A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of North Carolina’s Indigenous Peoples
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of North Carolina’s Indigenous Peoples
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of North Carolina’s Indigenous Peoples. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of North Carolina’s Indigenous Peoples

North Carolina, a state steeped in history and diverse landscapes, holds a rich tapestry of Indigenous cultures woven into its fabric. Understanding the distribution and history of Native American tribes within the state requires a nuanced exploration, best visualized through a map depicting their ancestral territories and contemporary locations. This map serves as a powerful tool for understanding the past, present, and future of Indigenous communities in North Carolina.
Historical Context: A Legacy of Resilience
Before European colonization, North Carolina was home to numerous Indigenous tribes, each with distinct languages, customs, and traditions. The map reveals the intricate network of these communities, highlighting their historical presence and the profound impact they had on the land and its resources.
The Eastern Woodlands: A Shared Heritage
The majority of North Carolina’s Indigenous tribes belonged to the Eastern Woodlands cultural tradition, characterized by their adaptability to the diverse environments of the region. They developed sophisticated agricultural practices, including the cultivation of corn, beans, and squash, and utilized the abundant resources of forests, rivers, and coastal areas. This shared heritage is reflected in the map, illustrating the interconnectedness of these tribes and their reliance on the land for sustenance and survival.
Navigating the Map: Unveiling the Past
The map provides a visual representation of the ancestral territories of various tribes, offering insights into their historical distribution and the complex relationships they fostered with each other.
- The Cherokee Nation: Occupying the western mountains of North Carolina, the Cherokee are known for their rich cultural heritage, including their syllabary, a unique writing system developed in the 19th century.
- The Tuscarora Nation: Located in the eastern part of the state, the Tuscarora are renowned for their resilience, having successfully resisted colonization for a significant period.
- The Lumbee Tribe: The largest tribe in North Carolina, the Lumbee have a long and complex history, their origins tracing back to the Siouan language family.
- The Haliwa-Saponi Tribe: Situated in the central part of the state, the Haliwa-Saponi Tribe is known for their strong cultural traditions, including their pottery and beadwork.
Modern-Day Tribes: Preserving Heritage and Culture
