A Comprehensive Exploration of Guyana’s Administrative Regions: Understanding the Geographic Landscape
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Exploration of Guyana’s Administrative Regions: Understanding the Geographic Landscape
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Exploration of Guyana’s Administrative Regions: Understanding the Geographic Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Exploration of Guyana’s Administrative Regions: Understanding the Geographic Landscape
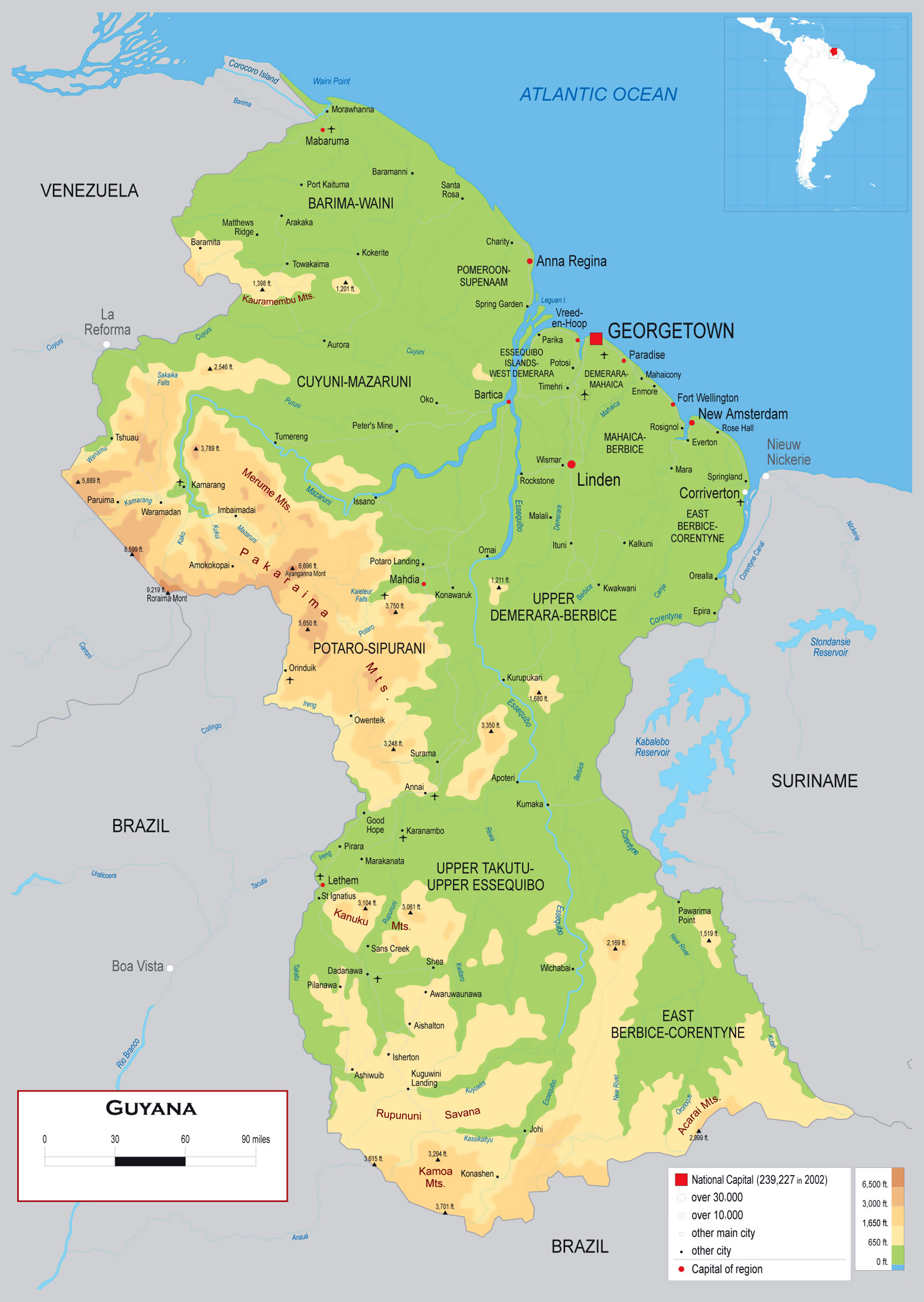
Guyana, a vibrant South American nation, boasts a diverse landscape, rich history, and unique cultural tapestry. To effectively understand the country’s administrative structure, geographic features, and socio-economic development, a thorough understanding of its regional divisions is crucial. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of Guyana’s ten administrative regions, delving into their geographical characteristics, key industries, and cultural nuances.
