A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Appalachian Mountains on a Map
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Appalachian Mountains on a Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Appalachian Mountains on a Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Appalachian Mountains on a Map
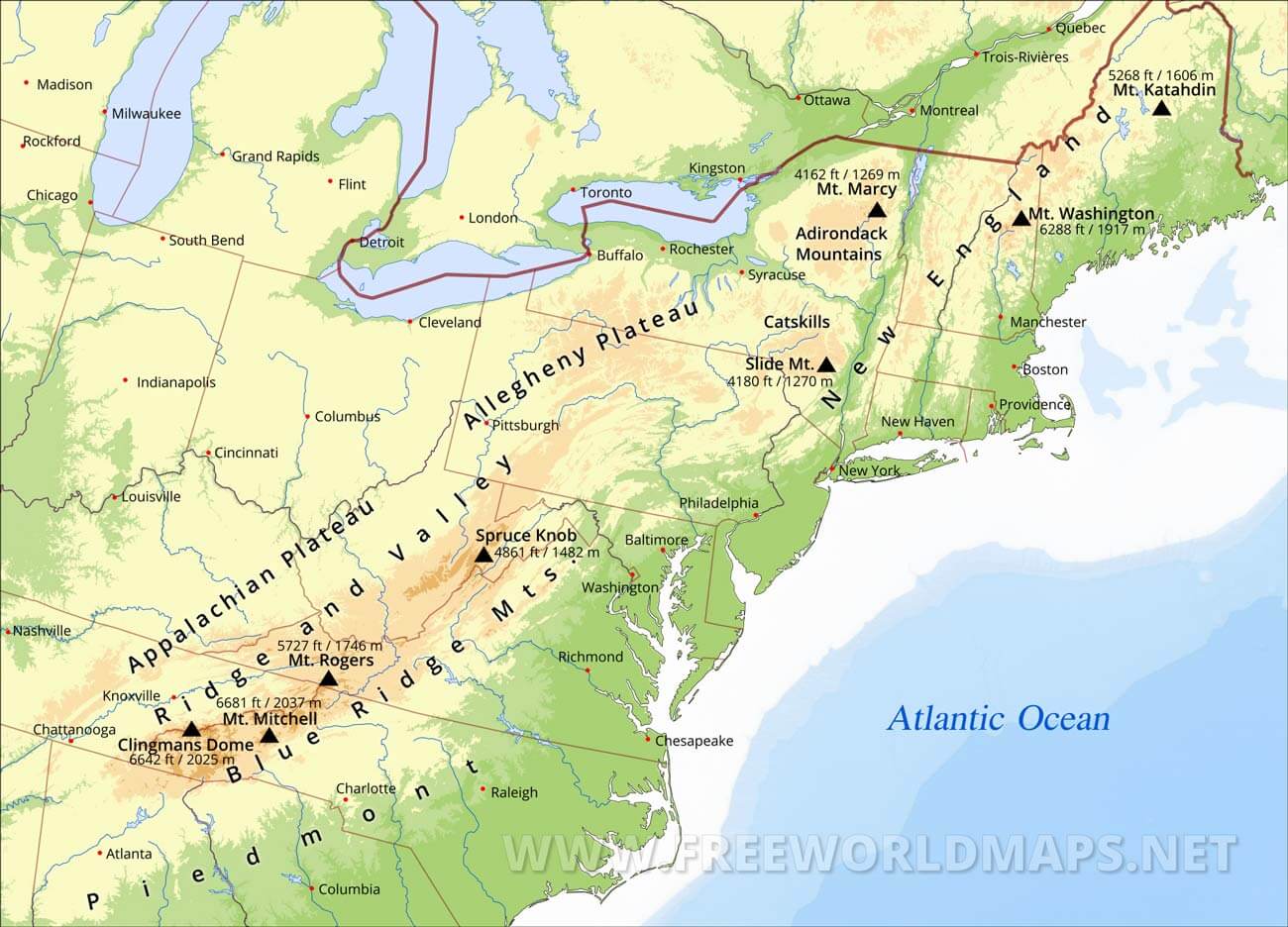
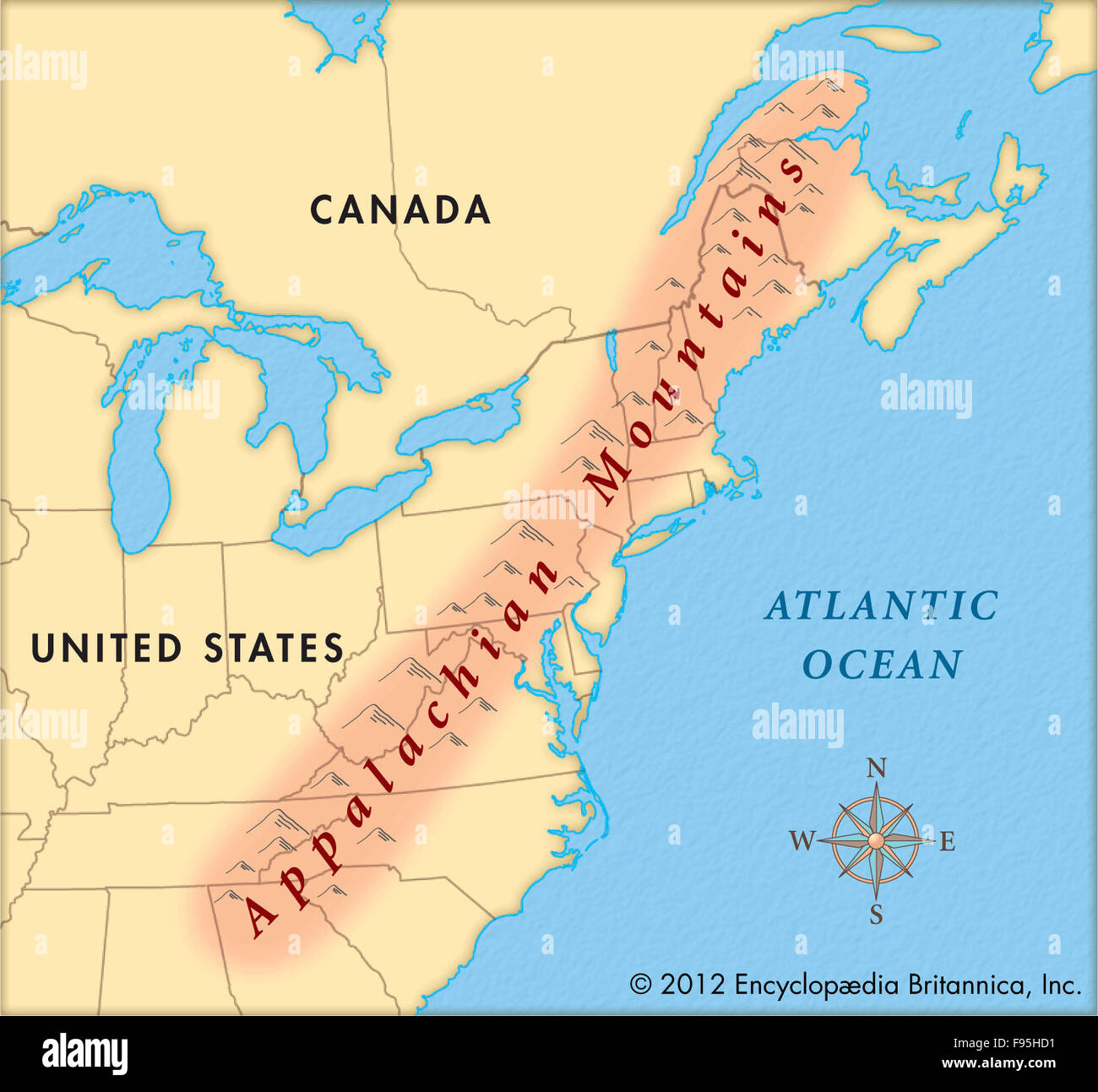
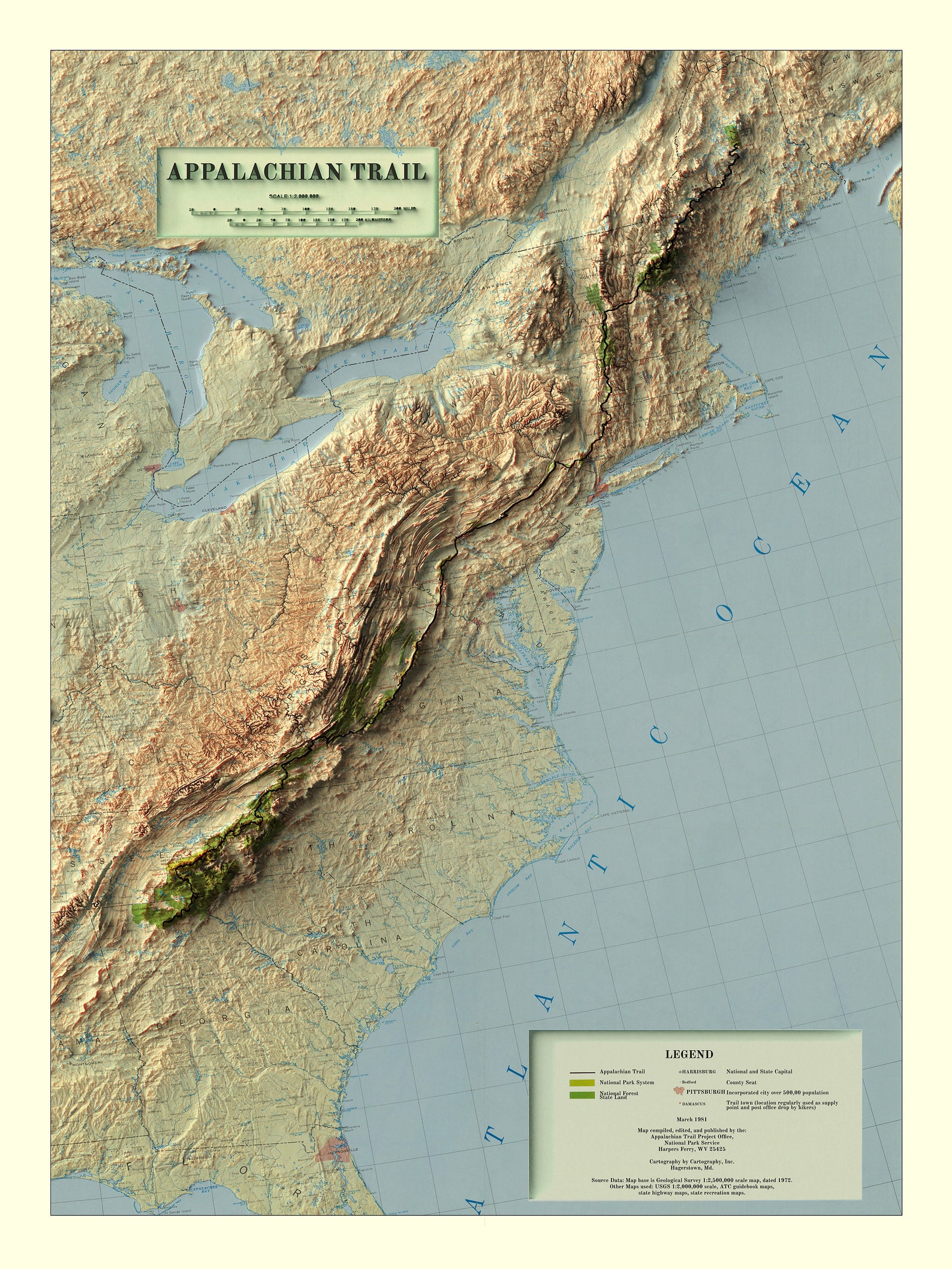
The Appalachian Mountains, a vast and ancient chain stretching from the Canadian Maritimes to Alabama, hold a unique place in the North American landscape. Their history, geology, and impact on human civilization are intertwined in a tapestry that continues to inspire and captivate. This article will guide you through the Appalachian Mountains, using maps to illuminate their geographical significance and delve into the cultural and environmental richness they embody.
