Navigating the Energy Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nord Stream Pipelines
Related Articles: Navigating the Energy Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nord Stream Pipelines
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Energy Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nord Stream Pipelines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Energy Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nord Stream Pipelines

The Nord Stream pipelines, spanning across the Baltic Sea, have become a focal point in the global energy landscape. Their significance extends beyond the mere transportation of natural gas, impacting geopolitical dynamics, economic relations, and environmental considerations. Understanding the intricate network of these pipelines requires a comprehensive approach, encompassing their history, route, functionality, and the complex web of factors surrounding them.
A Historical Overview
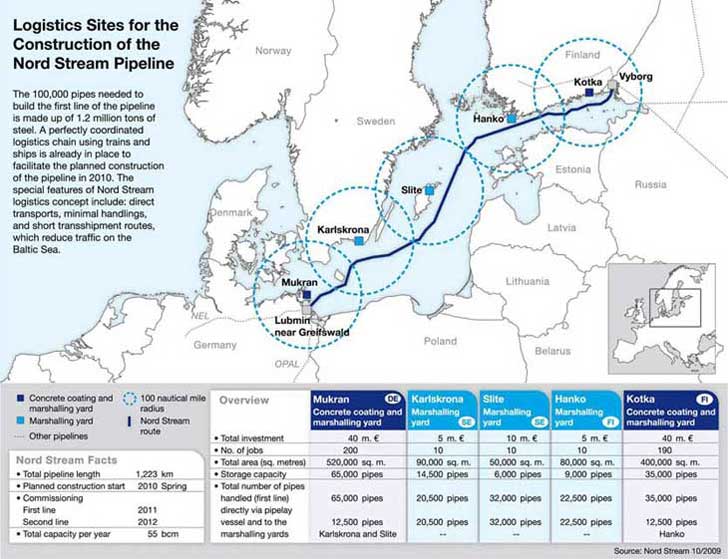
The Nord Stream project, a brainchild of the Russian energy giant Gazprom, emerged in the early 2000s as a means to diversify Russia’s gas export routes and circumvent transit fees imposed by some European countries. The first pipeline, Nord Stream 1, commenced operations in 2011, connecting Vyborg in Russia to Greifswald in Germany, with an annual capacity of 55 billion cubic meters (bcm) of natural gas.
The second pipeline, Nord Stream 2, completed in 2021, mirrored the route of its predecessor, doubling the transport capacity to 110 bcm annually. This expansion was met with mixed reactions, with some viewing it as a vital energy source for Europe, while others raised concerns about increasing Europe’s dependence on Russian gas.
Mapping the Pipelines
The Nord Stream pipelines traverse the Baltic Sea, traversing a distance of over 1,200 kilometers. Their route is characterized by a combination of geographical and political considerations.
-
Starting Point: The pipelines originate in Vyborg, Russia, located on the Gulf of Finland, close to the border with Finland. This location provides access to the vast natural gas reserves in Western Siberia.
-
Baltic Sea Crossing: The pipelines then proceed through the Baltic Sea, passing through the exclusive economic zones of Finland, Sweden, Denmark, and Germany. The seafloor topography and environmental considerations played a significant role in determining the exact route.
-
Ending Point: The pipelines terminate at Greifswald, Germany, a strategically important location for gas distribution within Europe. This port city provides access to the extensive European gas network, enabling onward transmission to various countries.
Operational Functionality
The Nord Stream pipelines are designed to transport natural gas from Russia to Germany, serving as a critical artery in the global energy trade. Their functionality relies on a combination of advanced technologies and rigorous safety measures.
-
Pipeline Design: The pipelines consist of two parallel lines, each composed of 122-kilometer-long pipe sections, welded together to form a continuous system. These pipes are made of high-strength steel, capable of withstanding the pressures and temperatures associated with natural gas transportation.
-
Compression Stations: Along the pipelines, strategically placed compressor stations are used to maintain the necessary pressure for gas flow. These stations utilize powerful turbines to compress the gas, ensuring its efficient and uninterrupted movement.
-
Monitoring Systems: Sophisticated monitoring systems are deployed throughout the pipelines, providing real-time data on pressure, flow rate, and other critical parameters. This allows for proactive maintenance and ensures operational safety.