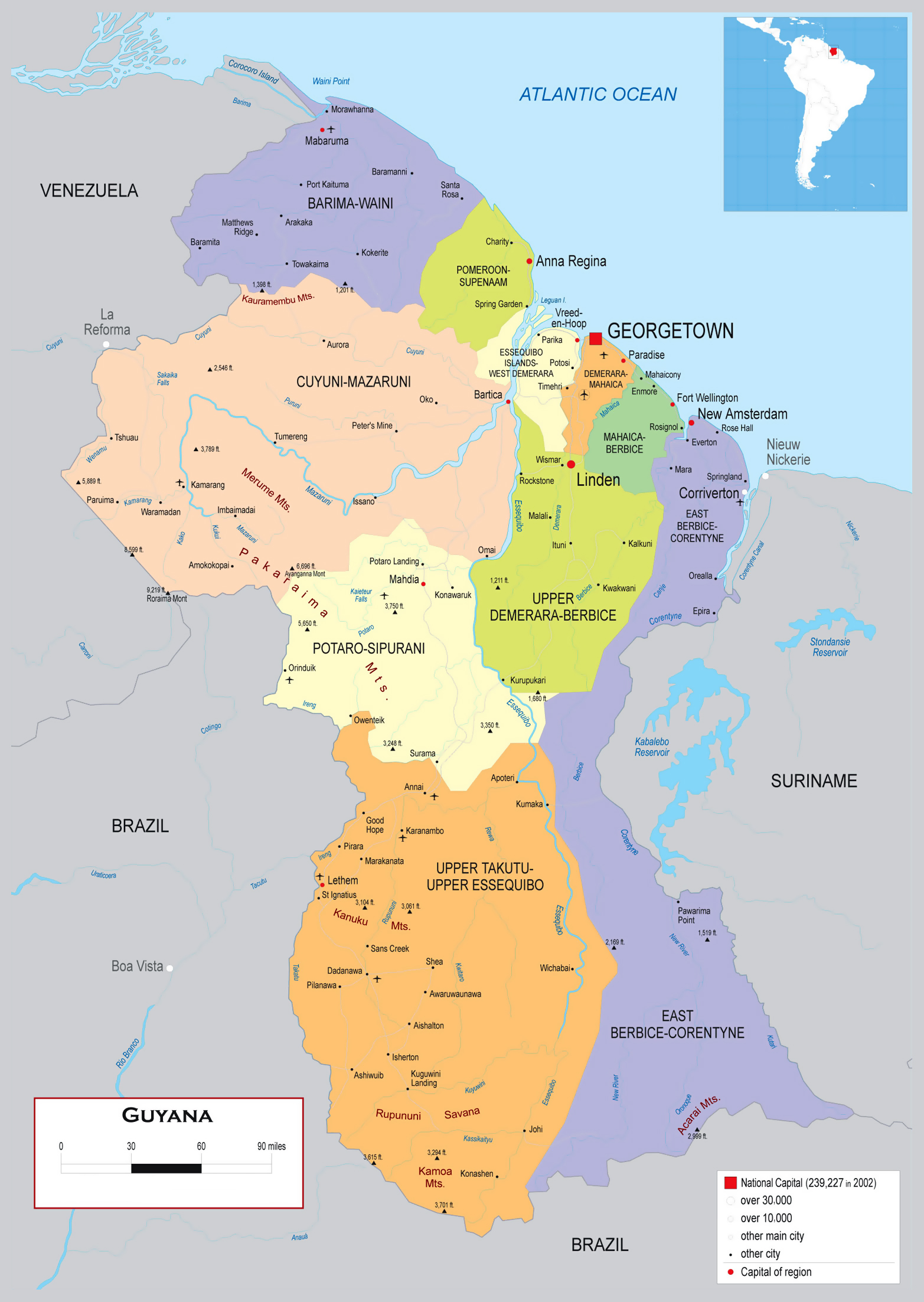
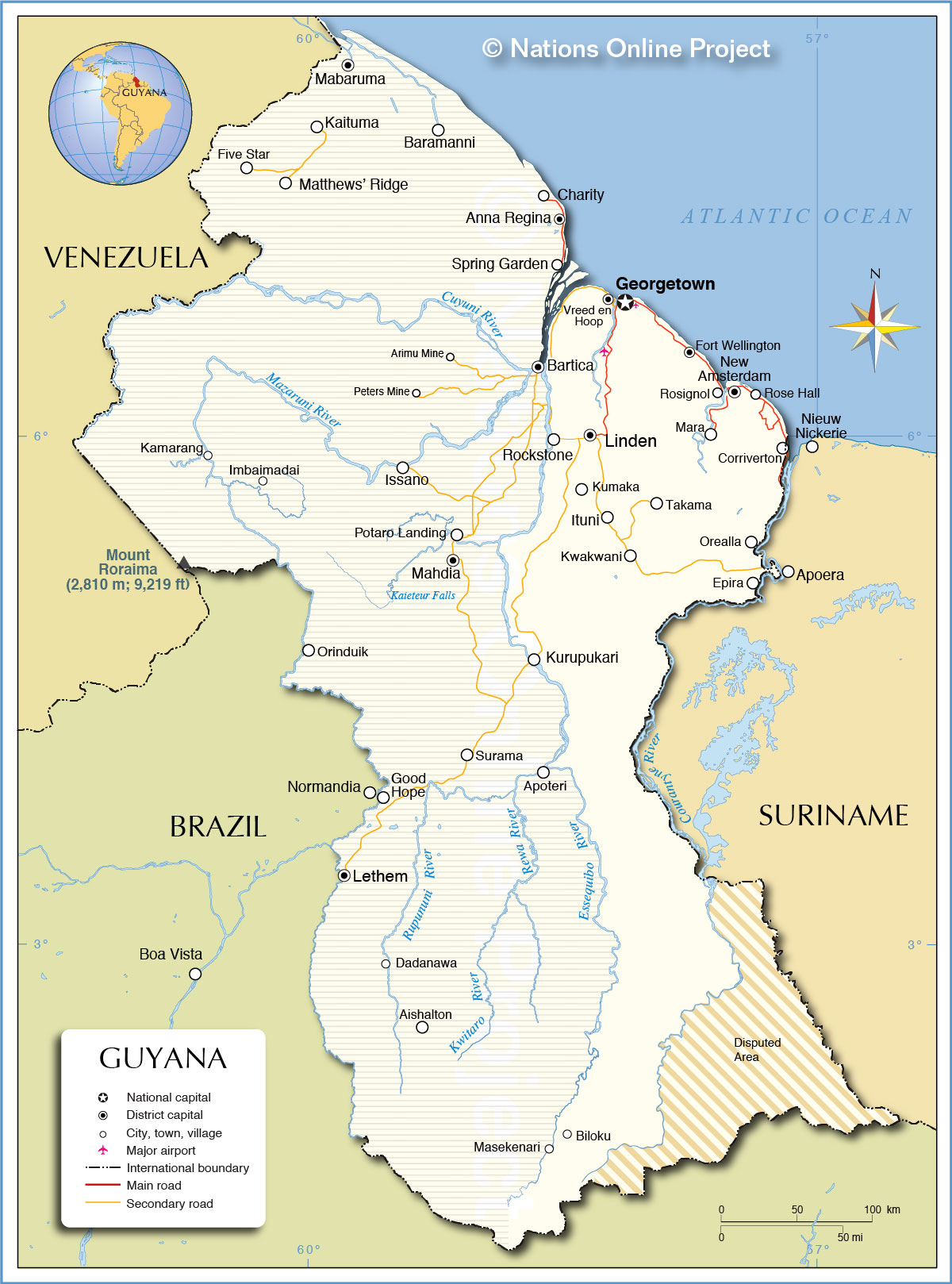
A Map of Guyana’s Administrative Regions: A Visual Guide
Guyana’s administrative regions are defined by their geographical boundaries and serve as the primary framework for governance and administrative operations. The map below provides a visual representation of these regions, showcasing their relative positions and sizes:
[Insert a map of Guyana’s administrative regions here]
Region 1: Barima-Waini – Where the Rainforest Meets the Sea
Located in the northwest of Guyana, Region 1 encompasses a vast expanse of pristine rainforest, coastal lowlands, and the majestic Kaieteur National Park. This region is home to diverse indigenous communities, including the Arawaks and Caribs, who maintain their traditional way of life in harmony with the surrounding environment.