Unveiling the Appalachian Range on a Map
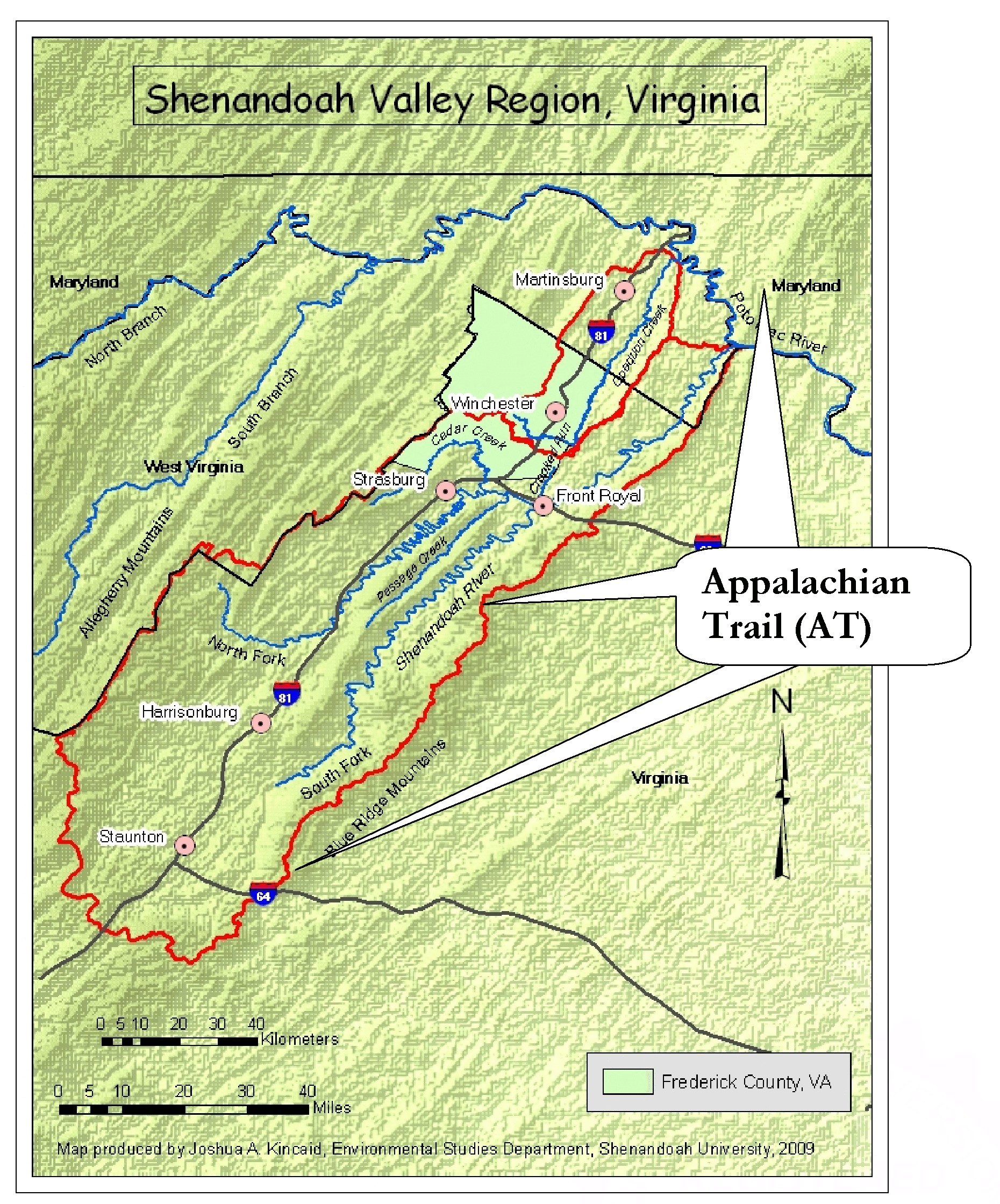
The Appalachian Mountains are not a singular peak, but rather a complex system of ridges, valleys, and plateaus. To understand their vastness, it’s crucial to visualize them on a map.
