A Comparative Look at Poland and Belarus: A Geographic Journey
Related Articles: A Comparative Look at Poland and Belarus: A Geographic Journey
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comparative Look at Poland and Belarus: A Geographic Journey. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comparative Look at Poland and Belarus: A Geographic Journey

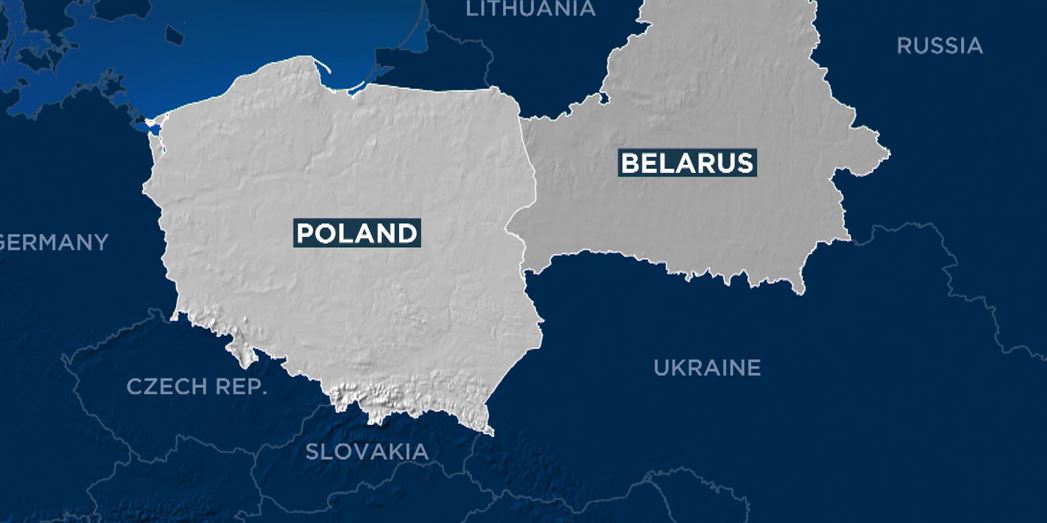
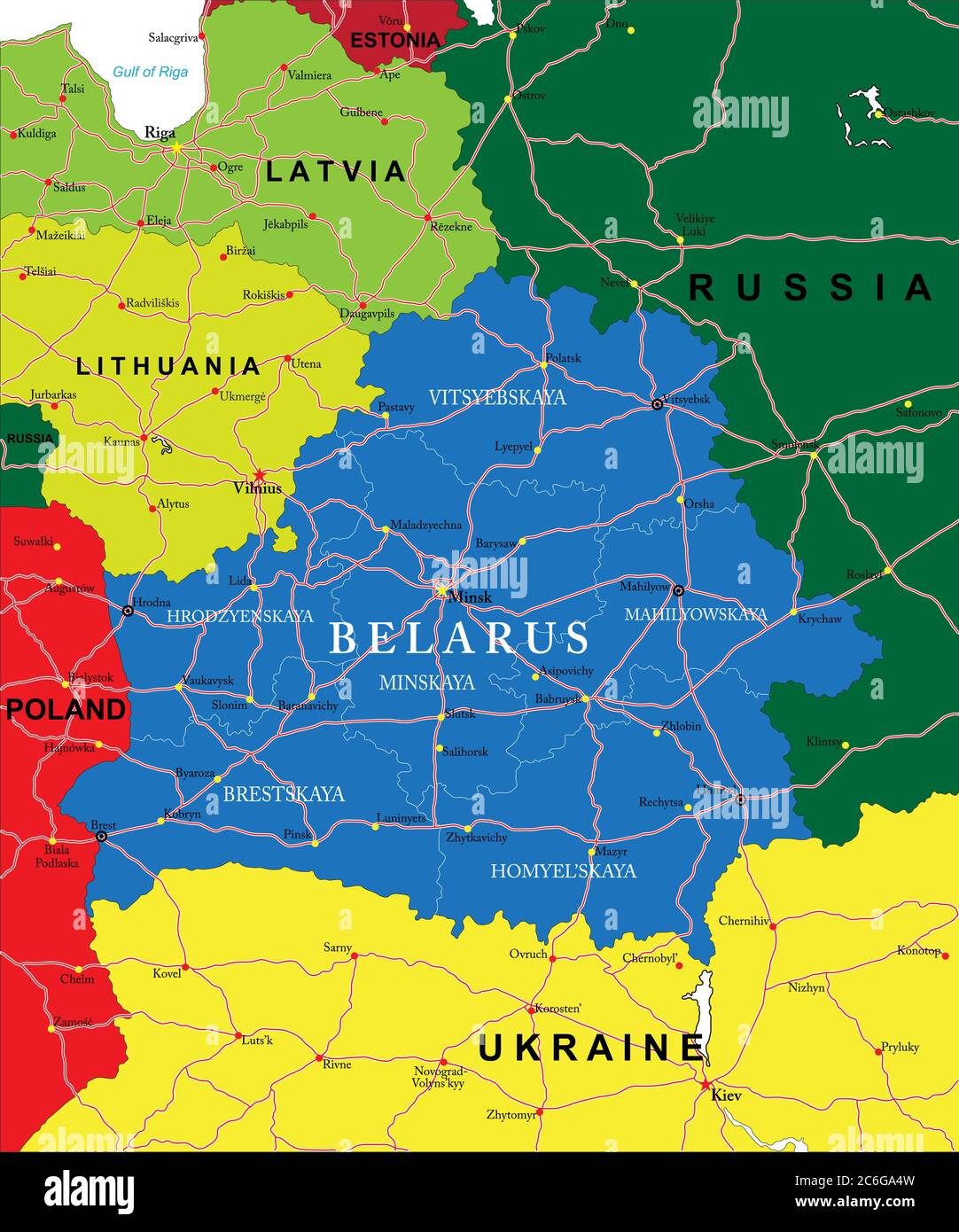
Poland and Belarus, two neighboring countries in Eastern Europe, share a rich history, diverse landscapes, and a complex geopolitical landscape. Understanding the geography of these nations, particularly their physical boundaries and spatial relationships, provides valuable insights into their past, present, and potential future.
The Geographic Landscape of Poland
Poland, nestled in the heart of Central Europe, occupies a strategic location. Its borders touch seven countries, including Germany, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Ukraine, Belarus, Lithuania, and Russia (Kaliningrad Oblast). This strategic position has historically made Poland a crossroads of trade, culture, and conflict.
Physical Geography:
- Diverse Landscapes: Poland boasts a varied topography, ranging from the flat plains of the Great Polish Plain to the rolling hills of the Carpathian Mountains in the south.
- The Baltic Sea Coast: Poland’s northern border is defined by the Baltic Sea, offering access to international trade and a significant coastline for maritime activities.
- The Vistula River: The longest river in Poland, the Vistula, flows through the heart of the country, playing a crucial role in transportation and agriculture.
- Forests and Lakes: Poland is home to extensive forests, particularly in the north and east, and numerous lakes, particularly in the Masurian Lake District.
Geographic Significance:
- Strategic Location: Poland’s location makes it a key link between Western and Eastern Europe. It serves as a crucial transportation corridor and a cultural bridge between the two regions.
- Economic Importance: Poland’s diverse geography supports a variety of industries, including agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism. The Baltic Sea coast is a significant economic driver, supporting fishing, shipping, and tourism.