Key Features of Region 1:
- Geography: Characterized by dense rainforest, rolling hills, and coastal plains.
- Economy: Primarily focused on forestry, mining (gold and diamonds), and agriculture.
- Culture: Rich in indigenous traditions, with strong cultural ties to the Arawak and Carib peoples.
- Tourism: Offers unique opportunities for eco-tourism, adventure travel, and cultural immersion.
Region 2: Pomeroon-Supenaam – Where Rivers Flow and Agriculture Thrives
Region 2, situated along the northern coast, is known for its fertile alluvial plains and extensive river systems. Agriculture plays a dominant role in the region’s economy, with rice, coconuts, and sugarcane being significant crops.
Key Features of Region 2:
- Geography: Defined by coastal plains, extensive river systems, and fertile alluvial soils.
- Economy: Agriculture-based, with rice, coconut, and sugarcane being major crops.
- Culture: Diverse cultural landscape, influenced by Indian, African, and European heritage.
- Tourism: Offers opportunities for birdwatching, river cruises, and exploring local markets.
Region 3: Essequibo Islands-West Demerara – The Heart of Guyana’s Economic Activity
Region 3, encompassing the densely populated West Demerara and Essequibo Islands, is the economic powerhouse of Guyana. This region boasts a thriving industrial sector, including sugar production, rice cultivation, and manufacturing.
Key Features of Region 3:
- Geography: Characterized by coastal plains, the Demerara River, and the Essequibo Islands.
- Economy: A major center for industrial activity, including sugar production, rice cultivation, and manufacturing.
- Culture: Diverse population, reflecting the country’s multi-ethnic heritage.
- Tourism: Offers opportunities for exploring historical sites, visiting sugar estates, and experiencing urban life.
Region 4: Demerara-Mahaica – The Capital’s Domain
Region 4 encompasses the capital city of Georgetown, a bustling metropolis that serves as the country’s administrative, economic, and cultural hub. This region is home to a diverse population, reflecting Guyana’s rich cultural heritage.
Key Features of Region 4:
- Geography: Coastal plains, the Demerara River, and the capital city of Georgetown.
- Economy: A major center for commerce, finance, and government services.
- Culture: A vibrant cultural melting pot, with a rich mix of ethnicities and traditions.
- Tourism: Offers opportunities for exploring historical sites, museums, and the city’s vibrant nightlife.
Region 5: Mahaica-Berbice – Where Coastal Plains Meet the Hinterland
Region 5 stretches along the coast, encompassing the Mahaica and Berbice rivers. This region is known for its agricultural activities, including rice cultivation, cattle ranching, and fruit production.
Key Features of Region 5:
- Geography: Coastal plains, the Mahaica and Berbice rivers, and the transition zone to the hinterland.
- Economy: Primarily agricultural, with rice, cattle, and fruits being key products.
- Culture: A blend of Indian, African, and European influences, with strong community ties.
- Tourism: Offers opportunities for exploring rural communities, visiting historical sites, and experiencing local culture.
Region 6: East Berbice-Corentyne – The Land of Rice and Sugar
Region 6, located in the southeast of Guyana, is renowned for its vast sugar plantations and rice fields. This region plays a vital role in Guyana’s agricultural sector, contributing significantly to the country’s food production.
Key Features of Region 6:
- Geography: Coastal plains, the Corentyne River, and the Berbice River.
- Economy: Dominated by sugar production, rice cultivation, and fishing.
- Culture: A diverse cultural landscape, with a strong Indian influence.