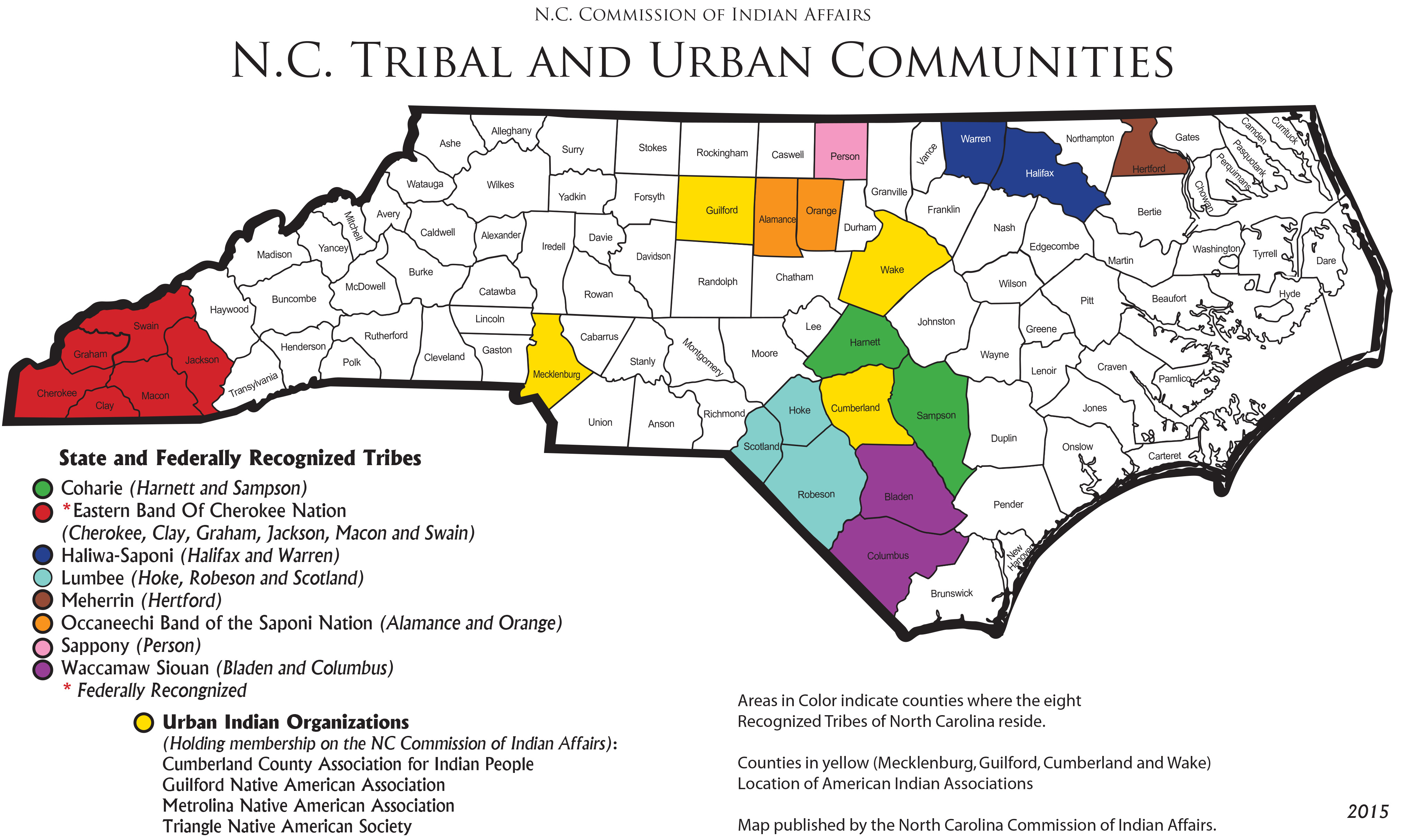
The map also highlights the present-day locations of federally recognized tribes in North Carolina. These communities continue to play a vital role in the state’s cultural landscape, preserving their traditions and advocating for their rights.
The Importance of Recognition and Respect
The map serves as a reminder of the enduring legacy of Indigenous peoples in North Carolina. It underscores the importance of acknowledging their history, culture, and contributions to the state. By understanding the map’s significance, we can foster a deeper appreciation for the diverse tapestry of cultures that have shaped North Carolina.
FAQs About the Map of North Carolina’s Indigenous Peoples
Q: What is the significance of the map for understanding the history of North Carolina?
A: The map provides a visual representation of the ancestral territories of various Indigenous tribes, offering insights into their historical distribution and the complex relationships they fostered with each other. It helps us understand the profound impact these tribes had on the land and its resources.
Q: How can I learn more about the history of specific tribes depicted on the map?
A: Numerous resources are available for exploring the history of individual tribes, including tribal websites, museums, and historical societies.
Q: What are the current challenges facing Indigenous communities in North Carolina?
A: Contemporary challenges include issues related to sovereignty, land rights, environmental protection, and access to healthcare and education.
Q: How can I support the efforts of Indigenous communities in North Carolina?
A: You can support Indigenous communities by patronizing their businesses, attending cultural events, and advocating for their rights.
Tips for Using the Map
- Explore the map’s legend: The legend provides information about the different symbols and colors used to represent different tribes and their territories.
- Focus on specific regions: The map can be used to explore the history and culture of specific regions of North Carolina.
- Connect with tribal communities: Reaching out to tribal communities directly can provide valuable insights into their perspectives and experiences.
Conclusion
The map of North Carolina’s Indigenous peoples is more than just a geographical representation; it is a powerful tool for understanding the state’s rich history, diverse cultures, and ongoing struggles. By engaging with this map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the resilience and contributions of Indigenous communities and foster a more inclusive and equitable society for all.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of North Carolina’s Indigenous Peoples. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!