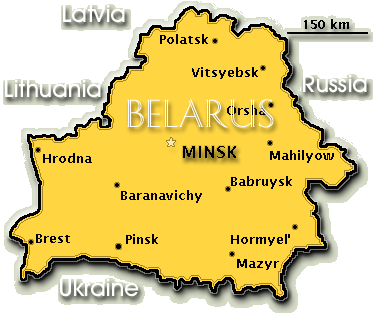
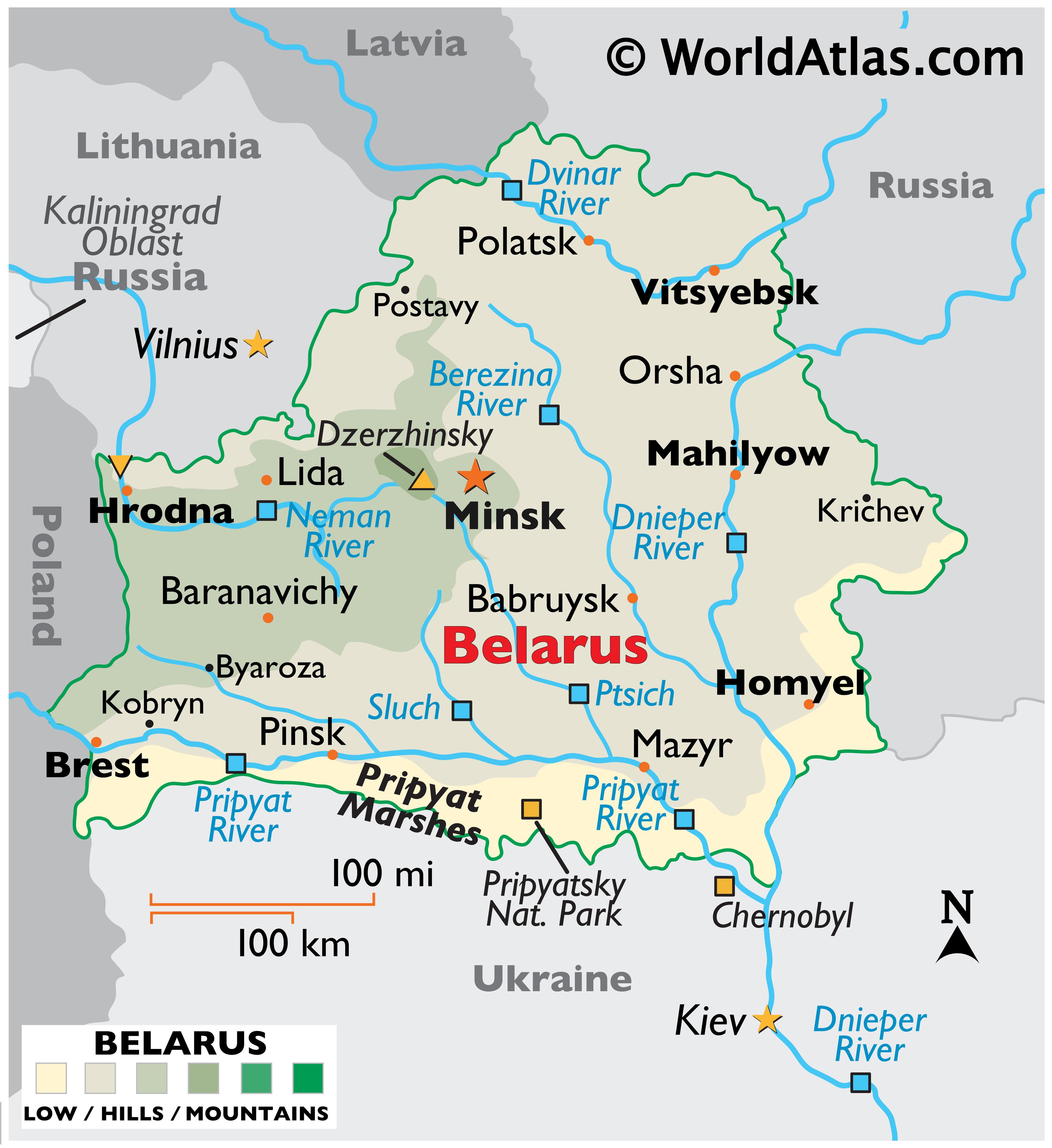
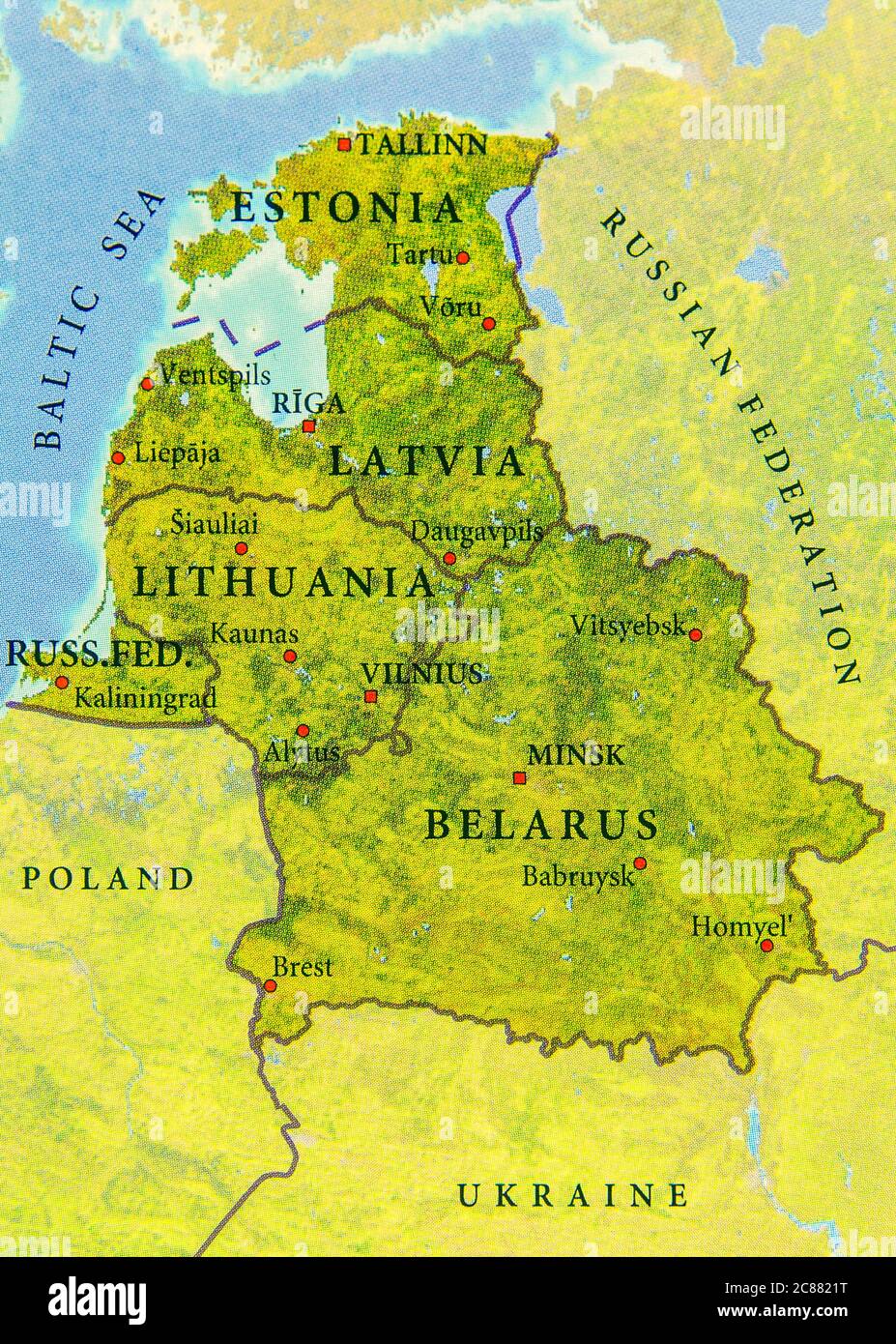
The Geographic Landscape of Belarus
Belarus, often referred to as the "Last European Dictatorship," is landlocked and shares borders with Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Russia, and Ukraine. While largely flat, the country exhibits some geographic diversity.