- Tourism: Offers opportunities for visiting sugar estates, experiencing local markets, and exploring the coastline.
Region 7: Cuyuni-Mazaruni – Where Gold and Diamonds Shine
Region 7, situated in the heart of Guyana’s interior, is a major center for gold and diamond mining. This region is characterized by its rugged terrain, dense forests, and the presence of the Cuyuni and Mazaruni rivers.
Key Features of Region 7:
- Geography: Rugged terrain, dense forests, and the Cuyuni and Mazaruni rivers.
- Economy: Dominated by gold and diamond mining, with significant potential for tourism.
- Culture: Home to indigenous communities, including the Wapishana and Akawaio people.
- Tourism: Offers opportunities for exploring the rainforest, visiting mining sites, and experiencing indigenous culture.
Region 8: Potaro-Siparuni – The Land of Kaieteur Falls
Region 8, located in the central interior of Guyana, is home to the magnificent Kaieteur Falls, one of the world’s tallest single-drop waterfalls. This region is characterized by its dense forests, rolling hills, and the presence of the Potaro River.
Key Features of Region 8:
- Geography: Dense forests, rolling hills, and the Potaro River, including the iconic Kaieteur Falls.
- Economy: Potential for tourism, mining, and forestry.
- Culture: Home to indigenous communities, including the Patamona and Macushi people.
- Tourism: Offers opportunities for experiencing the natural beauty of Kaieteur Falls, exploring the rainforest, and immersing in indigenous culture.
Region 9: Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo – Where the Savannah Meets the Forest
Region 9, located in the southwest of Guyana, is a vast and sparsely populated region, characterized by its rolling savannahs, dense forests, and the presence of the Takutu and Essequibo rivers.
Key Features of Region 9:
- Geography: Rolling savannahs, dense forests, the Takutu and Essequibo rivers, and the Rupununi Savannah.
- Economy: Potential for tourism, ranching, and agriculture.
- Culture: Home to indigenous communities, including the Wapishana and Makushi people.
- Tourism: Offers opportunities for exploring the savannahs, observing wildlife, and experiencing indigenous culture.
Region 10: Upper Demerara-Berbice – Where Industry Meets the Hinterland
Region 10, located in the south-central part of Guyana, is a region of significant industrial activity, with a focus on mining, forestry, and hydroelectric power generation. This region is also home to the town of Linden, a major industrial hub.
Key Features of Region 10:
- Geography: Rolling hills, the Demerara River, and the Berbice River.
- Economy: Mining, forestry, hydroelectric power generation, and agriculture.
- Culture: A blend of African, Indian, and European influences.
- Tourism: Offers opportunities for exploring the hinterland, visiting mining sites, and experiencing local culture.
The Importance of Guyana’s Regional Divisions
Guyana’s administrative regions play a vital role in the country’s governance, development, and socio-economic progress. They provide a framework for:
- Effective Administration: Each region is governed by a regional administration responsible for delivering essential services to its residents.
- Regional Development: The regional structure allows for tailored development plans that address the unique needs and challenges of each region.
- Resource Management: Regions are responsible for managing natural resources within their boundaries, promoting sustainable practices and environmental protection.
- Cultural Preservation: Regional divisions help preserve and promote the diverse cultural heritage of Guyana’s indigenous and ethnic communities.
- Economic Diversification: The distinct characteristics of each region allow for the development of diverse economic activities, fostering regional growth and national development.
FAQs about Guyana’s Administrative Regions
Q: What is the largest administrative region in Guyana?
A: Region 10, Upper Demerara-Berbice, is the largest administrative region in Guyana, encompassing a vast area of 20,000 square kilometers.
Q: Which region is home to the capital city of Georgetown?
A: Region 4, Demerara-Mahaica, is home to the capital city of Georgetown, the administrative, economic, and cultural hub of Guyana.
Q: Which region is known for its sugar plantations and rice fields?
A: Region 6, East Berbice-Corentyne, is renowned for its vast sugar plantations and rice fields, contributing significantly to Guyana’s agricultural sector.
Q: Which region is home to the iconic Kaieteur Falls?