- The Core of the Appalachians: The core of the Appalachian chain runs from the north-east to south-west, forming the backbone of the eastern United States. This central region, known as the "Appalachian Highlands," encompasses the highest peaks, including Mount Mitchell in North Carolina, the tallest peak east of the Mississippi River.
- Spreading Outwards: The Appalachian Mountains branch out from this core, forming distinct subranges with unique characteristics. The Blue Ridge Mountains, known for their scenic beauty, are a prominent example. The Allegheny Mountains, running through Pennsylvania and West Virginia, are characterized by their rolling hills and dense forests.
- Beyond the Peaks: The Appalachian Mountains extend beyond their mountainous core, encompassing the Piedmont region, a transitional zone between the mountains and the Atlantic Coastal Plain. This region, marked by rolling hills and fertile soil, has played a significant role in shaping the agricultural landscape of the East Coast.
A Journey Through Time: The Geology of the Appalachians
The Appalachian Mountains are a testament to the Earth’s dynamic history. Their formation, spanning millions of years, is a story of tectonic collisions, erosion, and uplift.
- Ancient Origins: The Appalachian Mountains were formed during the Paleozoic Era, when the supercontinent Pangaea began to break apart. This process led to the collision of the North American and African tectonic plates, creating a vast mountain range.
- The Force of Erosion: Over millions of years, wind, water, and ice sculpted the Appalachian Mountains, carving out valleys and shaping the landscape we see today. This erosion also exposed ancient rock formations, offering insights into the Earth’s history.
- A Legacy of Coal: The Appalachian Mountains are rich in coal deposits, a valuable resource formed from ancient plant matter compressed over millions of years. This resource played a critical role in the industrialization of the United States, but also contributed to environmental challenges.
Humanity’s Footprint: The Appalachian Way of Life
The Appalachian Mountains have been home to diverse cultures and communities for centuries. Their rugged beauty, abundant resources, and unique way of life have shaped the region’s identity.
- Native American Heritage: For millennia, indigenous tribes like the Cherokee, Iroquois, and Shawnee lived in harmony with the Appalachian environment. Their knowledge of the land, traditions, and stories continue to inform our understanding of the region.
- Early Settlers and Pioneers: From the 18th century onwards, European settlers arrived in the Appalachian Mountains, seeking opportunity and a new life. They established communities, carved out farms, and developed industries that shaped the region’s economy.
- A Culture of Resilience: Appalachian communities have faced challenges, including poverty, economic hardship, and environmental degradation. Yet, their resilience, strong sense of community, and cultural heritage have endured.
Preserving the Appalachian Legacy: Conservation Efforts
The Appalachian Mountains are facing a range of environmental challenges, including deforestation, pollution, and climate change. Conservation efforts are vital to protecting this precious natural resource for future generations.