Economic and Political Implications
The Nord Stream pipelines have had a significant impact on the economic and political landscape of Europe. Their construction and operation have generated substantial investment and created numerous jobs. However, the project has also sparked controversies, raising concerns about energy dependence, geopolitical influence, and environmental consequences.
-
Economic Benefits: The pipelines have provided a reliable and cost-effective means of transporting natural gas to Europe, contributing to energy security and economic growth. They have also facilitated trade and investment between Russia and European countries.
-
Geopolitical Tensions: The pipelines have been entangled in geopolitical tensions, with some countries viewing them as a tool for Russia to exert influence over European energy policy. The project has also been criticized for increasing Europe’s dependence on Russian gas, potentially giving Moscow leverage in diplomatic negotiations.
-
Environmental Concerns: The construction and operation of the pipelines have raised environmental concerns, particularly regarding potential impacts on marine ecosystems and seabed habitats. The pipelines have also been criticized for contributing to greenhouse gas emissions associated with natural gas production and consumption.
The Future of Nord Stream
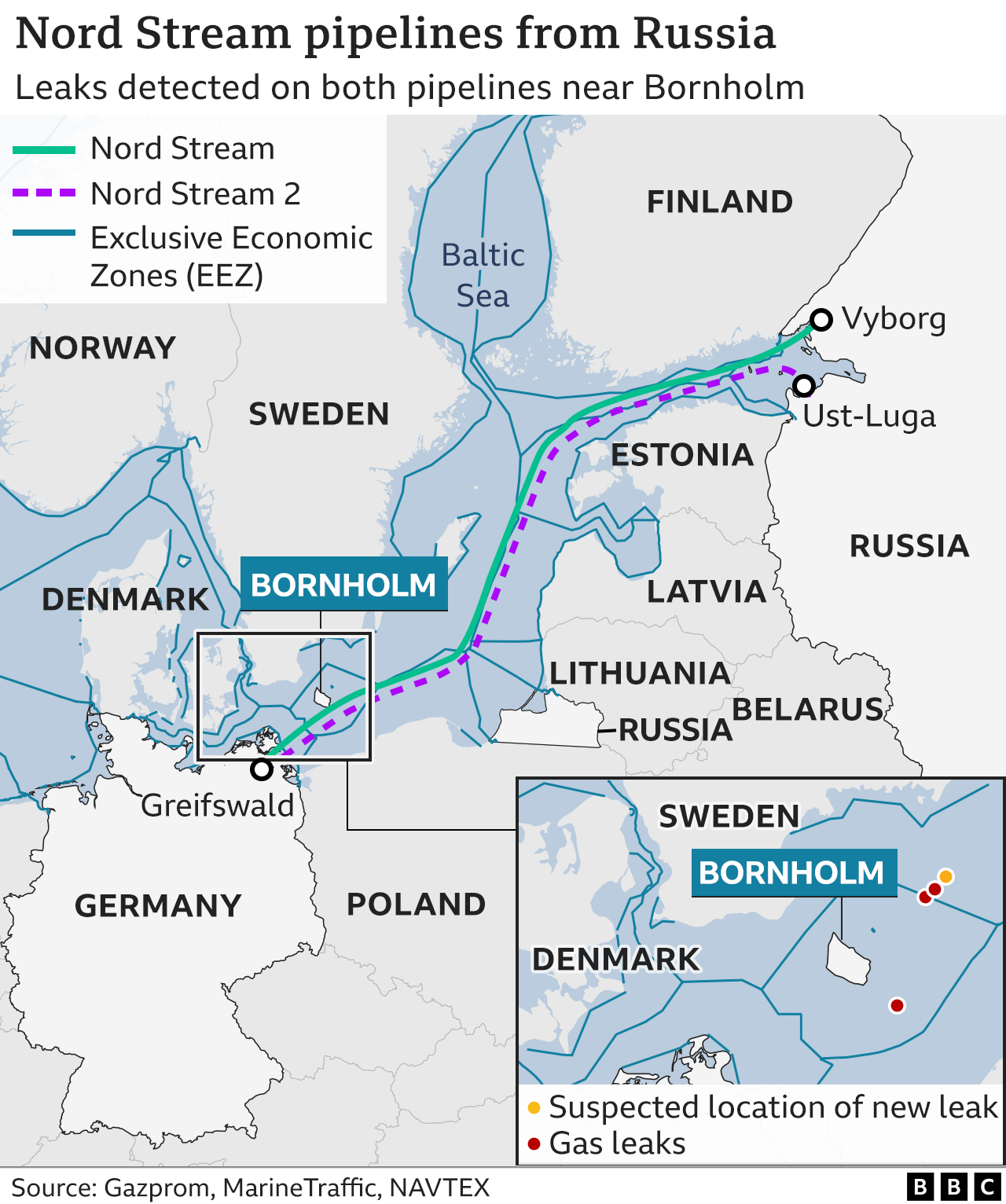
The future of the Nord Stream pipelines remains uncertain, with geopolitical tensions and energy security concerns casting a shadow over their continued operation. The recent events, including the sabotage of Nord Stream 1 and 2 in 2022, have further complicated the situation, raising questions about the pipelines’ reliability and long-term viability.