A: Region 8, Potaro-Siparuni, is home to the magnificent Kaieteur Falls, one of the world’s tallest single-drop waterfalls.
Q: Which region is considered the economic powerhouse of Guyana?
A: Region 3, Essequibo Islands-West Demerara, is the economic powerhouse of Guyana, boasting a thriving industrial sector and a significant contribution to the country’s GDP.
Tips for Exploring Guyana’s Regions
- Plan your itinerary carefully: Each region offers unique experiences, so choose your destinations based on your interests and travel preferences.
- Consider your transportation options: Guyana has a well-developed road network, but travel between regions can be challenging.
- Respect local customs and traditions: Guyana is a multi-cultural nation, so it’s important to be respectful of local customs and traditions.
- Engage with local communities: Interacting with local people provides valuable insights into Guyana’s rich culture and history.
- Support sustainable tourism practices: Choose eco-friendly accommodations and activities to minimize your environmental impact.
Conclusion
Guyana’s administrative regions offer a fascinating glimpse into the country’s diverse landscape, rich culture, and economic potential. Understanding the unique characteristics of each region is crucial for appreciating the complexities and beauty of this South American nation. Whether you’re interested in exploring pristine rainforests, experiencing indigenous culture, or witnessing the grandeur of Kaieteur Falls, Guyana’s regional divisions offer a wealth of experiences for travelers and explorers alike.
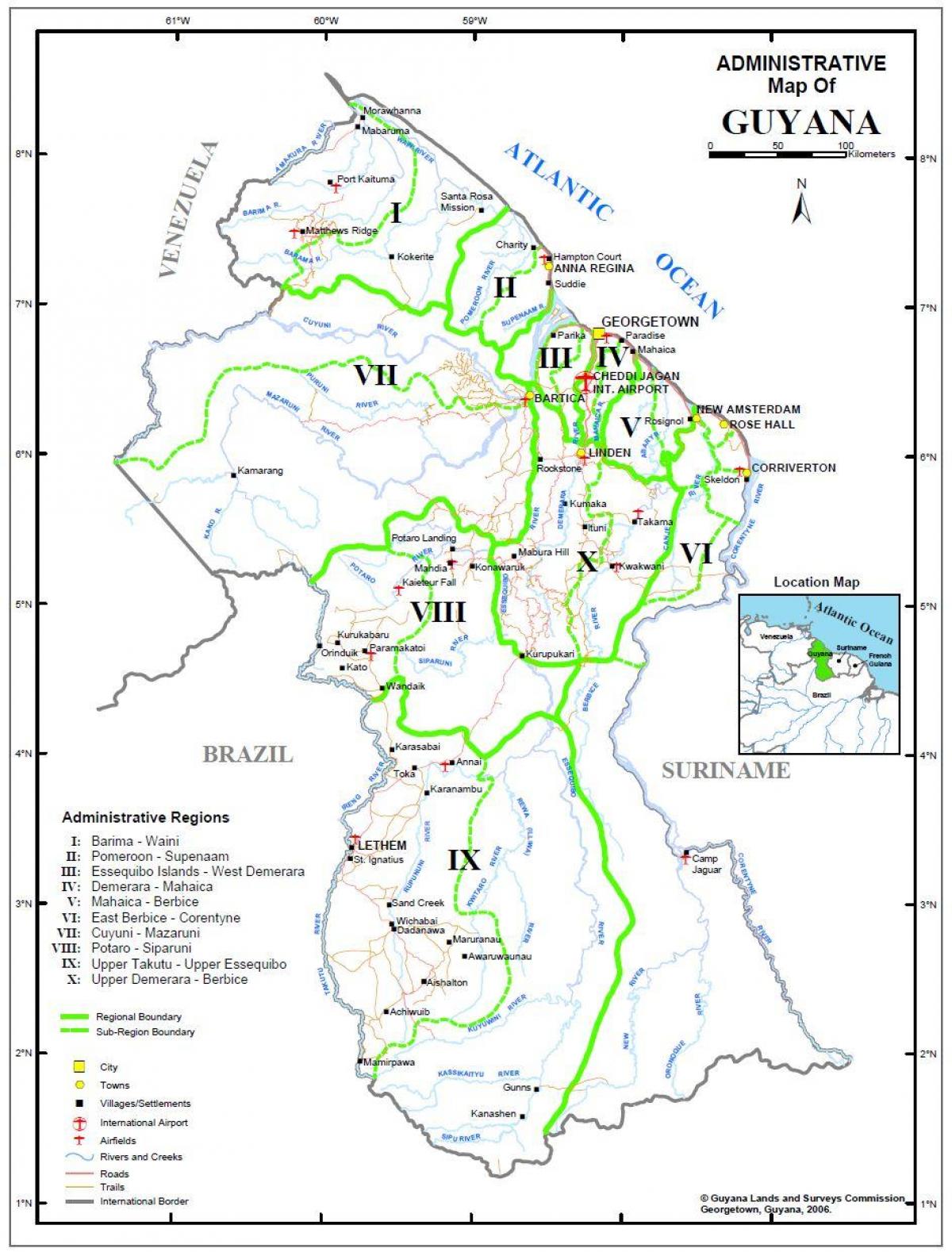

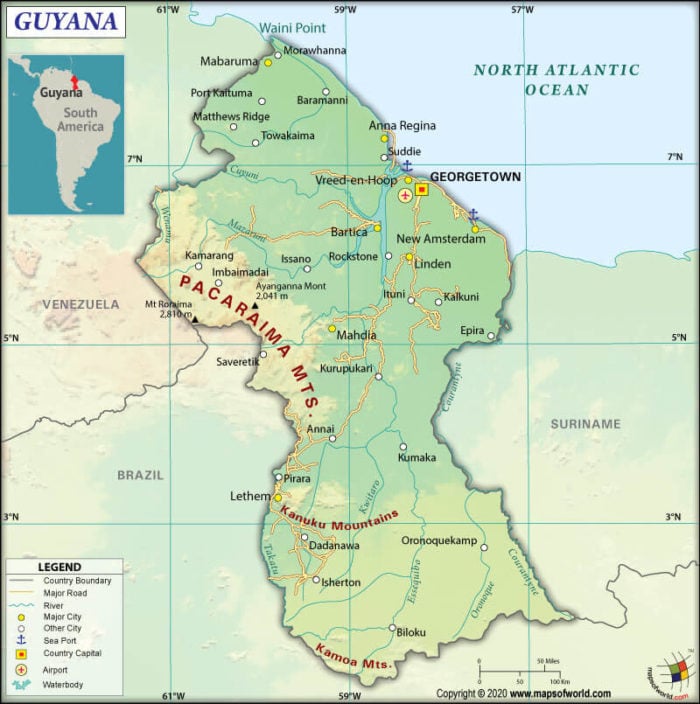

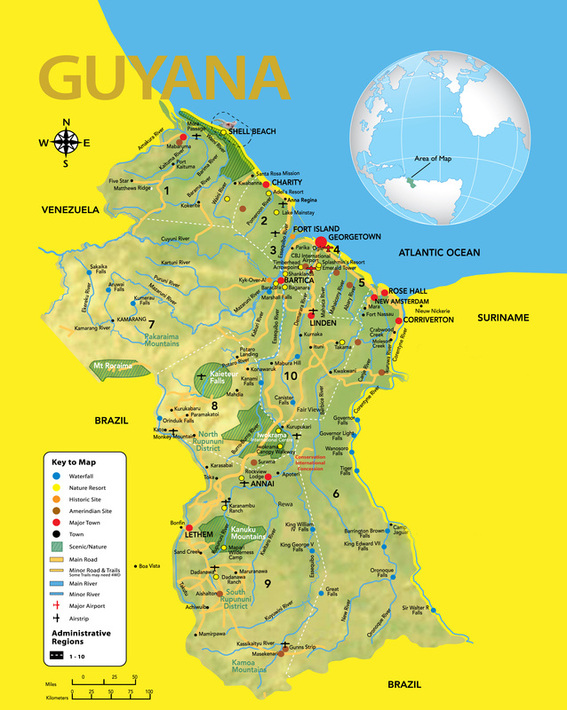

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Exploration of Guyana’s Administrative Regions: Understanding the Geographic Landscape. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!