Physical Geography:
- Predominantly Flat: Belarus is characterized by a predominantly flat landscape, with rolling hills and low-lying plains.
- The Dnieper River: The Dnieper River, one of the longest rivers in Europe, flows through Belarus, playing a significant role in transportation and agriculture.
- Forests and Swamps: Belarus is known for its vast forests, particularly in the north and east, and numerous swamps, a unique feature of the country’s landscape.
Geographic Significance:
- Strategic Location: Belarus’s location, situated between Russia and Europe, makes it a strategically important country. Its proximity to Russia has significantly influenced its political and economic development.
- Economic Importance: Belarus’s economy is heavily reliant on agriculture, particularly potato production, and manufacturing industries. The country also has significant natural resources, including potash and oil.
A Comparative Analysis
While both Poland and Belarus share some geographic similarities, their physical landscapes, historical development, and current geopolitical contexts differ significantly.
Similarities:
- Flat Landscapes: Both countries feature predominantly flat landscapes with rolling hills and plains.
- Extensive Forests: Both countries have significant forest cover, contributing to their biodiversity and environmental importance.
- Agriculture: Both countries have a strong agricultural tradition, with significant production of grains, potatoes, and other agricultural products.
Differences:
- Access to the Sea: Poland has a significant Baltic Sea coastline, providing access to international trade and maritime activities, while Belarus is landlocked.
- Historical Development: Poland has a long and rich history, having been a major power in Europe. Belarus, in contrast, has experienced a more turbulent history, with periods of foreign rule and political instability.
- Political System: Poland is a democratic republic, while Belarus is an authoritarian state with a strongman leader.
- Economic Development: Poland has experienced significant economic growth in recent decades, while Belarus’s economy has been more stagnant.
The Importance of Understanding the Geography of Poland and Belarus
The geographic features of Poland and Belarus have profoundly shaped their histories, cultures, and current political and economic landscapes. Understanding these features is crucial for:
- Historical Understanding: Geography provides valuable insights into the historical development of these nations, including migration patterns, trade routes, and military conflicts.
- Political Analysis: Geographic factors, such as location, borders, and natural resources, play a significant role in shaping political dynamics and international relations.
- Economic Development: The availability of natural resources, transportation infrastructure, and access to markets are key factors influencing economic development.
- Environmental Management: Understanding the geographical features, including ecosystems, water resources, and land use patterns, is crucial for sustainable environmental management.
FAQs
Q: What is the highest point in Poland?
A: The highest point in Poland is Rysy, a mountain in the Tatra Mountains, with an elevation of 2,499 meters (8,199 feet).
Q: What is the largest city in Belarus?
A: The largest city in Belarus is Minsk, the country’s capital, with a population of approximately 2 million.
Q: What is the main difference between the economies of Poland and Belarus?
A: Poland has experienced significant economic growth in recent decades, with a diverse economy based on manufacturing, services, and agriculture. Belarus’s economy has been more stagnant, with a heavy reliance on state-owned enterprises and a less diversified economic structure.
Q: What are some of the environmental challenges facing Poland and Belarus?
A: Both countries face environmental challenges related to air pollution, deforestation, and water pollution. Poland is particularly affected by acid rain caused by coal-fired power plants. Belarus faces challenges related to the Chernobyl disaster and the contamination of its water resources.
Tips for Travelers
- Poland: Explore the vibrant city of Krakow, visit the historical city of Warsaw, and discover the stunning beauty of the Tatra Mountains.
- Belarus: Experience the unique culture of Minsk, explore the pristine forests and lakes of the country, and visit the memorial complex at Chernobyl.
Conclusion
Poland and Belarus, despite sharing a border and some geographic similarities, are distinct nations with different histories, cultures, and political systems. Understanding the geography of these countries provides valuable insights into their past, present, and future. Their diverse landscapes, strategic locations, and unique challenges offer a fascinating glimpse into the complexities of Eastern Europe. By exploring these geographical features, we gain a deeper appreciation for the richness and diversity of this region.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comparative Look at Poland and Belarus: A Geographic Journey. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!