-
Geopolitical Uncertainty: The pipelines have become a focal point in the geopolitical rivalry between Russia and the West, with their fate intertwined with broader diplomatic relations and security concerns.
-
Energy Transition: The growing emphasis on renewable energy sources and the need to reduce carbon emissions are challenging the traditional role of natural gas in the energy mix. The future of the Nord Stream pipelines is likely to be influenced by the pace and direction of this energy transition.
-
Infrastructure Resilience: The recent sabotage attacks have highlighted the vulnerability of critical energy infrastructure to external threats. The future of the pipelines will depend on the ability of relevant stakeholders to enhance security measures and ensure their resilience against potential disruptions.
FAQs
1. What is the purpose of the Nord Stream pipelines?
The Nord Stream pipelines are designed to transport natural gas from Russia to Germany, serving as a critical artery in the global energy trade. They provide a direct and efficient route for the flow of natural gas, bypassing transit countries and reducing transportation costs.
2. Who owns and operates the Nord Stream pipelines?
The Nord Stream pipelines are owned and operated by Nord Stream AG, a consortium of European energy companies. The majority shareholder is Gazprom, the Russian energy giant, with other shareholders including Wintershall Dea (Germany), Uniper (Germany), Engie (France), and N.V. Nederlandse Gasunie (Netherlands).
3. What are the environmental impacts of the Nord Stream pipelines?
The construction and operation of the Nord Stream pipelines have raised environmental concerns, particularly regarding potential impacts on marine ecosystems and seabed habitats. The pipelines have also been criticized for contributing to greenhouse gas emissions associated with natural gas production and consumption.
4. Why were the Nord Stream pipelines sabotaged in 2022?
The sabotage of the Nord Stream pipelines in 2022 remains a subject of investigation. While the perpetrators have not been officially identified, the incident has been widely attributed to a deliberate act of sabotage, potentially linked to the ongoing geopolitical tensions between Russia and the West.
5. What are the potential future scenarios for the Nord Stream pipelines?
The future of the Nord Stream pipelines remains uncertain, with geopolitical tensions and energy security concerns casting a shadow over their continued operation. The recent events, including the sabotage of Nord Stream 1 and 2 in 2022, have further complicated the situation, raising questions about the pipelines’ reliability and long-term viability.
Tips
- Stay informed: Keep abreast of developments related to the Nord Stream pipelines by following reputable news sources and industry publications.
- Consider multiple perspectives: Engage with diverse viewpoints on the economic, political, and environmental implications of the pipelines, recognizing the complexity of the issues involved.
- Support sustainable energy solutions: Advocate for policies and investments that promote renewable energy sources and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Engage in constructive dialogue: Participate in discussions and debates about the future of energy infrastructure, fostering a spirit of collaboration and understanding.
Conclusion
The Nord Stream pipelines have become a complex and multifaceted issue, interwoven with global energy dynamics, geopolitical tensions, and environmental concerns. While their role in facilitating energy trade and economic growth is undeniable, the pipelines have also sparked controversies and raised questions about energy security, geopolitical influence, and environmental sustainability. The future of these pipelines remains uncertain, influenced by a confluence of factors, including the evolving energy landscape, geopolitical developments, and the need to address climate change. Understanding the intricate web of factors surrounding the Nord Stream pipelines is crucial for navigating the challenges and opportunities of the global energy transition.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Energy Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nord Stream Pipelines. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!