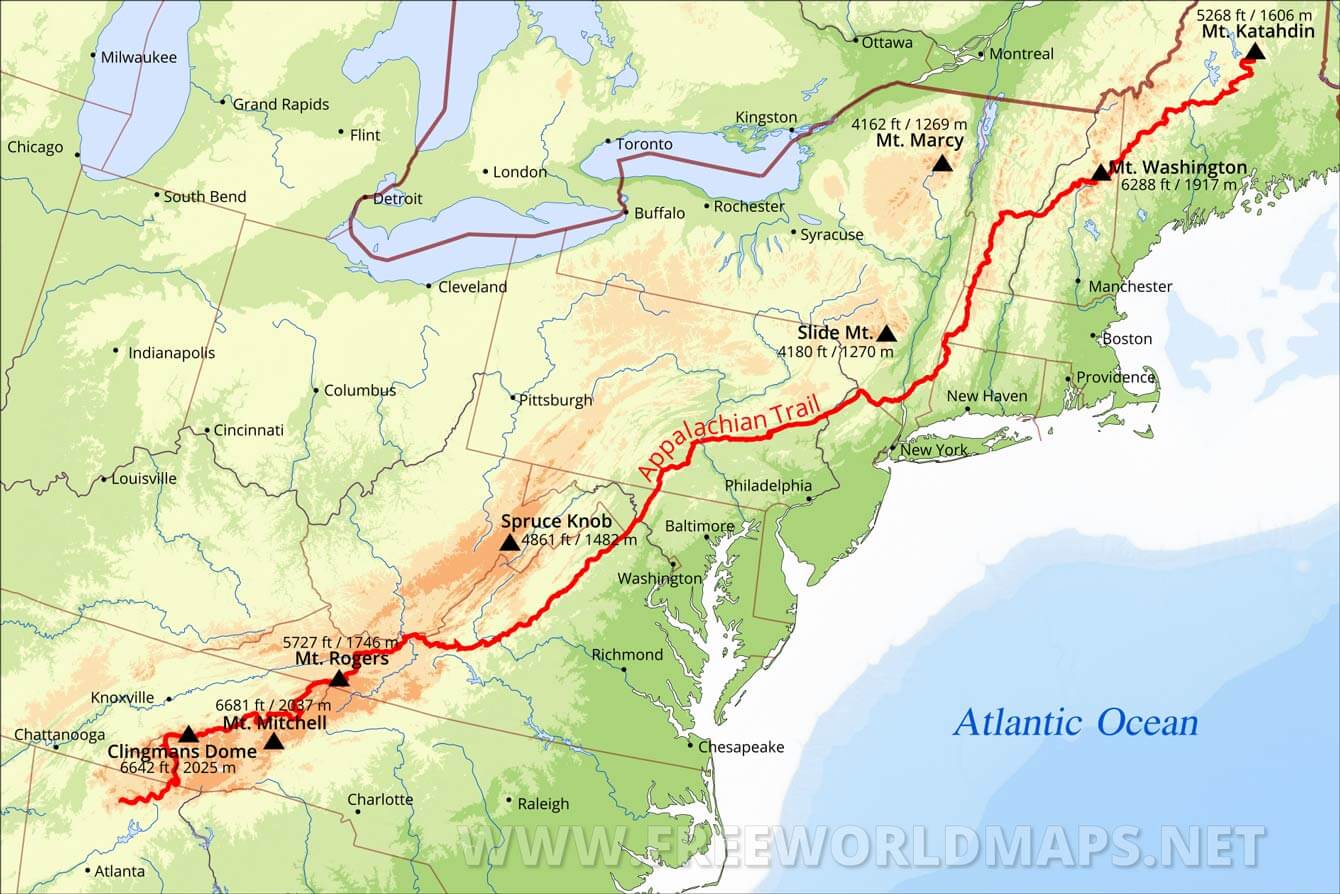
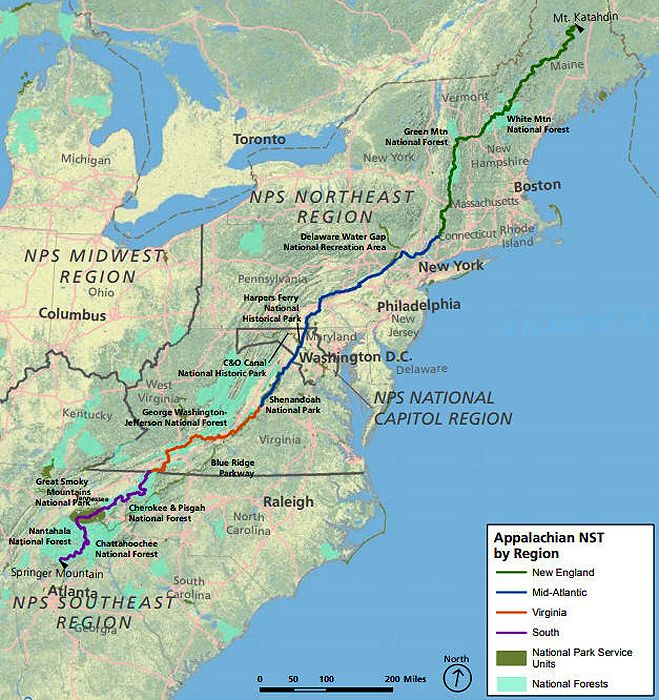
- National Parks and Forests: The Appalachian Mountains are home to numerous national parks and forests, including Great Smoky Mountains National Park, Shenandoah National Park, and the Appalachian National Scenic Trail. These protected areas provide habitat for diverse wildlife and offer opportunities for recreation and education.
- Environmental Stewardship: Local communities, conservation organizations, and government agencies are working together to address environmental challenges, promote sustainable land management practices, and protect the Appalachian ecosystem.
- The Future of the Appalachians: Protecting the Appalachian Mountains is crucial for preserving biodiversity, ensuring clean water, and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
FAQs about the Appalachian Mountains
Q: What is the highest peak in the Appalachian Mountains?
A: Mount Mitchell in North Carolina is the highest peak east of the Mississippi River, rising to an elevation of 6,684 feet (2,037 meters).
Q: What are the major rivers that flow through the Appalachian Mountains?
A: The Appalachian Mountains are drained by numerous rivers, including the Ohio River, the Tennessee River, the Susquehanna River, and the Potomac River.
Q: What are some of the major cities located in the Appalachian region?
A: Major cities in the Appalachian region include Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania; Charlotte, North Carolina; Knoxville, Tennessee; and Charleston, West Virginia.
Q: What are some of the popular tourist attractions in the Appalachian Mountains?
A: The Appalachian Mountains offer a wide array of tourist attractions, including national parks, scenic drives, hiking trails, historic sites, and cultural festivals. Popular destinations include Great Smoky Mountains National Park, Shenandoah National Park, the Appalachian National Scenic Trail, and the Blue Ridge Parkway.
Tips for Exploring the Appalachian Mountains
- Plan Ahead: Research your destination and choose activities that suit your interests and abilities.
- Pack Appropriately: Bring appropriate clothing, footwear, and supplies for hiking, camping, or other outdoor activities.
- Respect the Environment: Follow Leave No Trace principles to minimize your impact on the natural landscape.
- Be Aware of Wildlife: The Appalachian Mountains are home to a variety of wildlife, including black bears, deer, and snakes. Be cautious and aware of your surroundings.
- Enjoy the Local Culture: Explore the unique culture and traditions of Appalachian communities.
Conclusion
The Appalachian Mountains are more than just a geographical feature; they are a living tapestry of history, culture, and environmental significance. From their ancient geological origins to the diverse communities that call them home, the Appalachians offer a captivating journey through time. By understanding their importance and engaging in responsible stewardship, we can ensure that the beauty, resilience, and legacy of the Appalachian Mountains endure for generations to come.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Appalachian Mountains on a Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!