the volcano, type of eruption, hazard zones, real-time data from monitoring stations, historical eruption records, and population density.
3. Are these maps available to the public?
Yes, many maps of erupting volcanoes are publicly accessible through websites of government agencies, scientific organizations, and news outlets.
4. How accurate are these maps?
The accuracy of maps depends on the quality and availability of data. However, modern maps utilize advanced technology and data processing techniques to provide highly accurate representations of volcanic activity.
5. What are the limitations of these maps?
Maps are only as good as the data they rely on. They cannot predict the exact timing or intensity of an eruption, and they may not capture all potential hazards.
6. How can I learn more about maps of erupting volcanoes?
There are many resources available online, including websites of geological surveys, universities, and international organizations. You can also consult with local emergency management agencies for information specific to your area.
Tips for Using Maps of Erupting Volcanoes
- Consult Multiple Sources: Compare information from different maps and sources to get a comprehensive understanding of the situation.
- Pay Attention to Data Sources: Understand the limitations and reliability of the data used to create the map.
- Stay Informed: Monitor updates and changes to the map as the eruption progresses.
- Understand Hazard Zones: Be aware of the potential hazards associated with volcanic eruptions and how they might affect your area.
- Prepare for Evacuation: Have a plan in place for how to evacuate if necessary, including designated routes and meeting points.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Navigating the Fiery Landscape
Maps of erupting volcanoes serve as a vital tool for understanding, managing, and mitigating the risks associated with these powerful geological phenomena. They provide a clear and concise visual representation of volcanic activity, enabling scientists, emergency responders, and the public to make informed decisions and protect lives. By understanding the information presented on these maps and utilizing them effectively, we can navigate the fiery landscape of erupting volcanoes with greater awareness and preparedness.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Fiery Landscape: Understanding Maps of Erupting Volcanoes. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!